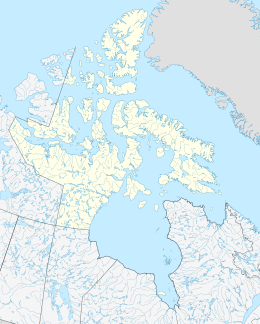
Akimiski Island[1] is the largest island in James Bay (a southeasterly extension of Hudson Bay), Canada, which is part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the territory of Nunavut. It has an area of 3,001 km2 (1,159 sq mi), making it the 163rd largest island in the world, and Canada's 29th largest island. Akimiski Island is 19 km (12 mi) from the province of Ontario. From the western side of the island, the Ontario coastline is visible.
 Closeup of Akimiski Island | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Nunavut |
| Coordinates | 53°00′30″N 081°16′30″W / 53.00833°N 81.27500°W[1] |
| Archipelago | Arctic Archipelago |
| Area | 3,001 km2 (1,159 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 34 m (112 ft) |
| Administration | |
Canada | |
| Territory | Nunavut |
| Region | Qikiqtaaluk |
| Demographics | |
| Population | Uninhabited |
The island's name is Swampy Cree[1] for "land across the water".[2]
The island has no year-round human inhabitants. The surface of Akimiski is flat and slopes gradually to the north. Most of the vegetation that covers the island consists of lichen, moss, sedges, and dwarf black spruce. The island is a coastal wetland that includes mudflats, tidal marshes, and tidal mudflats. Freshwater streams that flow into southwestern James Bay carry sediments and abundant nutrients that help to sustain the productive waterfowl habitat around Akimiski Island.
The Akimiski Island Group includes Akimiski, Gasket, and Gullery islands; Albert Shoal; and the Akimiski Strait Isles.
Climate
edit- Mean annual temperature: 2.5 °C (36.5 °F)
- Average rainfall: 450 mm (17.72 in)
- Average snowfall: 25 cm (9.84 in)[3]
| Climate data for Akimiski Island | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −14 (7) |
−12 (10) |
−6 (21) |
1 (34) |
10 (50) |
17 (63) |
19 (66) |
19 (66) |
13 (55) |
6 (43) |
−1 (30) |
−9 (16) |
4 (38) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −23 (−9) |
−22 (−8) |
−16 (3) |
−7 (19) |
−1 (30) |
3 (37) |
6 (43) |
8 (46) |
5 (41) |
1 (34) |
−6 (21) |
−17 (1) |
−6 (22) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 23 (0.9) |
18 (0.7) |
30 (1.2) |
35 (1.4) |
44 (1.7) |
57 (2.2) |
58 (2.3) |
56 (2.2) |
55 (2.2) |
60 (2.4) |
45 (1.8) |
27 (1.1) |
508 (20.1) |
| Source: [4] | |||||||||||||
Conservation
editAkimiski Island is the site of the Akimiski Island Migratory Bird Sanctuary, a Canadian Important Bird Area, site #NU036 (53°10′12″N 081°19′48″W / 53.17000°N 81.33000°W). Its eastern portion is also a federal Migratory Bird Sanctuary, and much of the coastline is a Key Migratory Bird Terrestrial Habitat site.[3]
Fauna
editThe coastal waters and wetlands of Akimiski Island (and James Bay in general) are important feeding grounds for many varieties of migratory birds.[5] Notable species include:[3]
Because James Bay and Hudson Bay are funnel-shaped, migrating birds from the Arctic concentrate in this area. During fall migration, an abundance of birds with both adults and young are present. In the springtime, the birds tend to reside in the southern areas of James Bay until the northern section thaws.
Among mammals, ringed seals, polar bears, and beluga whales can be found in the area.[6]
References
edit- ^ a b c "Akimiski Island". Geographical Names Data Base. Natural Resources Canada. Retrieved 2020-06-15.
- ^ "Akimiski Island, Nunavut, Canada: An Island in Dispute", Collections Canada
- ^ a b c "Akimiski Island James Bay, Nunavut". bsc-eoc.org. Archived from the original on 2011-06-12. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ "Records and Averages for Akimiski Island". Meteoblue.com. Climate ID: 2400600. Retrieved 2021-11-28.
- ^ Reiter, Matthew E. (February 2006). "Sympatric nesting eastern prairie population Canada Geese and Lesser Snow Geese" (PDF). umn.edu. Retrieved 2008-05-09. [dead link]
- ^ Canada, Environment and Climate Change. "Akimiski Island Migratory Bird Sanctuary - Canada.ca". www.ec.gc.ca. Archived from the original on 2017-09-18. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
Further reading
edit- Hill, Michael Robert John. Factors Influencing Pre- and Post-Fledging Growth and Survival of Canada Goose Goslings on Akimiski Island, Nunavut. Ottawa: National Library of Canada = Bibliothèque nationale du Canada, 2000. ISBN 0-612-42527-4
- Martini, I. P.; Glooschenko, W. A. (1984). "Emergent coasts of Akimiski Island, James Bay, Northwestern Territories, Canada: geology, geomorphology, and vegetation". Sedimentary Geology. 37 (4): 229–250. Bibcode:1984SedG...37..229M. doi:10.1016/0037-0738(84)90016-2.
- C.S. Blaney; P.M. Kotanen (2000). "The vascular flora of Akimiski Island, Nunavut Territory, Canada" (PDF). Canadian Field-Naturalist. 115 (1): 88–98. ISSN 0008-3550. Wikidata Q113676664.
External links
edit- NASA Photo : "STS085-713-070 Akimiski Island, Northwest Territory, Canada August 1997 Akimiski Island, a 2000-square-mile (5180 square kilometers) uninhabited island, is the largest island in James Bay (a southeasterly extension of Hudson Bay)."