Portal maintenance status: (September 2018)
|
The Painting Portal

Painting is a visual art, which is characterized by the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and airbrushes, may be used. One who produces paintings is called a painter.
In art, the term "painting" describes both the act and the result of the action (the final work is called "a painting"). The support for paintings includes such surfaces as walls, paper, canvas, wood, glass, lacquer, pottery, leaf, copper and concrete, and the painting may incorporate multiple other materials, including sand, clay, paper, plaster, gold leaf, and even whole objects.
Painting is an important form of visual art, bringing in elements such as drawing, composition, gesture, narration, and abstraction. Paintings can be naturalistic and representational (as in still life and landscape painting), photographic, abstract, narrative, symbolistic (as in Symbolist art), emotive (as in Expressionism) or political in nature (as in Artivism).
A portion of the history of painting in both Eastern and Western art is dominated by religious art. Examples of this kind of painting range from artwork depicting mythological figures on pottery, to Biblical scenes on the Sistine Chapel ceiling, to scenes from the life of Buddha (or other images of Eastern religious origin). (Full article...)
Selected general articles
-
Image 1

Raking light across a wall, gives a relief like impression.
Raking light, the illumination of objects from a light source at an oblique angle or almost parallel to the surface, provides information on the surface topography and relief of the artefact thus lit. It is widely used in the examination of works of art. (Full article...) -
Image 2

Live painting by Beo Beyond at Shôko Club in Barcelona, working with fluorescent colors which glow under blacklight.
Live painting is a form of visual performance art in which artists complete a visual art piece in a public performance, often at a bar, music concert, wedding reception, or public event, accompanied by a DJ or live music. The artwork which is created live may be planned or improvisational. This live art form is often contrasted with more studied fine art compositions from the same artists, which are generally executed in an artist studio or other private space.
Artists in a number of genres have performed live painting, including LeRoy Neiman creating a painting during the 1976 Summer Olympics. In the 1990s and 2000s, live painting became a hallmark of street art and graffiti artists. (Full article...) -
Image 3

Archip Kuindshi, Moonlit Night on the Dnieper 1882
The depiction of night in paintings is common in Western art. Paintings that feature a night scene as the theme may be religious or history paintings, genre scenes, portraits, landscapes, or other subject types. Some artworks involve religious or fantasy topics using the quality of dim night light to create mysterious atmospheres. The source of illumination in a night scene—whether it is the moon or an artificial light source—may be depicted directly, or it may be implied by the character and coloration of the light that reflects from the subjects depicted. They are sometimes called nocturnes, or night-pieces, such as Rembrandt's The Night Watch, or the German Romantic Caspar David Friedrich's Two Men Contemplating the Moon of 1819.
In America, James Abbott McNeill Whistler titled works as nocturnes to identify those paintings with a "dreamy, pensive mood" by applying the musical term, and likewise also titled (and retitled) works using other music expressions, such as a "symphony", "harmony", "study" or "arrangement", to emphasize the tonal qualities and the composition and to de-emphasize the narrative content. The use of the term "nocturne" can be associated with the Tonalist movement of the American of the late 19th century and early 20th century which is "characterized by soft, diffused light, muted tones and hazy outlined objects, all of which imbue the works with a strong sense of mood." Along with winter scenes, nocturnes were a common Tonalist theme. Frederic Remington used the term as well for his nocturne scenes of the American Old West. (Full article...) -
Image 4
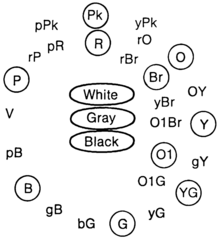
Hue relationships between the primary and secondary colors in the ISCC-NBS system of color designation
The ISCC–NBS System of Color Designation is a system for naming colors based on a set of 13 basic color terms and a small set of adjective modifiers. It was first established in the 1930s by a joint effort of the Inter-Society Color Council (ISCC), made up of delegates from various American trade organizations, and the National Bureau of Standards (NBS), a US government agency. As suggested in 1932 by the first chairman of the ISCC, the system's goal is to be "a means of designating colors in the United States Pharmacopoeia, in the National Formulary, and in general literature ... such designation to be sufficiently standardized as to be acceptable and usable by science, sufficiently broad to be appreciated and used by science, art, and industry, and sufficiently commonplace to be understood, at least in a general way, by the whole public." The system aims to provide a basis on which color definitions in fields from fashion and printing to botany and geology can be systematized and regularized, so that each industry need not invent its own incompatible color system.
In 1939, the system's approach was published in the Journal of Research of the National Bureau of Standards, and the ISCC formally approved the system, which consisted of a set of blocks within the color space defined by the Munsell color system as embodied by the Munsell Book of Color. Over the following decades, the ISCC–NBS system's boundaries were tweaked and its relation to various other color standards were defined, including for instance those for plastics, building materials, botany, paint, and soil. (Full article...) -
Image 5The Jerwood Painting Prize was a prize for originality and excellence in painting in the United Kingdom, awarded and funded by the Jerwood Foundation. It was open to all artists born or resident in the UK, regardless of age or reputation. Winners of the prize include Craigie Aitchison, Patrick Caulfield, Prunella Clough and Maggi Hambling. The prize was instituted in 1994, and at £30,000 was the largest of its kind in Britain. The prize is no longer awarded. (Full article...)
-
Image 6
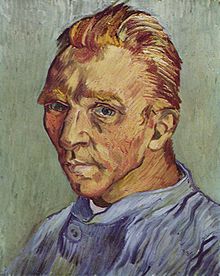
Vincent van Gogh, Self-portrait without beard, end September 1889, (F 525), Oil on canvas, 40 × 31 cm., Private collection. This may have been Van Gogh's last self-portrait. Given as a birthday gift to his mother.
A self-portrait is a portrait an artist makes of themself. Although self-portraits have been made since the earliest times, the practice of self-portraiture only gaining momentum in the Early Renaissance in the mid-15th century that artists can be frequently identified depicting themselves as either the main subject, or as important characters in their work. With better and cheaper mirrors, and the advent of the panel portrait, many painters, sculptors and printmakers tried some form of self-portraiture. Portrait of a Man in a Turban by Jan van Eyck of 1433 may well be the earliest known panel self-portrait. He painted a separate portrait of his wife, and he belonged to the social group that had begun to commission portraits, already more common among wealthy Netherlanders than south of the Alps. The genre is venerable, but not until the Renaissance, with increased wealth and interest in the individual as a subject, did it become truly popular.
By the Baroque period, most artists with an established reputation at least left drawings of themselves. Printed portraits of artists had a market, and many were self-portraits. They were also sometimes given as gifts to family and friends. If nothing else, they avoided the need to arrange for a model, and for the many professional portrait-painters, a self-portrait kept in the studio acted as a demonstration of the artist's skill for potential new clients. The unprecedented number of self-portraits by Rembrandt, both as paintings and prints, made clear the potential of the form, and must have further encouraged the trend. (Full article...) -
Image 7
In art, a pendant is one of two paintings, statues, reliefs or other type of works of art intended as a pair. Typically, pendants are related thematically to each other and are displayed in close proximity. For example, pairs of portraits of married couples are very common, as are symmetrically arranged statues flanking an altar.
Pendants may be the work of a single artist or of two artists, who in some instances might be in competition with one another. An example of the latter case is the pairing of the marble groups The Triumph of Faith over Idolatry by Jean-Baptiste Théodon and Religion Overthrowing Heresy and Hatred by Pierre Le Gros the Younger on the Altar of Saint Ignatius of Loyola (1695–1697/98), in the Church of the Gesù, Rome. (Full article...) -
Image 8

View of Tivoli at Sunset, 1644, with cows and cowherds as staffage, by Claude Lorrain
In painting, staffage (French pronunciation: [stafaʒ]) are the human and animal figures depicted in a scene, especially a landscape, that are not the primary subject matter of the work. Typically they are small, and there to add an indication of scale and add interest.
Before the adoption of the word into the visual arts in the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, Staffage in German could mean "accessories" or "decoration". The word can be used in two senses: as a general term for any figures in a work, even when they are, at least ostensibly, the main subject, and as a descriptive term for figures to whom no specific identity or story is attached, included merely for compositional or decorative reasons. In the latter sense, staffage are accessories to the scene, yet add life to the work; they provide depth to the painting and reinforce the main subject, as well as giving a clear scale to the rest of the composition. (Full article...) -
Image 9Historic paint analysis, or architectural paint research, is the scientific analysis of a broad range of architectural finishes, and is primarily used to determine the color and behavior of surface finishes at any given point in time. This helps us to understand the building's structural history and how its appearance has changed over time.
Historic paint analysis shares a common methodology with the conservation and restoration of paintings used to conserve and restore two- and three dimensional works of art. This involves the identification of components such as organic or inorganic pigments and dyes contained in the pigments. Historic paint analysis also identifies the pigments' media of suspension such as (water, oil, or latex and the paints' associated substrate. A variety of techniques are used to identify and analyze the pigment layers and finish exposure, including Finish Exposure, optical microscopy, fluorescent light microscopy, polarized light microscopy, and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. (Full article...) -
Image 10
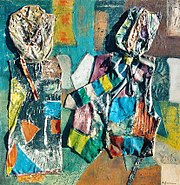
Alberto Baumann, "Inheritance of the Twentieth Century" (1980).
In visual art, mixed media describes artwork in which more than one medium or material has been employed.
Assemblages, collages, and sculpture are three common examples of art using different media. Materials used to create mixed media art include, but are not limited to, paint, cloth, paper, wood and found objects.
Mixed media art is distinguished from multimedia art which combines visual art with non-visual elements, such as recorded sound, literature, drama, dance, motion graphics, music, or interactivity. (Full article...) -
Image 11

Fra Angelico and Fra Filippo Lippi, Adoration of the Magi, c. 1440/1460, National Gallery of Art
A tondo (pl.: tondi or tondos) is a Renaissance term for a circular work of art, either a painting or a sculpture. The word derives from the Italian rotondo, "round". The term is usually not used in English for small round paintings, but only those over about 60 cm (two feet) in diameter, thus excluding many round portrait miniatures – for sculpture the threshold is rather lower.
A circular or oval relief sculpture is also called a roundel. The infrequently-encountered synonym rondo usually refers to the musical form. (Full article...) -
Image 12The paint and sip industry is a set of experience-based businesses that hire professional artists to provide step-by-step instructions to reproduce a pre-selected work of art while they drink wine or other beverages. When class attendees finish, they get to keep their creations.
These classes typically focus on painting as a fun activity for relieving stress, rather than as a technical skill requiring practice like the classes at an atelier or an art school. Alcohol is used to reduce inhibitions and "overthinking" in order to make the creative process feel easier. (Full article...) -
Image 13

KJ 314
Industrial paint robots have been used for decades in automotive paint applications.
Early paint robots were hydraulic versions, which are still in use today but are of inferior quality and safety to the latest electronic offerings. The newest robots are accurate and deliver results with uniform film builds and exact thicknesses. (Full article...) -
Image 14

Raphael, The Expulsion of Heliodorus from the Temple, from the Vatican, 1512. The original grand manner.
Grand manner refers to an idealized aesthetic style derived from classicism and the art of the High Renaissance. In the eighteenth century, British artists and connoisseurs used the term to describe paintings that incorporated visual metaphors in order to suggest noble qualities. It was Sir Joshua Reynolds who gave currency to the term through his Discourses on Art, a series of lectures presented at the Royal Academy from 1769 to 1790, in which he contended that painters should perceive their subjects through generalization and idealization, rather than by the careful copy of nature. Reynolds never actually uses the phrase, referring instead to the "great style" or "grand style", in reference to history painting:
:How much the great style exacts from its professors to conceive and represent their subjects in a poetical manner, not confined to mere matter of fact, may be seen in the cartoons of Raffaelle. In all the pictures in which the painter has represented the apostles, he has drawn them with great nobleness; he has given them as much dignity as the human figure is capable of receiving yet we are expressly told in Scripture they had no such respectable appearance; and of St. Paul in particular, we are told by himself, that his bodily presence was mean. Alexander is said to have been of a low stature: a painter ought not so to represent him. Agesilaus was low, lame, and of a mean appearance. None of these defects ought to appear in a piece of which he is the hero. In conformity to custom, I call this part of the art history painting; it ought to be called poetical, as in reality it is.
Originally applied to history painting, regarded as the highest in the hierarchy of genres, the Grand Manner came thereafter also to be applied to portrait painting, with sitters depicted life size and full-length, in surroundings that conveyed the nobility and elite status of the subjects. Common metaphors included the introduction of classical architecture, signifying cultivation and sophistication, and pastoral backgrounds, which implied a virtuous character of unpretentious sincerity undefiled by the possession of great wealth and estates. (Full article...) -
Image 15In art criticism of the 1960s and 1970s, flatness described the smoothness and absence of curvature or surface detail of a two-dimensional work of art. (Full article...)
-
Image 16The Peintres de la Réalité [pɛ͂tʀ də la ʀealite] (French for "Painters of Reality") were founded after the Second World War by Henri Cadiou to connect artists who were specialized on still life and genre motifs. It later evolved to the Mouvement trompe l'oeil / Réalité. The painting of the group is no reappearance of antiquity or of the 17th century, but the logical consequence of the place in the 20th century development of a realism that has taken over the sequence of surrealism to the modern trompe-l'œil to lead.
1973, the group exhibited at the Cultural Center of New York and the Corcoran Gallery in Washington. In 1989, after the death of Henri Cadiou, Pierre Gilou continued his father's work within the group. In 1993, the group had a sensational success as part of the Grand Palais in Paris, the exhibition "le triomphe du trompe-l'oeil" had more than 65,000 visitors in two weeks. (Full article...) -
Image 17

Robert Delaunay, 1912–13, Le Premier Disque, 134 cm (52.7 in.), private collection
Abstract art uses visual language of shape, form, color and line to create a composition which may exist with a degree of independence from visual references in the world. Abstract art, non-figurative art, non-objective art, and non-representational art are all closely related terms. They have similar, but perhaps not identical, meanings.
Western art had been, from the Renaissance up to the middle of the 19th century, underpinned by the logic of perspective and an attempt to reproduce an illusion of visible reality. By the end of the 19th century many artists felt a need to create a new kind of art which would encompass the fundamental changes taking place in technology, science and philosophy. The sources from which individual artists drew their theoretical arguments were diverse, and reflected the social and intellectual preoccupations in all areas of Western culture at that time. (Full article...) -
Image 18Inscape, in visual art, is a term especially associated with certain works of Chilean artist Roberto Matta, but it is also used in other senses within the visual arts. Though the term inscape has been applied to stylistically diverse artworks, it usually conveys some notion of representing the artist's psyche as a kind of interior landscape. The word inscape can therefore be read as a kind of portmanteau, combining interior (or inward) with landscape. (Full article...)
-
Image 19

Henri Matisse, The Dance I, 1909, Museum of Modern Art. One of the cornerstones of 20th-century modern art.
20th-century Western painting begins with the heritage of late-19th-century painters Vincent van Gogh, Paul Cézanne, Paul Gauguin, Georges Seurat, Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, and others who were essential for the development of modern art. At the beginning of the 20th century, Henri Matisse and several other young artists including the pre-cubist Georges Braque, André Derain, Raoul Dufy and Maurice de Vlaminck, revolutionized the Paris art world with "wild", multi-colored, expressive landscapes and figure paintings that the critics called Fauvism. Matisse's second version of The Dance signified a key point in his career and in the development of modern painting. It reflected Matisse's incipient fascination with primitive art: the intense warm color of the figures against the cool blue-green background and the rhythmical succession of the dancing nudes convey the feelings of emotional liberation and hedonism.
Initially influenced by Toulouse-Lautrec, Gauguin, and other late-19th-century innovators, Pablo Picasso made his first cubist paintings based on Cézanne's idea that all depiction of nature can be reduced to three solids: cube, sphere, and cone. With the painting Les Demoiselles d'Avignon (1907; see gallery) Picasso created a new and radical picture depicting a raw and primitive brothel scene with five prostitutes, violently painted women, reminiscent of African tribal masks and his own new proto-Cubist inventions. Analytic cubism, exemplified by Violin and Candlestick, Paris, was jointly developed by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque from about 1908 through 1912. Analytic cubism was followed by Synthetic cubism, characterized by the introduction of different textures, surfaces, collage elements, papier collé and a large variety of merged subject matter. (Full article...) -
Image 20

John the Baptist (John in the Wilderness), by Caravaggio, 1604, in the Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art, Kansas City
Tenebrism, from Italian tenebroso ('dark, gloomy, mysterious'), also occasionally called dramatic illumination, is a style of painting using especially pronounced chiaroscuro, where there are violent contrasts of light and dark, and where darkness becomes a dominating feature of the image. The technique was developed to add drama to an image through a spotlight effect, and is common in Baroque paintings. Tenebrism is used only to obtain a dramatic impact while chiaroscuro is a broader term, also covering the use of less extreme contrasts of light to enhance the illusion of three-dimensionality. (Full article...) -
Image 21

Ghost sign advertising Bile Beans in York, England
A ghost sign is an old hand-painted advertising sign that has been preserved on a building for an extended period of time. The sign may be kept for its nostalgic appeal, or simply indifference by the owner. (Full article...) -
Image 22

Attributed to Cristofano dell'Altissimo or Leonardo da Vinci - Portrait of a man, signed Pinxit Mea
Pinxit (from Latin: 'one painted') is a stylized amendment added to the signature depiction of the name of the person responsible for a work of art, found conventionally in the Late Middle Ages and the Renaissance. It is sometimes abbreviated P, PIN, or PINX, as in some paintings by Raphael. The locution me pinxit is found on a 12th-century crucifix, not in a sense connected to individual authorship but rather as a more impersonal devotional statement, a "pious [formula] appropriate for liturgical gifts".
Its use by Duccio c. 1255–1260 – c. 1318–1319) on the Maestà in Siena Cathedral is seen as an "audacious" claim by the author, who asserts an individual status on a par with that of the city. By the Late Middle Ages in Venice and elsewhere pinxit (or other forms of pingere, in Gothic lettering) had become customary, and was often found on a cartellino, "any form of fictive paper carrying an inscription", established in Venice by the 1440s. Other verbs used to establish authorship include conjugations of facere ("to make"; fecit ("made by") was frequently used by Titian) or fingere ("to conceive"). (Full article...) -
Image 23

Sign painters create a new sign on the walls of the Hotel Figueroa in Los Angeles, California
Sign painting is the craft of painting lettered signs on buildings, billboards or signboards, for promoting, announcing, or identifying products, services and events. Sign painting artisans are signwriters, although in North America they are usually referred to as sign painters. (Full article...) -
Image 24

BALVINO MAURICIO, José Honorato Lozano, 1864
Letras y figuras (Spanish, "letters and figures") is a genre of painting pioneered by José Honorato Lozano during the Spanish colonial period in the Philippines. The art form is distinguished by the depiction of letters of the alphabet using a genre of painting that contoured shapes of human figures, animals, plants, and other objects called Tipos del País popularized by Damián Domingo. The letters depicted spell out a phrase or a name, usually that of the patron who commissioned the work. The paintings were done with watercolor on Manila paper. The earliest example of this art form dates from 1845; the latest existing specimens were completed during the latter portion of the American period in the 1930s during the administration of the Commonwealth of the Philippines.
In 1995, an album of José Honorato Lozano's paintings were auctioned at Christie’s at the starting bid of £300,000. (Full article...) -
Image 25

Self-portrait of Nicolas Régnier painting a portrait of Vincenzo Giustiniani, 1623–24, Fogg Art Museum.
Portrait painting is a genre in painting, where the intent is to represent a specific human subject. The term 'portrait painting' can also describe the actual painted portrait. Portraitists may create their work by commission, for public and private persons, or they may be inspired by admiration or affection for the subject. Portraits often serve as important state and family records, as well as remembrances.
Historically, portrait paintings have primarily memorialized the rich and powerful. Over time, however, it became more common for middle-class patrons to commission portraits of their families and colleagues. Today, portrait paintings are still commissioned by governments, corporations, groups, clubs, and individuals. In addition to painting, portraits can also be made in other media such as prints (including etching and lithography), photography, video and digital media. (Full article...)
Selected painting techniques
-
Image 1

Example of a theorem painting (c.1850) from the Metropolitan Museum of Art
Theorem stencil, sometimes also called theorem painting or velvet painting, is the art of making stencils and using them to make drawings or paintings on fabric or paper.
A vogue for theorem stencil painting began in England at the turn of the 18th century and through the mid-1800s. The art was first taught to women in academies and boarding schools throughout colonial New England. It continued to be taught into the mid-1800s in many other areas. (Full article...) -
Image 2

Imitation wood grain on plastic flooring
Graining is the practice of imitating wood grain on a non-wood surface, or on relatively undesirable wood surface, in order to give it the appearance of a rare or higher quality wood, thereby increase that surface's aesthetic appeal. Graining was common in the 19th century, as people were keen on imitating hard, expensive woods by applying a superficial layer of paint onto soft, inexpensive woods or other hard surfaces. Graining can be accomplished using either rudimentary tools or highly specialized tools. A specialized thick brush used for graining is often called a mottler. Fan brushes, floggers, softening brushes, texture combs and even fingers are used to create various effects. The painting is carried out in layers, with the first layer being a base. Today that is usually done with latex paint in a gold or orange or tan tone, depending on the type of wood the artist is aiming to imitat. A second layer of tempera or thinned paint is applied over the dry base, by means of a sponge or large inexpensive brush. During the 19th century, however, brushes were more commonly used. It can also be applied on bricks and brass, as is more common today.
Graining can also mean the production of any artificial texture on any surface. For example, in printing, making the smooth metal sheets used in modern printing processes coarse. A stoneworking equivalent of graining is marbling. (Full article...) -
Image 3Ink wash painting (simplified Chinese: 水墨画; traditional Chinese: 水墨畫; pinyin: shuǐmòhuà); is a type of Chinese ink brush painting which uses washes of black ink, such as that used in East Asian calligraphy, in different concentrations. It emerged during the Tang dynasty of China (618–907), and overturned earlier, more realistic techniques. It is typically monochrome, using only shades of black, with a great emphasis on virtuoso brushwork and conveying the perceived "spirit" or "essence" of a subject over direct imitation. Ink wash painting flourished from the Song dynasty in China (960–1279) onwards, as well as in Japan after it was introduced by Zen Buddhist monks in the 14th century. Some Western scholars divide Chinese painting (including ink wash painting) into three periods: times of representation, times of expression, and historical Oriental art. Chinese scholars have their own views which may be different; they believe that contemporary Chinese ink wash paintings are the pluralistic continuation of multiple historical traditions.
In China, Japan and, to a lesser extent, Korea, ink wash painting formed a distinct stylistic tradition with a different set of artists working in it than from those in other types of painting. In China especially it was a gentlemanly occupation associated with poetry and calligraphy. It was often produced by the scholar-official or literati class, ideally illustrating their own poetry and producing the paintings as gifts for friends or patrons, rather than painting for payment. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Badger Studying a Sutra by Shibata Zeshin (Japan)
Lacquer painting is a form of painting with lacquer which was practised in East Asia for decoration on lacquerware, and found its way to Europe and the Western World both via Persia and the Middle East and by direct contact with Continental Asia. The artistic form was revived and developed as a distinct genre of fine art painting by Vietnamese artists in the 1930s; the genre is known in Vietnamese as "sơn mài." (Full article...) -
Image 5Industrial Painting is defined by the 1959 "Manifesto of Industrial Painting: For a unitary applied art", a text by Giuseppe Pinot-Gallizio which was originally published in Notizie Arti Figurative No. 9 (1959). A French translation was soon published in Internationale Situationniste no.3 (1959).
In May 1997, Molly Klein translated the original Italian-language version into English: (Full article...) -
Image 6

The mural Westward the Course of Empire Takes Its Way was made using stereochromy
Mineral painting or Keim's process, also known as stereochromy, is a mural or fresco painting technique that uses a water glass-based paint to maximize the lifetime of the finished work.
The name "stereochromy" was first used in about 1825 by Johann Nepomuk von Fuchs and Schlotthaurer. In the original technique, pigments were applied to plaster or stone and sealed with water glass to preserve and enhance the colors. The method was then improved in the 1880s by Adolf Wilhelm Keim and renamed mineral painting or Keim's process. (Full article...) -
Image 7

Captain Joseph – Chinese reverse glass painting from c. 1785 – 1789.
Reverse painting on glass is an art form consisting of applying paint to a piece of glass and then viewing the image by turning the glass over and looking through the glass at the image. Another term used to refer to the art of cold painting and gilding on the back of glass is verre églomisé, named after the French decorator Jean-Baptiste Glomy (1711–86), who framed prints using glass that had been reverse-painted. In German it is known as Hinterglasmalerei.
This art form has been around for many years. It was widely used for sacral paintings since the Middle Ages. The most famous was the art of icons in the Byzantine Empire. Later the painting on glass spread to Italy, where in Venice it influenced its Renaissance art. Since the middle of the 18th century, painting on glass became favored by the Church and the nobility throughout Central Europe. A number of clock faces were created using this technique in the early-to-mid-19th century. Throughout the 19th century painting on glass was widely popular as folk art in Austria, Bavaria, Moravia, Bohemia and Slovakia. Unfortunately, during the inter-war period (1914–1945) this traditional "naive" technique fell nearly to a complete oblivion and its methods of paint composition and structural layout had to be re-invented by combining acrylic and oil paints. A new method of reverse painting emerged using polymer glazing methods that permitted the artworks to be painted direct to an acrylic UV coating on the glass. The unique under glass effect retains a curious depth even though the layered painting on the glass was bonded to a final linen support and now stretcher bar mounted after being carefully removed from the original 'glass easel'. Current glass painting may disappear with the advent of using aerospace mylar as a preliminary support. (Full article...) -
Image 8

The Ghent Altarpiece by Jan van Eyck and his brothers, 1432. A large altarpiece on panel. The outer wings are hinged, and painted on both sides.
A panel painting is a painting made on a flat panel of wood, either a single piece or a number of pieces joined together. Until canvas became the more popular support medium in the 16th century, panel painting was the normal method, when not painting directly onto a wall (fresco) or on vellum (used for miniatures in illuminated manuscripts). Wood panels were also used for mounting vellum paintings. (Full article...) -
Image 9Buon fresco (Italian for 'true fresh') is a fresco painting technique in which alkaline-resistant pigments, ground in water, are applied to wet plaster.
It is distinguished from the fresco-secco (or a secco) and finto fresco techniques, in which paints are applied to dried plaster. (Full article...) -
Image 10A rotary atomizer is an automatic electrostatic paint applicator used in high volume, automatic production painting environments. Also called a 'paint bell', "rotary bell atomizer" or 'bell applicator', it is preferred for high volume paint application for its superior transfer efficiency, spray pattern consistency, and low compressed air consumption, when compared to a paint spray gun. It can be mounted in a fixed position, reciprocating arm, or an industrial robot. (Full article...)
-
Image 11

The Loves of the Gods, in the Palazzo Farnese, by Annibale Carracci, a renowned example of quadro riportati
Quadro riportato (plural quadri riportati) is the Italian phrase for "carried picture" or "transported paintings". It is used in art to describe gold-framed easel paintings or framed paintings that are seen in a normal perspective and painted into a fresco. The final effect is similar to illusionism, but the latter encompasses painted statues, reliefs and tapestries.
The ceiling is intended to look as if a framed painting has been placed overhead; there is no illusionistic foreshortening, figures appearing as if they were to be viewed at normal eye level. Mengs' Parnassus (1761) in the Villa Albani (now Villa Albani-Torlonia) is a famous example — a Neoclassical criticism against Baroque illusionism. Often, however, quadri riportati were combined with illusionistic elements, as in Annibale Carracci's Farnese Ceiling (1597–1600) in Rome. (Full article...) -
Image 12Marouflage is a technique for affixing a painted canvas (intended as a mural) to a wall, using an adhesive that hardens as it dries, such as plaster or cement. (Full article...)
-
Image 13Giornata is an art term, originating from an Italian word which means "a day's work." The term is used in Buon fresco mural painting and describes how much painting can be done in a single day of work. This amount is based on the artist's past experience of how much they can paint in the many hours available while the plaster remains wet and the pigment is able to adhere to the wall. (Full article...)
-
Image 14

Xia Gui (Song dynasty) – Mountain Market- Clear with Rising Mist, one of the 8 scenes of the Eight Views of Xiaoxiang, a favourite subject in the Chinese ink wash painting tradition, showing the variety of effects achievable with black ink.
A wash is a term for a visual arts technique resulting in a semi-transparent layer of colour. A wash of diluted ink or watercolor paint applied in combination with drawing is called pen and wash, wash drawing, or ink and wash. Normally only one or two colours of wash are used; if more colours are used the result is likely to be classified as a full watercolor painting.
The classic East Asian tradition of ink wash painting uses black ink in various levels of dilution. Historically associated with the four arts of the scholar-officials, the technique was often applied to landscapes in traditional Chinese, Japanese, and Korean painting. (Full article...) -
Image 15Brain painting is a non-invasive P300-based brain-computer interface (BCI) that allows painting without the use of muscular activity. The technology combines electroencephalography, signal processing algorithms and visual stimulation on a monitor to detect where the user focuses his attention, allowing him to voluntarily trigger commands to a painting software. The research project aims at assisting people afflicted with the Locked-in syndrome due to neurological or neuromuscular disease (e.g. amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS), who are severely restricted in communication with their environment, and therefore cut off from the possibility of creative expression. (Full article...)
-
Image 16

1883 reconstruction of color scheme of the entablature on a Doric temple
Polychrome is the "practice of decorating architectural elements, sculpture, etc., in a variety of colors." The term is used to refer to certain styles of architecture, pottery, or sculpture in multiple colors.
When looking at artworks and architecture from antiquity and the European Middle Ages, people tend to believe that they were monochrome. In reality, the pre-Renaissance past was full of colour, and all the Greco-Roman sculptures and Gothic cathedrals, that are now white, beige, or grey, were initially painted in bright colours. As André Malraux stated: "Athens was never white but her statues, bereft of color, have conditioned the artistic sensibilities of Europe [...] the whole past has reached us colorless." Polychrome was and is a practice not limited only to the Western world. Non-Western artworks, like Chinese temples, Oceanian Uli figures, or Maya ceramic vases, were also decorated with colours. (Full article...) -
Image 17

Masking tape being peeled off of a canvas, to reveal the protected, unpainted area below
In art, craft, and engineering, masking is the use of materials to protect areas from change, or to focus change on other areas. This can describe either the techniques and materials used to control the development of a work of art by protecting a desired area from change; or a phenomenon that (either intentionally or unintentionally) causes a sensation to be concealed from conscious attention.
The term is derived from the word mask, in the sense that it hides the face from view. (Full article...) -
Image 18As an art form, vitreography is a style of contained 3-dimensional scenes displayed in a shadow box frame. (Full article...)
-
Image 19An abandoned roof felt factory in Santalahti, Finland which has been painted with graffiti, including work by 1UP (top left), 2012
Graffiti (singular graffiti or graffito, the latter only used in graffiti archeology) is writing or drawings made on a wall or other surface, usually without permission and within public view. Graffiti ranges from simple written "monikers" to elaborate wall paintings, and has existed since ancient times, with examples dating back to ancient Egypt, ancient Greece, and the Roman Empire.
Modern graffiti is a controversial subject. In most countries, marking or painting property without permission is considered vandalism. Modern graffiti began in the New York City subway system and Philadelphia in the early 1970s and later spread to the rest of the United States and throughout the world. (Full article...) -
Image 20Leaf painting is the process of painting with dyed leaves. Deriving from Japan, China or India, it became popular in Vietnam. Its two main forms are: Cutting and pasting dry leaf to make leaf paintings or using paint to draw onto the surface of dry leaf to make leaf paintings.
Every product is unique, quite different from the others because of the leaves' veins, the forms, and the colors before or after dying. (Full article...) -
Image 21

Madonna painting on caterpillar silk, Chester Cathedral
Cobweb painting, sometimes known as gossamer painting, is the delicate process of painting on canvases made from caterpillar and spider webs that have been collected, layered, cleaned, and framed. Fewer than 100 cobweb paintings are known to exist, many of which are housed in private collections. (Full article...) -
Image 22Action painting, sometimes called "gestural abstraction", is a style of painting in which paint is spontaneously dribbled, splashed or smeared onto the canvas, rather than being carefully applied. The resulting work often emphasizes the physical act of painting itself as an essential aspect of the finished work or concern of its artist. (Full article...)
-
Image 23

A 6th-century encaustic icon from Saint Catherine's Monastery, Egypt.
Encaustic painting, also known as hot wax painting, is a form of painting that involves a heated wax medium to which colored pigments have been added. The molten mix is applied to a surface—usually prepared wood, though canvas and other materials are sometimes used. The simplest encaustic medium could be made by adding pigments to wax, though recipes most commonly consist of beeswax and damar resin, potentially with other ingredients. For pigmentation, dried powdered pigments can be used, though some artists use pigmented wax, inks, oil paints or other forms of pigmentation.
Metal tools and special brushes can be used to shape the medium as it cools. Also, heated metal tools, including spatulas, knives and scrapers, can be used to manipulate the medium after it has cooled onto the surface. Additionally, heat lamps, torches, heat guns, and other methods of applying heat are used by encaustic artists to fuse and bind the medium. Because encaustic medium is thermally malleable, the medium can be also sculpted, and materials can be encased, collaged or layered into the medium. (Full article...) -
Image 24

Raphael's La belle jardinière, showing the use of unione
According to the theory of the art historian Marcia B. Hall, which has gained considerable acceptance, unione (Italian: [uˈnjoːne]) is one of the canonical painting modes of the Renaissance; that is, one of four modes of painting colours available to Italian High Renaissance painters, along with sfumato, chiaroscuro and cangiante. Unione was developed by Raphael, who exemplified it in the Stanza della Segnatura.
Unione is similar to sfumato, but is more useful for the edges of chiaroscuro, where vibrant colors are involved. As with chiaroscuro, unione conveys the contrasts, and as sfumato it strives for harmony and unity, but also for coloristic richness. Unione is softer than chiaroscuro in the search for the right tonal key. There should be the harmony between light and dark, without the excesses and accentuation of a chiaroscuro mode. (Full article...) -
Image 25

Paasche F#1 Single-action external mix airbrush
An airbrush is a small, air-operated tool that atomizes and sprays various media, most often paint, but also ink, dye, and make-up. Spray painting developed from the airbrush and is considered to employ a type of airbrush. (Full article...)
Need help?
Do you have a question about Painting that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
Get involved
For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Painting-related articles, see WikiProject Painting.
General images
-
Image 4An Ethiopian illuminated Evangelist portrait of Mark the Evangelist, from the Ethiopian Garima Gospels, 6th century AD, Kingdom of Aksum (from History of painting)
-
Image 6Andreas Achenbach, Clearing Up, Coast of Sicily (1847), The Walters Art Museum (from Painting)
-
Image 8Cueva de las Manos (Spanish for Cave of the Hands) in the Santa Cruz province in Argentina, c. 7300 BC (from History of painting)
-
Image 10Bharat Mata by Abanindranath Tagore (1871–1951), a nephew of the poet Rabindranath Tagore, and a pioneer of the movement (from History of painting)
-
Image 13Jean de Court (attributed), painted Limoges enamel dish in detail (mid-16th century), Waddesdon Bequest, British Museum (from Painting)
-
Image 19The Eternal Father Painting the Virgin of Guadalupe. Attributed to Joaquín Villegas (1713 – active in 1753) (Mexican) (painter, Museo Nacional de Arte. (from History of painting)
-
Image 20Hellenistic Greek terracotta funerary wall painting, 3rd century BC (from History of painting)
-
Image 21Sesshū Tōyō, Landscapes of the Four Seasons (1486), ink and light color on paper (from Painting)
-
Image 22Diego Rivera, Recreation of Man at the Crossroads (renamed Man, Controller of the Universe), originally created in 1934, Mexican muralism movement (from History of painting)
-
Image 31Jean Metzinger, La danse (Bacchante) (c. 1906), oil on canvas, 73 x 54 cm, Kröller-Müller Museum (from Painting)
-
Image 35Max Beckmann, The Night (Die Nacht), 1918–1919, Kunstsammlung Nordrhein-Westfalen, Düsseldorf (from History of painting)
-
Image 37Two Scribes Seated with Books and a Writing Table Fragment of a decorative margin Northern India (Mughal school), ca. 1640–1650 (from History of painting)
-
Image 39The depiction of a bull found in the Lubang Jeriji Saleh, Indonesia, in 2018, is the world’s oldest known figurative painting. The painting is estimated to have been created around 40,000 to 52,000 years ago, or even earlier. (from Painting)
-
Image 40Loquats and Mountain Bird, anonymous artist of the Southern Song dynasty; paintings in leaf album style such as this were popular in the Southern Song (1127–1279). (from History of painting)
-
Image 42Francis Picabia, (Left) Le saint des saints c'est de moi qu'il s'agit dans ce portrait, 1 July 1915; (center) Portrait d'une jeune fille americaine dans l'état de nudité, 5 July 1915: (right) J'ai vu et c'est de toi qu'il s'agit, De Zayas! De Zayas! Je suis venu sur les rivages du Pont-Euxin, New York, 1915 (from History of painting)
-
Image 44Barnett Newman, Untitled Etching 1 (First Version), 1968, Minimalism (from History of painting)
-
Image 45In 2021, researchers discovered ancient cave art in Leang Tedongnge, Sulawesi, Indonesia, estimated to be at least 45,500 years old. Depicting a warty pig, this artwork is recognized as the world’s oldest known example of figurative or representational art. (from History of painting)
-
Image 46Spring Morning in the Han Palace, by Ming-era artist Qiu Ying (1494–1552 AD) (from History of painting)
-
Image 48Krishna and Radha, might be the work of Nihâl Chand, master of Kishangarh school of Rajput Painting (from Painting)
-
Image 50In 2021, researchers discovered ancient cave art in Leang Tedongnge, Sulawesi, Indonesia, estimated to be at least 45,500 years old. Depicting a warty pig, this artwork is recognized as the world’s oldest known example of figurative or representational art. (from Painting)
-
Image 53Francisco de Zurbarán, Still Life with Pottery Jars (Spanish: Bodegón de recipientes) (1636), oil on canvas, 46 x 84 cm, Museo del Prado, Madrid (from Painting)
-
Image 58Joan Miró, Horse, Pipe and Red Flower, 1920, abstract Surrealism, Philadelphia Museum of Art (from History of painting)
-
Image 59The Sakyamuni Buddha, by Zhang Shengwen, 1173–1176 AD, Song dynasty period. (from History of painting)
-
Image 61Marcel Duchamp, Nude Descending a Staircase, No. 2, 1912, Philadelphia Museum of Art (from History of painting)
-
Image 62A fresco showing Hades and Persephone riding in a chariot, from the tomb of Queen Eurydice I of Macedon at Vergina, Greece, 4th century BC (from History of painting)
-
Image 64Hand stencils in the "Tree of Life" cave painting in Gua Tewet, Kalimantan, Indonesia (from History of painting)
-
Image 65Silk painting depicting a man riding a dragon, painting on silk, dated to 5th–3rd century BC, Warring States period, from Zidanku Tomb no. 1 in Changsha, Hunan Province (from History of painting)
-
Image 67Khan Bahadur Khan with Men of his Clan, c. 1815, from the Fraser Album, Company Style (from Painting)
-
Image 69Gwion Gwion rock paintings found in the north-west Kimberley region of Western Australia c. 15,000 BC (from History of painting)
-
Image 72Piet Mondrian, Composition en rouge, jaune, bleu et noir (1921), Gemeentemuseum Den Haag (from Painting)
-
Image 73Rudolf Reschreiter, Blick von der Höllentalangerhütte zum Höllentalgletscher und den Riffelwandspitzen, Gouache (1921) (from Painting)
-
Image 75Mona Lisa (1503–1517) by Leonardo da Vinci is one of the world's most recognizable paintings. (from Painting)
-
Image 76Mother Goddess A miniature painting of the Pahari style, dating to the eighteenth century. Pahari and Rajput miniatures share many common features. (from History of painting)
-
Image 79Pictographs from the Great Gallery, Canyonlands National Park, Horseshoe Canyon, Utah, c. 1500 BCE (from History of painting)
-
Image 81Muromachi period, Shingei (1431–1485), Viewing a Waterfall, Nezu Museum, Tokyo. (from History of painting)
-
Image 82Honoré Daumier, The Painter (1808–1879), oil on panel with visible brushstrokes (from Painting)
-
Image 83Nino Pisano, Apelles or the Art of painting in detail (1334–1336); relief of the Giotto's Bell Tower in Florence, Italy
Categories
Topics
General painting topics
- 20th-century Western painting
- Abstract art
- Accidentalism
- Animal-made art
- Architectural painting
- Binder
- Boston Expressionism
- Boston School
- Cabinet painting
- Coloring book
- Combine painting
- Conservation and restoration of paintings
- Conservation and restoration of panel paintings
- Digital painting
- En plein air
- Figura serpentinata
- Figure painting
- Flatness
- French standard sizes for oil paintings
- Genre art
- Genre painting
- Ghost sign
- Grand manner
- Hierarchy of genres
- Historic paint analysis
- House painter and decorator
- Incised painting
- Inscape
- ISCC–NBS system
- Jerwood Painting Prize
- Letras y figuras
- Live painting
- Local color
- Mixed media
- Mural
- Night in paintings (Eastern art)
- Night in paintings (Western art)
- Nocturne
- Nude
- Oil painting
- Oil painting reproduction
- Orange peel
- Overdoor
- Paint and sip industry
- Paint Dancing
- Paint robot
- Painterliness
- History of painting
- Panoramic painting
- Peintres de la Réalité
- Pendant painting
- Pentimento
- Picture frame
- Pinxit
- Pliage
- Portrait painting
- Prime version
- Problem picture
- Raking light
- Range-finder painting
- Scottish genre art
- Self-portrait
- Sign painting
- Signwriter
- Staffage
- Style
- Tenebrism
- Theory of painting
- Tondo
- Volume solid
- Wash
- Watercolor painting
- Western painting
Painting techniques
- Acrylic painting techniques
- Action painting
- Airbrush
- Al-Qatt Al-Asiri
- Atelier
- Bark painting
- Brain painting
- Brunaille
- Buon fresco
- Cangiante
- Carnation
- Ceramic glaze
- China painting
- Cobweb art
- Cobweb painting
- Craquelure
- Distemper
- Double-sided painting
- Drip painting
- Drybrush
- Electrostatic coating
- Encaustic painting
- Fat over lean
- Figure painting
- Fingerpaint
- Fore-edge painting
- Freehand brush work
- Fresco
- Fresco-secco
- Gambier Parry process
- Generative art
- Giornata
- Glaze
- Glue-size
- Gongbi
- Graffiti
- Graining
- Grisaille
- Haboku
- Illusionism
- Illusionistic ceiling painting
- Impasto
- Imprimatura
- Industrial painting
- Ink wash painting
- Intonaco
- Keim's process
- Lacquer painting
- Leaf painting
- Licked finish
- Lining of paintings
- Maki-e
- Marouflage
- Masking
- Matte painting
- Microbial art
- Mineral painting
- Mischtechnik
- Mold painting
- Mouth and foot painting
- Nocturne
- Notan
- Oil sketch
- Ombré
- Overpainting
- Overspray
- Paint by number
- Painting
- Panel painting
- Papier collé
- Pastiglia
- Pen painting
- Pinstriping
- Pointillism
- Polychrome
- Powder painting
- Prestezza
- Protoquadro
- Quadratura
- Quadro riportato
- Repoussoir
- Reverse glass painting
- Rosemåling
- Rotational bell painting
- Sandpainting
- Sfumato
- Shaped canvas
- Shigajiku
- Silk painting
- Speed line
- Speed painting
- Spray painting
- Tempera
- Texture
- Theorem stencil
- Trompe-l'œil
- Underdrawing
- Underpainting
- Unione
- Velvet painting
- Verdaccio
- Verdaille
- Vitreography
- Wash
- Watercolor painting
- Wet-on-wet
- Working in layers
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus