70°40′15″N 70°08′12″E / 70.67088°N 70.13672°E

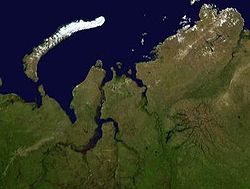
The Yamal Peninsula (Russian: полуостров Ямал, romanized: poluostrov Yamal) is located in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug of northwest Siberia, Russia. It extends roughly 700 km (435 mi) and is bordered principally by the Kara Sea, Baydaratskaya Bay on the west, and by the Gulf of Ob on the east. At the northern end of this peninsula lie the Malygina Strait and, beyond it, Bely Island. Across the river lies the Gyda Peninsula. In the language of its indigenous inhabitants, the Nenets, "Yamal" means "End of the Land".
The Yamal peninsula is inhabited by a multitude of migratory bird species. The well-preserved remains of Lyuba, a 37,000-year-old mammoth calf, were found by a reindeer herder on the peninsula in the summer of 2007. The animal was female and was determined to be one month old[1] at the time of death.[2]
Geography
editThe peninsula consists mostly of permafrost ground and there are numerous lakes of thermokarst origin, the biggest of which are Neito and Yambuto in the central part.[3][4]
Many hydrocarbon fields have been discovered on the Yamal Peninsula, including large gas fields. The main hydrocarbon resources are concentrated in the permeable Aptian-Cenomanian complex.[5]
Reindeer husbandry
editAccording to anthropologist Sven Haakanson, the Yamal peninsula is the place within the Russian Federation where traditional large-scale nomadic reindeer husbandry is best preserved.[6][7] Nenets and Khanty reindeer herders hold about half a million domestic reindeer.
Development
editThe area is largely undeveloped, but work is ongoing with several large infrastructure projects, including a gas pipeline and several bridges.[8] Yamal holds Russia's biggest natural gas reserves.[9] The 572 km Obskaya–Bovanenkovo railway, completed in 2011, is the northernmost railway in the world.[10] Russian gas monopolist Gazprom had planned to develop the Yurkharovskoye gas field by 2011–2012. The peninsula's gas reserves are estimated to be 55 trillion cubic meters (tcm).[8] Russia's largest energy project in history, known as the Yamal project, puts the future of nomadic reindeer herding at considerable risk.[citation needed]
Yamal craters
editIn 2014, Yamal was the discovery site of a distinct sinkhole, or pingo, which quickly drew the attention of world media.[11] The sinkhole appeared to be the result of a huge explosion and several hypotheses were suggested to explain the formation of the crater, including a hit by a meteorite or a UFO, or the collapse of an underground gas facility.[12]
A spokesperson for the Yamal branch of the Emergencies Ministry said, "We can definitely say that it’s not a meteorite.".[13] Cryovolcanism has been pointed out as the most probable cause in recent researches.[14]
The 60-meter (66-yard) crater is believed by a senior researcher from the Scientific Research Center of the Arctic, Andrei Plekhanov, in remarks to the Associated Press, to be likely the result of a "buildup of excessive pressure" underground because of warming regional temperatures in that portion of Siberia.[15] Tests conducted by Plekhanov's team showed unusually high concentrations of methane near the bottom of the sinkhole.[16][17]
The destabilization of gas hydrates containing huge amounts of methane gas is believed to have caused the craters on the Yamal Peninsula.[18]
As of 2015, the Yamal peninsula had at least five similar craters.[19]
Another crater appeared in August 2020.[20]
Offshore methane leaks
editAccording to researchers at Norway's Centre for Arctic Gas Hydrate (CAGE), through a process called geothermal heat flux, the Siberian permafrost, which extends to the seabed of the Kara Sea, a section of the Arctic Ocean between the Yamal Peninsula and Novaya Zemlya, is thawing. According to a CAGE researcher, Aleksei Portnov:[18]
"The permafrost is thawing from two sides... [T]he interior of the Earth is warm and is warming the permafrost from the bottom up. It is called geothermal heat flux and it is happening all the time, regardless of human influence."
— CAGE 2014
"The thawing of permafrost on the ocean floor is an ongoing process, likely to be exaggerated by the global warming of the world´s oceans."
— CAGE 2014
Methane is leaking in an area of at least 7500 m2. In some areas gas flares extend up to 25 m (82 ft). Prior to their research it was proposed that methane was tightly sealed into the permafrost by water depths up to 100 m (330 ft). Close to the shore however, where the permafrost seal tapers to a depth of as little as 20 m (66 ft), there are significant amounts of gas leakage.[18]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Ice Baby, National Geographic Magazine, May 2009, archived from the original on 19 April 2009, retrieved 28 December 2014
- ^ "Russia: Mammoth's Corpse Found". The New York Times. 11 July 2007. Retrieved 23 December 2017.
- ^ "R-41_42 Topographic Chart (in Russian)". Retrieved 6 June 2022.
- ^ Google Earth
- ^ Surikova, E S; Solmin, A E; Guseva, S M (30 October 2018). "Regional model of the geological structure of the Yamal and Gydan oil-and-gas areas". IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 193 (1): 012067. Bibcode:2018E&ES..193a2067S. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/193/1/012067.
- ^ Haakanson, Sven, Reindeer herders, Yamal Culture, Washington: Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History, retrieved 28 December 2014
- ^ Haakanson, Sven David (2000). Ethnoarchaeology of the Yamal Nenets: Utilizing Emic and Etic Evidence in the Interpretation of Archaeological Residues. Ethnoarchaeology (PhD). Harvard University. pp. 472 pages.
- ^ a b Harding, Luke (20 October 2009). "Yamal peninsula: The world's biggest gas reserves". Theguardian.com. Retrieved 23 December 2017.
- ^ "Yamal megaproject". Gazprom.com. Retrieved 12 April 2016.
- ^ "Obskaya–Bovanenkovo Railroad". Railway Technology. Retrieved 12 April 2016.
- ^ Gates, Sara (16 July 2014). "Giant hole forms in Siberia, and nobody can explain why". HuffPost. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- ^ Bogoyavlensky, Vasily (October 2015). "Gas Blowouts on the Yamal and Gydan Peninsulas" (PDF). GEO ExPro. Vol. 12, no. 5. GEO Publishing Ltd. pp. 74–78. ISSN 1744-8743. Retrieved 27 July 2016.
- ^ Winter, Lisa (16 July 2014). "Huge Crater Mysteriously Appears in Siberia". IFL Science. Retrieved 5 August 2014.
- ^ Buldovicz, Sergey N.; Khilimonyuk, Vanda Z.; Bychkov, Andrey Y.; Ospennikov, Evgeny N.; Vorobyev, Sergey A.; Gunar, Aleksey Y.; Gorshkov, Evgeny I.; Chuvilin, Evgeny M.; Cherbunina, Maria Y.; Kotov, Pavel I.; Lubnina, Natalia V.; Motenko, Rimma G.; Amanzhurov, Ruslan M. (10 September 2018). "Cryovolcanism on the Earth: Origin of a Spectacular Crater in the Yamal Peninsula (Russia)". Scientific Reports. 8 (1): 13534. Bibcode:2018NatSR...813534B. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-31858-9. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 6131154. PMID 30202065.
- ^ "News". news.msn.com. Archived from the original on 11 August 2014. Retrieved 23 December 2017.
- ^ Moskvitch, Katia (2014). "Mysterious Siberian crater attributed to methane". Nature. doi:10.1038/nature.2014.15649. S2CID 131534214. Retrieved 23 December 2017.
- ^ Luntz, Stephen (2 August 2014). "Scientists May Have Solved The Siberian Crater Mystery". Business Insider. Retrieved 5 August 2014.
- ^ a b c Sojtaric, Maja (18 December 2014), Methane is leaking from permafrost offshore Siberia, Tromsø, Norway: Centre for Arctic Gas Hydrate (CAGE), archived from the original on 28 December 2014, retrieved 28 December 2014
- ^ Winter, Lisa (26 February 2015). "There are more bizarre craters opening up in Siberia, and scientists still don't know what's causing them". businessinsider.com. Retrieved 27 July 2016.
We know now of seven craters in the Arctic area. Five are directly on the Yamal peninsula, one in Yamal Autonomous district, and one is on the north of the Krasnoyarsk region, near the Taimyr peninsula,...
- ^ Liesowska, Anna (29 August 2020). "Giant new 50-metre deep crater opens up in Arctic tundra". siberiantimes.com. Retrieved 30 December 2023.
External links
edit- Ялмал, статья ЭСБЕ (in Russian)
- Статья БСЭGreat Soviet Encyclopedia (in Russian)
- Yamal Culture (in English)
- Article on Nenets culture, religion and history (in English)