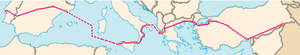
European route E 90 is an A-Class West–East European route, extending from Lisbon in Portugal in the west to the Turkish–Iraqi border in the east. It is connected to the M5 of the Arab Mashreq International Road Network.
| E90 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Major junctions | |
| West end | Lisbon, Portugal |
| East end | Zakho, Iraq |
| Location | |
| Countries | |
| Highway system | |

Itinerary
editThe E 90 routes through five European countries, and includes four sea-crossings: Barcelona, Spain - Mazara del Vallo, Italy; Messina, Italy to Reggio Calabria, Italy; Brindisi, Italy, to Igoumenitsa, Greece, and Eceabat, Turkey, to Çanakkale, Turkey.
- A 2 / IP 7: Lisbon - Setúbal (Start of concurrency with E01) - Landeira (End of concurrency with E01)
- A 6 / IP 7: Landeira ( E01) - Évora (Start of concurrency with E802) - Estremoz (End of concurrency with E802) - Elvas
- A-5: Badajoz - Mérida ( E803) ( E903) - Madrid
- M-30: Madrid ( E5 E901)
- A-2: Zaragoza ( E7 E804)
- AP-2: Zaragoza - Lleida - El Vendrell ( E15)
- AP-7: El Vendrell (Start of concurrency with E15) - Rubí (End of concurrency with E15)
- AP-2: Rubí ( E15) - Barcelona
- B-23: Barcelona
- A-2: Barcelona
- B-10: Barcelona
Gap
- A 29: Mazara del Vallo ( E931) - Alcamo ( E933) - Palermo (Towards E25)
- A 20: Palermo (Towards E25) - Campofelice di Roccella
- A 19: Campofelice di Roccella - Messina ( E45)
- : Messina - Villa San Giovanni
- A 2: Villa San Giovanni ( E45) - Reggio Calabria
- RA 4: Reggio Calabria
- SS 106: Reggio Calabria - Catanzaro ( E848) - Crotone ( E846) - Sibari ( E848) - Metaponto ( E847) - Taranto ( E843)
- SS 7: Taranto ( E843) - Brindisi ( E55)
- SS 16 / SS 613: Brindisi ( E55)
Ferry
The Greek portion of E90 consists of the A2 Egnatia Odos, after the road built on top of a pre-Roman trail that spanned from the Adriatic to the Aegean, Via Egnatia. It was later extended to Byzantium (Constantinople) to the east and Rome to the west. The name Egnatia comes from the Roman proconsul, Gnaius Egnatius, who built the original road.[1] In its design phase, Egnatia Odos was planned to have 1650 bridges, 43 river crossings, 11 railway crosses, and 50 interchanges with existing roads.
- A 2: Igoumenitsa ( E55 E92) - Ioannina ( E951, Towards E92 E853) - Kalabaka ( E92) - Kozani ( E65) - Thessaloniki ( E75 E79 E86) - Komotini ( E85) - Kipoi
- D.110: İpsala - Keşan ( E84 E87)
- D.550: Keşan ( E84, Start of concurrency with E87) - Gelibolu (End of concurrency with E87)
- : Gelibolu - Lapseki
- D.200: Lapseki - Karacabey (Start of concurrency with E881) - Bursa
- O-5: Bursa (End of concurrency with E881)
- O-22: Bursa
- D.200: Bursa - Eskişehir - Sivrihisar ( E96) - Ankara ( E89)
- O-20: Ankara ( E88 E89)
- D.750: Ankara ( E88) - Aksaray - Ulukışla
- O-21A: Ulukışla
- O-21: Ulukışla - Tarsus ( E982)
- O-51: Tarsus ( E982) - Adana
- O-52: Adana - Toprakkale ( E91) - Gaziantep - Şanlıurfa ( E99)
- D.400: Şanlıurfa - Nusaybin ( Qamishli) - Cizre
- D.430: Cizre - Silopi
References
edit- ^ Jog, Gauri M.; Brilakis, Ioannis K.; Angelides, Demos C. (2011-07-01). "Testing in harsh conditions: Tracking resources on construction sites with machine vision". Automation in Construction. 20 (4): 328–337. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2010.11.003. ISSN 0926-5805.
