| Main page | New articles & Tasks |
 The Energy Portal Welcome to Wikipedia's Energy portal, your gateway to energy. This portal is aimed at giving you access to all energy related topics in all of its forms.
|
Page contents: Selected article • Selected image • Selected biography • Did you know? • General images • Quotations • Related portals • Wikiprojects • Major topics • Categories • Help • Associated Wikimedia |
Introduction
Energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια (enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).
Forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system, and rest energy associated with an object's rest mass. These are not mutually exclusive.
All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven primarily by radiant energy from the sun. The energy industry provides the energy required for human civilization to function, which it obtains from energy resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear fuel, and renewable energy. (Full article...)
Selected article
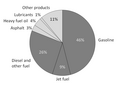
Natural gas, often referred to as simply 'gas', is a gaseous fossil fuel consisting primarily of methane. Natural gas is found in oil fields, natural gas fields, and in coal beds (as coalbed methane). Before use as a fuel, natural gas undergoes extensive processing to remove almost all materials other than methane.
Natural gas is a major source of electricity generation, and particularly high efficiencies can be achieved through combining gas turbines with a steam turbine in combined cycle mode. Natural gas burns cleaner than other fossil fuels, producing about 30% less carbon dioxide than oil and about 45% less than coal, per unit of energy released. It is also expected that natural gas reserves will peak around 2030, some 20 years after peak oil production. Compressed natural gas is also used as a cleaner alternative to other automobile fuels such as gasoline (petrol) and diesel. Natural gas is also used domestically for cooking and for central heating.
The major difficulty in the use of natural gas is transportation and storage because of its low density. Pipeline transport is economical, but is impractical across oceans. Liquefied natural gas can be shipped in LNG carriers, however the required liquefaction facilities add to the cost. The practice of flaring gas released in the course of recovering petroleum, so adding to greenhouse gas emissions, is now illegal in many countries.
Selected image

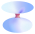
Photo credit: Andreas Tille
Geysers erupt periodically due to surface water being heated by geothermal heat.
Did you know?
- The development of renewable energy in Iceland means that by 2050 the country should be the world's first zero-carbon economy?
- World's two largest oil shale-fired power plants (Narva Power Plants) generate more than 90% of power in Estonia?
- NW Natural in Portland, Oregon was the first gas company in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States when it started in 1859?
- The Assistant Secretary of Energy for Fossil Energy is responsible for America's Strategic Petroleum Reserve?
- Despite declines in production in recent years, Victoria still produces almost 20% of Australia's crude oil?
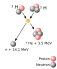
- 4.26 million tonnes of the Sun are converted to energy every second by nuclear fusion?
- The first gasworks in the United Kingdom was built by the Gas Light and Coke Company, incorporated by Royal Charter in 1812?
- The Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan pipeline was a central plot point in the James Bond film The World Is Not Enough?
Selected biography
Fermi was well-known for his simplicity in solving problems. Whenever possible, he avoided complicated mathematics and obtained quick results based on order of magnitude estimates. Fermi also meticulously recorded his calculations in notebooks, and later used to solve many new problems that he encountered based on these earlier known problems.
After accepting the 1938 Nobel Prize in Stockholm, Fermi immigrated to New York with his family to escape the anti-Semitic laws of Fascist Italy, as his wife Laura was Jewish.
After working at Columbia University, Fermi went to the University of Chicago and began studies that led to the construction of the world's first nuclear reactor Chicago Pile-1 (CP-1). The first artificial, self-sustaining, nuclear chain reaction was initiated within CP-1, on December 2, 1942.
In the news
- 13 December 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Russia launches one of its largest attacks on the Ukrainian energy infrastructure since the conflict began, with about 290 missiles fired and drones striking multiple regions. The Russian Defense Ministry claims that the attack was in response to a recent Ukrainian ATACMS attack on Taganrog-Central air base in Rostov Oblast, Russia. (The Kyiv Independent) (UNN)
- 4 December 2024 – 2024 Cuba blackouts
- Another round of blackouts in Cuba leave millions of households without power. The energy ministry says that it is prioritizing restoring electricity to hospitals and water pumping facilities. (Reuters)
- 30 November 2024 – Ibar-Lepenac attack
- Police arrest eight people linked to an explosion on a canal near Zubin Potok, Mitrovica District, Kosovo, that supplies water to the country's two main power plants. The Kosovar government blames Serbia for the "terrorist" acts, which Serbia denies. (Al Jazeera) (Euronews) (Le Monde)
- 28 November 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Russian strikes against Ukrainian infrastructure, Ukrainian energy crisis
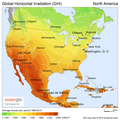
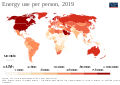
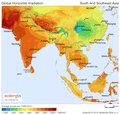
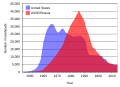
General images
Quotations
- "The world's second-largest emitter of greenhouse gases is China. Yet, China was entirely exempted from the requirements of the Kyoto Protocol. India and Germany are among the top emitters. Yet, India was also exempt from Kyoto." – George W. Bush, 2001
- "The newly industrialized States cannot, for example, be asked to apply restrictive environmental standards to their emerging industries unless the industrialized States first apply them within their own boundaries." – Pope John Paul II, 1990
- "We should work together to make sure the international community upholds the goals and framework established in the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change and its Kyoto Protocol and the principle of common but differentiated responsibilities." – Hu Jintao, 2007
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects connected with energy:
Other WikiProjects that may be of interest:
Major topics
Major categories
National energy supply, use & conservation
National electricity sector
Politics, economics, environment
- Climate change
- Energy conservation
- Energy economics
- Energy crises
- Energy development
- Energy policy
- Peak oil
Energy sources
- Fuels
- Biofuels
- Fossil fuels
- Fusion power
- Nuclear technology
- Renewable energy
- Energy conversion
- Electric power
- Energy storage
Energy-related design
Scientific usage
Help

Puzzled by energy?
Can't answer your question?
Don't understand the answer?
- Ask at the reference desk
- Read the Wikipedia help pages
For further ideas, to leave a comment, or to learn how you can help improve and update this portal, see the talk page.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus