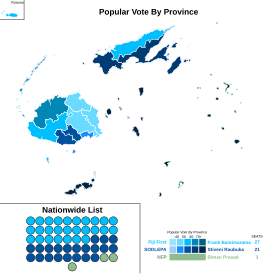
General elections were held in Fiji on 14 November 2018.[1] The result was a victory for the ruling FijiFirst party of Prime Minister Frank Bainimarama, which received just over 50% of the vote and 27 of the 51 seats in Parliament, a loss of five seats.[2] The main opposition party, Social Democratic Liberal Party, gained six seats, whilst the National Federation Party retained its three seats.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 51 seats in the Parliament of Fiji 26 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Registered | 637,527 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 71.92% ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The elections also saw female representation in Parliament rise to nearly 20 percent, with 10 of the 51 members being women.[3]
Background and campaign
editOn 10 March, SODELPA launched their party manifesto for the election in Sydney, making it the first time a Fijian political party has launched their party manifesto overseas. The event attracted many supporters among the Fijian diaspora, especially Fijian Australians.[4]
On 30 September, Prime Minister Frank Bainimarama announced that the elections would be held on 14 November 2018. President Jioji Konrote subsequently dissolved parliament in accordance with section 58(3) of the constitution, on the advice of the Prime Minister.
234 candidates representing six political parties contested in the elections. 56 of the candidates were women.[5] Candidate numbers for the ballot paper were drawn on 18 October.[6] The Labour Party and Freedom Alliance Party presented a combined party list under the Labour Party banner.
During a campaign rally, FijiFirst leader Frank Bainimarama stated that he wanted to win all 51 parliamentary seats and govern without an opposition, arguing that the two main opposition parties represented i-Taukei and Indo-Fijian interests rather than all Fijians.[7] The SODELPA party promised to restore the Great Council of Chiefs within a hundred days if elected, and to consider changing the electoral system to restore communal constituencies.[8] They later explicitly promised to restore the 1997 constitution.[9]
During the election campaign SODELPA leader Sitiveni Rabuka was tried and acquitted on charges of falsely declaring his assets and liabilities to the Supervisor of Elections.[10] An appeal by the Fiji Independent Commission Against Corruption,[11] which could have resulted in Rabuka's disqualification two days from the poll, was dismissed, with FICAC ordered to pay costs.[12] Shortly before the appeal was decided Rabuka was again called in by police on unspecified charges.[13]
On election day, voting was suspended at 26 polling stations due to torrential rain and flooding.[14] Ballots cast at those stations were shredded. Polling recommenced with fresh ballot papers on Saturday 17 November.
Electoral system
editThe 51 members of Parliament were elected from a single nationwide constituency by open list proportional representation with an electoral threshold of 5%. Seats are allocated using the d'Hondt method.[15][16]
Prior to the election the Electoral Commission increased the number of seats from 50 to 51 in accordance with section 54 of the Fiji constitution to maintain the ratio of population to seats. The commission determined the ratio in 2014 was one seat for every 17,472 citizens. With the Fiji Bureau of Statistics projecting a population of 886,416 as of 1 March 2017 achieving the same ratio would require 50.73 seats which the commission rounded up to 51 for the 2018 election.[17]
Schedule
editKey dates relating to the general election were as follows:
| 30 September (Sunday) | Prime Minister Frank Bainimarama announces elections to be held on 14 November 2018. |
| 30 September (Sunday) | President Jioji Konrote dissolves parliament in accordance with section 58(3) of the constitution, on the advice of the Prime Minister. |
| 1 October (Monday) | President Jioji Konrote issues the writ of election |
| 1 October (Monday) | Registration of voters ends at 6 p.m. |
| 2 October (Tuesday) | Candidate nominations open at 8 a.m. |
| 15 October (Monday) | Candidate nominations close at 12 p.m. |
| 24 October (Wednesday) | Postal voting applications close at 5 p.m. |
| 5 November (Monday) | Pre-poll voting begins |
| 10 November (Saturday) | Pre-poll voting ends |
| 12 November (Monday) | Media blackout on campaigning commences at 12.00 a.m. for 48 hours |
| 14 November (Wednesday) | Election Day – polling places open from 7.30 a.m. to 6 p.m. |
| 14 November (Wednesday) | Election Night – provisional results will be progressively released from 6 p.m. |
| 18 November (Sunday) | Official results declared |
| 18 November (Sunday) | President Jioji Konrote receives the Writ of Election from the Electoral Commission. |
Opinion polls
editResults
edit| Party | Votes | % | +/– | Seats | +/– | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FijiFirst | 227,241 | 50.02 | –9.15 | 27 | –5 | |
| Social Democratic Liberal Party | 181,072 | 39.85 | +11.67 | 21 | +6 | |
| National Federation Party | 33,515 | 7.38 | +1.93 | 3 | 0 | |
| Unity Fiji Party | 6,896 | 1.52 | +1.52 | 0 | New | |
| HOPE | 2,811 | 0.62 | +0.62 | 0 | New | |
| Fiji Labour Party | 2,800 | 0.62 | –1.73 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 454,335 | 100.00 | – | 51 | +1 | |
| Valid votes | 454,335 | 99.08 | ||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 4,197 | 0.92 | ||||
| Total votes | 458,532 | 100.00 | ||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 637,527 | 71.92 | ||||
| Source: FEO | ||||||
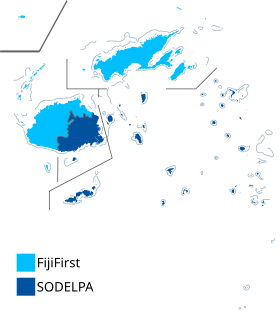
By division
edit| Division | FijiFirst | SODELPA | NFP | UFP | HOPE | FLP | Total votes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central | 44.5 | 45.4 | 7.4 | 1.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 148,131 | ||
| Eastern | 44.7 | 45.6 | 7.1 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 76,750 | ||
| Northern | 46.0 | 45.8 | 6.4 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 67,560 | ||
| Western | 60.2 | 28.7 | 7.9 | 1.8 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 152,766 | ||
| Postal votes | 44.6 | 44.6 | 8.3 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 9,128 | ||
| Fiji | 50.0 | 39.9 | 7.4 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 454,335 | ||
| Source: 2018 Election Results | |||||||||
Aftermath
editThe ruling FijiFirst Party lost 5 seats, but retained a majority in Parliament. FijiFirst leader Frank Bainimarama blamed poor weather for the loss of votes.[18] Bainimarama was sworn in as Prime Minister on 20 November 2018.[19]
Reactions
editAustralian foreign minister Marise Payne congratulated Bainimarama's re-election in an official statement.[20]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ FEO Launches 2018 General Elections Publication Handbook Fiji Sun, 19 January 2018
- ^ Fiji election: Bainimarama returned as PM in slim victory The Guardian, 18 November 2018
- ^ More women, bigger opposition in Fiji parliament Radio New Zealand, 19 November 2018
- ^ "SODELPA Manifesto Launch Plan in Australia Surprises Some Members".
- ^ "Six political parties to contest Fijian elections". RNZ. 16 October 2018. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
- ^ "Candidate numbers drawn". FBC. 18 October 2018. Archived from the original on 15 November 2018. Retrieved 15 November 2018.
- ^ "Bainimarama hits out at opposition". RNZI. 8 October 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
- ^ "Fiji's Great Council of Chiefs restored in 100 days under SODELPA - Rabuka". RNZI. 19 October 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
- ^ Vilimaina Naqelevuki (6 November 2018). "2018 General Election: SODELPA to bring back 1997 Constitution if it wins". Fiji Times. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
- ^ "Campaign continues after Rabuka found not guilty". RNZI. 26 October 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
- ^ "Fiji CJ to rule on FICAC appeal two days before election". RNZI. 31 October 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
- ^ "Appeal against Rabuka dismissed by Chief Justice". RNZI. 12 November 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
- ^ "Fiji's Rabuka not worried about latest police summons". RNZI. 10 November 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
- ^ "Voting suspended at 26 polling stations in Fiji due to weather". RNZ. 14 November 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
- ^ Electoral system IPU
- ^ Electoral system for national legislature – Fiji Archived 4 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine IDEA
- ^ Singh, Swastika (8 March 2017). "51 parliament seats will be contested in 2018 elections". fijivillage. Communications Fiji Limited. Retrieved 19 February 2022.
- ^ "Fiji's election winner blames rain for drop in support". RNZI. 20 November 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
- ^ "Frank Bainimarama sworn in as Fiji PM". RNZI. 20 November 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
- ^ "Fiji's 2018 election result". foreignminister.gov.au. 18 November 2018. Archived from the original on 25 October 2022. Retrieved 22 October 2022.