This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (February 2014) |
The Yazghulami language (also Yazgulami, Yazgulyami, Iazgulem, Yazgulyam, Yazgulam, Yazgulyamskiy, Jazguljamskij, (Tajik: язғуломӣ (Yazghulomi)) is a member of the Southeastern subgroup of the Iranian languages, spoken by around 9,000 people along the Yazghulom River in Gorno-Badakhshan, Tajikistan. Together with Shugni, it is classified in a Shugni-Yazgulami subgroup of the areal group of Pamir languages.[3] Virtually all speakers are bilingual in the Tajik language.[4]
| Yazghulami | |
|---|---|
| зѓамиѓай (zǵamiǵai) | |
| йуздоми звег (yuzdomi zveg) | |
| Pronunciation | [zɡʲamiˈɡʲai][1] |
| Native to | Tajikistan |
Native speakers | 9,000[2] (2010) |
| Cyrillic, Latin | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | yah |
| Glottolog | yazg1240 |
| ELP | Yazgulyami |
| Linguasphere | 58-ABD-f |
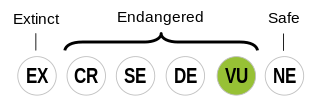 Yazghulami is classified as Vulnerable by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |
The Yazghulami people are an exception among the speakers of Pamir languages in that they do not adhere to Ismailism.
Dialects
editThe Yazghulami language consists of two dialects: one of these is spoken higher in the mountains, the other lower. The differences are not significant and are limited to the vocabulary. Differences in the vocabulary are also detectable between the languages used in different villages in the lower mountains. The extinct Vanji language (also Vanži, Wanji) was once the nearest linguistic relative of Yazghulami. Yazghulami shares many grammatical and lexical features with the other languages spoken in the Pamirs,[5] but even its most closely related living relative, Shughni, is not mutually intelligible with it.
History
editThe language was first recorded by Russian traveller G. Arandarenko in 1889, listing 34 Yazghulami words recorded in 1882. The language was described in greater detail by French linguist Robert Gauthiot in Notes sur le yazgoulami, dialecte iranien des Confins du Pamir (1916). The most significant research to date on the Yazghulami language was done by Russian linguist Dzhoi (Joy) I. Ėdel’man, resulting in multiple publications from the 1960s through the early 2000s. Most of her works are in the Russian language.
In 1954 the Yazghulami living in villages at higher elevations (deeper into the Yazghulam valley) were resettled, about 20% of them forcibly, to the Vakhsh valley, where they live dispersed among the Tajiks, Uzbeks, Russians and other ethnic groups.
Phonology
editThe Yazghulami language has 45 phonemes: 8 vowels and 37 consonants.[5][6] The phonology of the Yazghulami language differs from the basic "Shughni-Roshani" type in its system of dorsal consonants: in addition to the velar and uvular stops /ɡ/, /k/, /q/ and fricatives /x/, /ɣ/, /χ/, /ʁ/, Yazghulami has a palatalised and a labialised series /kʲ/, /ɡʲ/ (palatalised velars), /kʷ/, /ɡʷ/, /xʷ/ (labialised velars, there is no labialised voiced velar fricative) and /qʷ/, /χʷ/, /ʁʷ/ (labialised uvulars).[6] A significant number of labialised consonants etymologically correspond to Proto-Iranian *Cv or *Cu, e.g. xʷarɡ < *hvaharā- "sister", while others are unrelated to Proto-Iranian v, e.g. skʷon < skana- "puppy".
This threefold system of articulation of dorsals has been compared typologically to the three reconstructed rows of dorsals in the Proto-Indo-European language.[3]
Vowels
editThe following are the vowels of Yazghulami:
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | ʉ | u |
| Mid | ɛ | ə | ɔ |
| Open | a | ɑː |
- /ʉ/ was recognized as a separate phoneme by earlier researchers, but a recent study finds that it now contrasts with /u/ only in the speech of older speakers.[1]
Consonants
editThe following are the consonants of Yazghulami:
| Labial | Dental/ Alveolar |
Post- alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | Uvular | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | sibilant | plain | lab. | pal. | plain | lab. | |||||
| Nasal | m | n | |||||||||
| Plosive/ Affricate |
voiceless | p | t | t͡s | t͡ʃ | k | kʷ | kʲ | q | qʷ | |
| voiced | b | d | d͡z | d͡ʒ | ɡ | ɡʷ | ɡʲ | ||||
| Fricative | voiceless | f | θ | s | ʃ | x | xʷ | χ | χʷ | ||
| voiced | v | ð | z | ʒ | ɣ | ʁ | ʁʷ | ||||
| Approximant | w | l | j | ||||||||
| Rhotic | r | ||||||||||
Grammar
editThe basic word order of Yazghulami is subject–object–verb (SOV).
In the past tense, Yazghulami has tripartite marking—one of the very few languages in the world to have this feature. This means that the subject of an intransitive sentence is marked differently from both the subject and the object of a transitive sentence.[8] This tripartite alignment only appears in singular pronouns in past tense clauses. Plural pronouns in past tense clauses and all pronouns in non-past tense clauses show nominative-accusative alignment.[9]
Morphological marking of core cases does not occur on nouns, however, the preposition na(ʒ) "from" is optionally used to indicate that the following noun is the direct object. All nominal forms may be marked for dative case or for either of two genitive cases by means of enclitics: =ra (dative), =i (genitive 1), and =me (genitive 2). The genitive 1 case marks attributive possession and is practically identical in function with the Tajik izofat =i which links a modifier to its noun. However, the order of constituents in the two languages is reversed, meaning that in Yazghulami the modifier precedes its noun (qatol-i kud "big-i house") whereas in Tajik the modifier follows the noun (χona-i kalon "house-i big"). The genitive 2 case is used only to mark predicative possession, e.g. ju kud=ai mo=me "this house is mine".[1]
Literature
edit- Ėdel’man, D. I. (1966). Jazguljamskij jazyk. Moscow: Nauka.
- Ėdel’man, D. I. (1971). Jazguljamsko-russkij slovar’. Moscow: Nauka.
- Edelman, D. I. and Leila R. Dodykhudoeva. (2009). "The Pamir Languages" in: Gernot Windfuhr (ed.), The Iranian Languages, 773‑786. London: Routledge.
- Gauthiot, Robert. (1916). "Notes sur le Yazgoulami: Dialecte Iranien des Confins du Pamir". Journal Asiatique, vol. 11, no. 7, p. 239‑270.
- Grierson, George A. (1920). "Ishkashmi, Zebaki, and Yazghulami, an account of three Eranian dialects." London, Royal Asiatic Society.[1] [2]
- Jamison, Rachel E. (2022). The enclitic =da and the marking of indicative and subjunctive mood in Yazghulami (MA Thesis). Dallas International University.
- Payne, John. (1989). "Pamir languages" in: Rüdiger Schmitt (ed.), Compendium Linguarum Iranicarum, 417‑444. Wiesbaden: Reichert.
- Zarubin, I. I. (1936). "Two Yazghulāmī Texts". Bulletin of the School of Oriental Studies, University of London, vol. 8, no. 2/3, p. 875‑881.
References
edit- ^ a b c Jamison, Rachel (2022). The enclitic =da and the marking of indicative and subjunctive mood in Yazghulami (PDF). Dallas International University.
- ^ Eberhard, David M.; Simons, Gary F.; Fennig, Charles D., eds. (2023). "Yazghulami". Ethnologue: Languages of the World. Dallas, Texas: SIL International.
- ^ a b Edelman, D. (Joy) I.; Dodykhudoeva, Leila R. (2009). "The Pamir Languages". In Windfuhr, Gernot (ed.). The Iranian Languages. London, Routledge. pp. 773–786.
- ^ Tiessen, Gabriela; Abbess, Elisabeth; Müller, Katja; Tiessen, Calvin (2005). "Language Access and Tajik Language Proficiency among the Yazghulami of Tajikistan" (PDF). In Clifton, John M. (ed.). Studies in Languages of Tajikistan. National State University of Tajikistan and North Eurasia Group, SIL International. pp. 107–149.
- ^ a b Pakhalina, T. M. (1969). Pamirskie jazyki [The Pamir Languages]. Moscow: Nauka.
- ^ a b c Edelman, D. I. (1966). Jazguljamskij jazyk [The Yazghulami Language]. Moscow: Nauka.
- ^ Narin, Matilda (2016). Phonological features of Yazghulami: A field study. Stockholm University.
- ^ Dixon, R.M.W. (1994). Ergativity. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 40.
- ^ Payne, John R. (1980). "The Decay of Ergativity in Pamir Languages". Lingua. 51: 147–186.