Wikipedia:Today's featured article/August 2005
| << | Today's featured articles for August 2005 | >> | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Su | Mo | Tu | We | Th | Fr | Sa |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |||
August 1
Henry Moore was a British artist and sculptor. Born into a poor mining family in the Yorkshire town of Castleford, he became well-known for his large-scale abstract cast bronze and carved marble sculptures; substantially supported by the British art establishment, Moore helped to introduce a particular form of modernism into Britain. His ability to satisfy large-scale commissions made him exceptionally wealthy towards the end of his life. However, he lived frugally and most of his wealth went to endow the Henry Moore Foundation, which continues to support education and promotion of the arts. His signature form is a pierced reclining figure, first influenced by a Toltec-Maya sculpture known as "Chac Mool", which he had seen as a plaster cast in Paris in 1925. Early versions are pierced conventionally as a bent arm reconnects with the body. Later, more abstract versions, are pierced directly through the body in order to explore the concave and convex shapes. These more extreme piercings developed in parallel with Barbara Hepworth's sculptures. Hepworth first pierced a torso after misreading a review of one of Henry Moore's early shows.
Recently featured: Chagas disease – Hero of Belarus – Open cluster
August 2
The Common Unix Printing System is a modularised computer printing system for Unix-like operating systems that allows computers to act as powerful print servers. A computer running CUPS is a host which can accept print jobs from client computers, process them, and send them to the appropriate printer. CUPS consists of a Unix print spooler and scheduler, a filter system that convert the print data to a format that the printer will understand, and a backend system that sends this data to the print device. CUPS uses the Internet Printing Protocol as the basis for managing print jobs and queues. It also provides the traditional System V and Berkeley command line interfaces, along with limited support for the server message block protocol. The device drivers CUPS supplies are based on the PostScript Printer Description. There are a number of user interfaces for different platforms that can configure CUPS, and it has an inbuilt web-based interface.
Recently featured: Henry Moore – Chagas disease – Hero of Belarus
August 3
Marshall, Texas, is a major cultural and educational center in Northeast Texas, located near the Louisiana and Arkansas borders in the Ark-La-Tex region. As of the 2000 census, the city had a total population of 23,935. The county seat of Harrison County, the city is known for its Civil War, railroad, and civil rights movement history, for holding one of the largest light festivals in the United States, the Wonderland of Lights, and, as the self-proclaimed Pottery Capital of the World, for its sizable pottery industry. It is also known variously as the Cultural Capital of East Texas, the Gateway of Texas, the Athens of Texas, and the City of Seven Flags.
Recently featured: Common Unix Printing System – Henry Moore – Chagas disease
August 4
Carl Friedrich Gauss was a German mathematician and scientist who contributed significantly to many fields, including number theory, analysis, differential geometry, geodesy, magnetism, astronomy and optics. Sometimes known as "the prince of mathematicians", Gauss introduced concepts which have had a profound impact in many areas and his work is ranked alongside that of Newton and Archimedes. Gauss was a child prodigy, and he made his first ground-breaking mathematical discoveries while still a teenager. He completed Disquisitiones Arithmeticae, his magnum opus, at the age of 24. This work was fundamental in consolidating number theory as a discipline, and it has shaped the direction of modern research up to the present day.
Recently featured: Marshall, Texas – Common Unix Printing System – Henry Moore
August 5
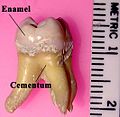
Tooth enamel is the most highly mineralized and hardest substance of the body. Enamel is one of the three major parts of the human tooth, the others being dentin and cementum. It is the normally visible dental tissue of a tooth, and must be supported by underlying dentin. Minerals compose 96% of enamel, with water and organic material composing the rest. Since enamel is semi-translucent, the color of dentin and any restorative dental material underneath the enamel highly affects the outer appearance of the tooth. The color of enamel is a light yellow to grayish white. It varies in thickness over the surface of the tooth. Often, enamel is thickest at the cusp, up to 2.5 mm, and tapers down to a minuscule amount at its border, which is seen clinically as the cementoenamel junction.
Recently featured: Carl Friedrich Gauss – Marshall, Texas – Common Unix Printing System
August 6
Grunge music is an independent-rooted music genre that was inspired by hardcore punk, thrash metal, and alternative rock. The genre became commercially successful in the late 1980s and early 1990s, peaking in mainstream popularity between 1991 and 1994. Bands from cities in the U.S. Pacific Northwest such as Seattle, Washington, Olympia, Washington, and Portland, Oregon, were responsible for creating grunge music and later made it popular with mainstream audiences. The genre is closely associated with Generation X, due to its popularization being in tandem with the popularizing of the generation's name. The popularity of grunge was one of the first phenomena that distinguished the popular music of the 1990s from that of the 1980s.
Recently featured: Tooth enamel – Carl Friedrich Gauss – Marshall, Texas
August 7
The Second Crusade was the second major crusade launched from Europe, called in 1145 in response to the fall of the County of Edessa the previous year. Edessa was the first of the Crusader states to have been founded during the First Crusade, and was the first to fall. The Second Crusade was announced by Pope Eugenius III, and was the first of the crusades to be led by European kings, namely Louis VII of France and Conrad III of Germany. The armies of the two kings marched separately across Europe and were separately defeated by the Seljuk Turks. Louis and Conrad and the remnants of their armies reached Jerusalem and in 1148 participated in an ill-advised attack on Damascus. The crusade in the east was a failure for the crusaders and a great victory for the Muslims. It would ultimately lead to the fall of Jerusalem and the Third Crusade at the end of the 12th century. The only success came on the opposite end of the Mediterranean, where English crusaders, on the way by ship to the Holy Land, fortuitously stopped and helped capture Lisbon in 1147.
Recently featured: Grunge music – Tooth enamel – Carl Friedrich Gauss
August 8
The exposed geology of the Death Valley area records many events associated with plate tectonics. The oldest rocks in the area that now comprise Death Valley National Park and environs are extensively metamorphosed by intense heat and pressure and are at least 1700 million years old. Rifting of the supercontinent Rodinia some 700 to 800 million years ago (mya) allowed sea water to invade until the continental crust broke, giving birth to the Pacific Ocean. The region's first known fossils of complex life were buried at the base of the submerged precipice. Some 80 million years ago a subduction zone formed off the coast as the Farallon Plate started to dive below the North American Plate; volcanoes and uplifting mountains were created in the region as a result. Stretching of the crust under western North America started around 16 mya, creating the Basin and Range province. By 2 to 3 mya this province had spread to the Death Valley area, ripping it apart and creating Death Valley, Panamint Valley and surrounding ranges. These valleys partially filled with sediment and, during the wet times of ice ages, with lakes such as Lake Manly. By 10,500 years ago these lakes were increasingly cut off from glacial melt from the Sierra Nevada, starving them of water and concentrating salts and minerals. The desert environment seen today developed after these lakes dried up.
Recently featured: Second Crusade – Grunge music – Tooth enamel
August 9
Sharon Tate was an American actress. During the 1960s she played small roles in television, before starting her film career. After receiving positive reviews as a light comedienne, she was hailed as one of Hollywood's promising newcomers. Tate's celebrity status and role as a style icon of the "Swinging Sixties" increased after fashion magazines began featuring her as a model and cover girl. Married to the film director Roman Polański, Tate was eight months pregnant when she, along with four others, was murdered in her Benedict Canyon home by followers of Charles Manson, in a crime that shocked the nation. A decade after the murders, her mother Doris Tate, appalled at the growing cult status of the killers and the possibility that any of them might be granted parole, joined a campaign to ensure they remained in prison. This was part of the catalyst which led to amendments to California law in 1982, which allowed crime victims and their families to make victim impact statements.
Recently featured: Geology of the Death Valley area – Second Crusade – Grunge music
August 10
Augustan literature is a style of English literature whose origins correspond roughly with the reigns of Queen Anne, King George I, and George II. In contemporary critical parlance, it refers to the literature of 1700 up to approximately 1760. It is a literary epoch that featured the rapid development of the novel, an explosion in satire, the mutation of drama from political satire into melodrama, and an evolution toward poetry of personal exploration. The chronological anchors of the era are generally vague, largely since the label's origin in contemporary 18th-century criticism has made it a shorthand designation for a somewhat nebulous age of satire. This new Augustan period exhibited exceptionally bold political writings in all genres, with the satires of the age marked by an arch, ironic pose, full of nuance, and a superficial air of dignified calm that hid sharp criticisms beneath.
Recently featured: Sharon Tate – Geology of the Death Valley area – Second Crusade
August 11
The Tasmanian Devil is a carnivorous marsupial found exclusively on the Australian island of Tasmania. At the size of a small dog, but stocky and muscular, the Tasmanian Devil is the largest carnivorous marsupial in the world. The devil is characterised by its black fur, offensive odour when stressed, extremely loud and disturbing screech, and vicious temperament when feeding. Known to hunt, as well as to scavenge carrion, communal eating is one of the few social activities in which the usually solitary devil participates. The Tasmanian Devil became extinct on the Australian mainland about 400 years prior to European settlement in 1788. The people of Tasmania saw devils as a threat to livestock and hunted them until 1941, when the animals were officially protected. Since the late 1990s devil facial tumour disease has reduced the devil population significantly and threatens the survival of the species. The impact of the disease on devil population may lead to listing of the devil as an endangered species.
Recently featured: Augustan literature – Sharon Tate – Geology of the Death Valley area
August 12
The Battle of Jutland was the largest naval battle of World War I, and the only full-scale clash of battleships in that war. It was fought on 31 May–1 June 1916, in the North Sea near Jutland. The combatants were the Kaiserliche Marine's High Seas Fleet, commanded by Vice Admiral Reinhard Scheer, and the Royal Navy's Grand Fleet, commanded by Admiral Sir John Jellicoe. The Germans planned to lure Vice Admiral Sir David Beatty's battlecruiser squadrons into the path of the main German battle fleet and so destroy them. But the British had learned from signal intercepts that a major fleet operation was in prospect, and on 30 May Jellicoe sailed with the Grand Fleet to rendezvous with Beatty. On the afternoon of 31 May, Beatty and Hipper encountered each other, and in a running battle Hipper drew the British into the path of the High Seas Fleet. Fourteen British and eleven German ships were sunk with great loss of life. Both sides claimed victory. The British had lost more ships and many more sailors, but Scheer's plan of destroying Beatty's squadrons had failed. For the remainder of the war, the German High Seas Fleet stayed in port. and never again contested control of the seas. Instead, the German Navy turned its efforts and resources to unrestricted submarine warfare.
Recently featured: Tasmanian Devil – Augustan literature – Sharon Tate
August 13
Helen Gandy was an American civil servant. Gandy, who at age 21 left her native New Jersey for Washington, D.C., was for 54 years the secretary to Federal Bureau of Investigation director J. Edgar Hoover. Hoover called her "indispensable" and she exercised great behind-the-scenes influence on Hoover and the workings of the Bureau; Hoover's biographers, Theoharis and Cox, describe her as "a wraith-like, grim-faced spinster from New Jersey" whose "stern face recalled Cerberus at the gate". Following Hoover's death in 1972, she spent weeks destroying his "Personal File," thought to be where the most incriminating material he used to manipulate and control the most powerful figures in Washington was kept.
Recently featured: Battle of Jutland – Tasmanian Devil – Augustan literature
August 14
The Flag of India, sometimes also known as the Tiranga, which in Hindi means tricolour, was adopted as the national flag of the Republic of India on July 22 1947, during an ad hoc meeting of the Constituent Assembly just before India's independence on August 15 1947. In India, the term "tricolour" almost always refers to the Indian national flag. The flag is a horizontal tricolour of saffron at the top, white in the middle and green at the bottom. In the centre is a navy blue wheel with twenty-four spokes, known as the Ashoka Chakra, taken from the Ashoka pillar at Sarnath. The flag is also the Indian army's war flag, hoisted daily on military installations. The Indian National Flag was designed by Pingali Venkayya. Official flag specification requires that the flag be made only of khadi–a special type of hand-spun yarn. The display and use of the flag are strictly enforced by the Indian Flag Code.
Recently featured: Helen Gandy – Battle of Jutland – Tasmanian Devil
August 15
The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy is a science fiction comedy series written by Douglas Adams. It originated in 1978 as a radio comedy broadcast on BBC Radio 4. Since then it has been adapted to other media formats, including stage shows, a series of five books published between 1979 and 1992, (the first of which was entitled The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy), a 1981 TV series, a 1984 computer game, as well as comic book adaptations of the first three novels. The many versions, although in some ways contradictory, all follow the same basic plot. Arthur Dent, a hapless Englishman, escapes the destruction of Earth by an alien race called the Vogons with his friend Ford Prefect, an alien from a small planet in the vicinity of Betelgeuse and researcher for the eponymous guide. Zaphod Beeblebrox, Ford's semi-cousin and Galactic President, unknowingly saves the pair from death. He brings them aboard his stolen spaceship, the Heart of Gold, whose crew rounds out the main cast of characters: Marvin the Paranoid Android, and Trillian, a woman known by Arthur as the only other surviving human being. After this, the characters get involved in a quest to find the legendary planet of Magrathea and the Question to the Ultimate Answer.
Recently featured: Flag of India – Helen Gandy – Battle of Jutland
August 16
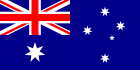
The Commonwealth of Australia is a country in the southern hemisphere comprising the world's smallest continent and a number of islands, the largest of which is Tasmania. Australia has been inhabited for about 50,000 years by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples. Eastern Australia was claimed by the British in 1770, and officially settled as a British penal colony on 26 January, 1788. As the population grew and new areas were explored, six largely self-governing Crown Colonies were established within Australia over the course of the 19th century. On 1 January 1901 the six colonies federated and the Commonwealth of Australia was formed. Since federation, Australia has had a stable liberal democratic political system and remains a Commonwealth Realm. Australia currently has a population of about 20 million, concentrated mainly in the coastal cities of Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Adelaide and Perth.
Recently featured: The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy – Flag of India – Helen Gandy
August 17
The Canadian Heraldic Authority is an agency of the Government of Canada responsible for heraldry in Canada. The Authority is responsible for the creation and granting of new coats of arms (armorial bearings), flags and badges for Canadian citizens and corporate bodies. The Authority also registers existing armorial bearings, which have been granted by other recognized heraldic authorities, approves military badges, flags and other insignia of the Canadian Armed Forces, registers genealogical information related to the inheritance of arms, and provides information on correct heraldic practices. It is the Canadian counterpart of the College of Arms, and the Court of the Lord Lyon.
Recently featured: Australia – The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy – Flag of India
August 18
George F. Kennan was an advisor, diplomat, political analyst, and historian, best known as "the father of containment" and as a key figure in the emergence of the Cold War. During his term as the State Department's first director of the Policy Planning Staff in the late 1940s, his writings gave rise to the Truman Doctrine and the U.S. foreign policy of "containing" the Soviet Union, thrusting him into a lifelong role as a leading authority on the Cold War. His "Long Telegram" from Moscow in 1946, and the subsequent 1947 article "Sources of Soviet Conduct" argued that the Soviet regime was inherently expansionistic and that its influence had to be "contained" in areas of vital strategic importance to the United States. These texts quickly emerged as foundational texts of the Cold War, expressing the Truman administration's new anti-Soviet policy. Kennan also played a leading role in the development of definitive Cold War programs and institutions, most notably the Marshall Plan. Shortly after the doctrine had been enshrined as official U.S. policy, Kennan began to criticize the policies that he had seemingly helped launch, and Kennan's influence was increasingly marginalized.
Recently featured: Canadian Heraldic Authority – Australia – The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy
August 19
Blaise Pascal was a French mathematician, physicist, and religious philosopher. Pascal's earliest work was in the natural and applied sciences. His important contributions to these fields include the construction of mechanical calculators, the study of fluids, and clarification of concepts such as pressure and vacuum by expanding the work of Evangelista Torricelli. Pascal also lent his pen to the defense of the scientific method. In mathematics, Pascal did groundwork in projective geometry, writing a significant treatise on the subject at the age of sixteen. In correspondence with Fermat beginning in 1654, Pascal helped establish probability theory. His ideas in this area have had major ramifications in economics and the social sciences. Following a mystical experience in late 1654, he fell away from mathematics and physics and devoted himself to reflection and writing about philosophy and theology. This period was characterized by the composition of his two most famous works, the Lettres provinciales and the Pensées.
Recently featured: George F. Kennan – Canadian Heraldic Authority – Australia
August 20
Porgy and Bess is an opera with music by George Gershwin and libretto by Ira Gershwin and DuBose Heyward. It was based on Heyward's novel Porgy and the play of the same name that he co-wrote with his wife Dorothy. All three works deal with African American life in the fictitious Catfish Row in Charleston, South Carolina in the early 1930s. Originally conceived by Gershwin as an "American folk opera", the work was first performed in various forms in the fall of 1935, but was not widely accepted in the United States as a legitimate opera until the late 1970s and 1980s: it is now considered part of the standard operatic repertoire. Porgy and Bess is also regularly performed internationally, and several recordings of the complete work, including Gershwin's cuts, have been made. "Summertime" is by far the best-known piece from the work, and countless interpretations of this and other individual numbers have also been recorded and performed. The opera is admired for Gershwin's innovative synthesis of European orchestral techniques with American jazz and folk music idioms.
Recently featured: Blaise Pascal – George F. Kennan – Canadian Heraldic Authority
August 21
The Anschluss was the 1938 incorporation of Austria in "Greater Germany" under the Nazi regime. The events of March 12, 1938 were the first major step in Adolf Hitler's long-desired expansion of the Third Reich, preceding the inclusion of the Sudetenland later in 1938 and the invasion of Czechoslovakia in 1939, and finally leading to World War II with the assault on Poland. Although the Wehrmacht entered into Austria to enforce the Anschluss, no fighting took place, in part because of prior political pressure exerted by Germany, but primarily because of the well-planned internal overthrow by the Austrian Nazi Party of Austria's state institutions in Vienna on March 11, the day before German troops marched across the border. The international response to the Anschluss was moderate: the United Kingdom held to its policy of appeasement and did not enforce the Treaty of Versailles, which ended World War I and specifically prohibited any attachment of Germany and Austria. Austria ceased to exist as an independent nation until a preliminary Austrian government was finally reinstated on April 27, 1945, and was legally recognized by the Allies in the following months.
Recently featured: Porgy and Bess – Blaise Pascal – George F. Kennan
August 22
The Congress of the United States is the legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, comprising the House of Representatives and the Senate. The House consists of 435 members, each of whom represents a congressional district and serves for a two-year term. Seats in the House are apportioned among the states on the basis of population; by contrast, each state is represented in the Senate by two members, regardless of population. There are a total of 100 Senators, who serve six-year terms. The United States Constitution vests all the legislative powers of the federal government in the Congress. The powers of Congress are limited to those expressly enumerated in the Constitution; all other powers are reserved to the states and the people, except where the Constitution provides otherwise. Significant powers of Congress include the authority to regulate interstate and foreign commerce, to levy taxes, to establish federal courts inferior to the Supreme Court, and to declare war. The Senate is fully equal to the House of Representatives, and not a mere "chamber of review," as is the case with the upper houses of the bicameral legislatures of many other nations.
Recently featured: Anschluss – Porgy and Bess – Blaise Pascal
August 23
A. E. J. Collins was a cricketer and soldier, most famous for his achievement, as a schoolboy, of the highest-ever recorded score in cricket, 628 not out, over four afternoons in June 1899. Collins' record-making innings drew a large crowd and increasing media interest: spectators at the Old Cliftonian match being played nearby were drawn away to watch a junior school house cricket match. Collins joined the British Army in 1902. He studied at the Royal Military Academy, Woolwich, before becoming an officer in the Royal Engineers. He served in France during World War I, where he was killed in action in 1914.
Recently featured: Congress of the United States – Anschluss – Porgy and Bess
August 24
Autism is classified as a neurodevelopmental disorder that manifests itself in markedly abnormal social interaction, communication ability, patterns of interests, and patterns of behavior. Although the specific etiology of autism is unknown, genetic factors appear to be important. By definition, autism must manifest delays in "social interaction, language as used in social communication, or symbolic or imaginative play," with "onset prior to age 3 years." (DSM-IV) There have been large increases in the reported incidence of autism, for reasons that are heavily debated in the scientific community. There are cases of autistic children who have improved their social and other skills to the point where they can fully participate in mainstream education and social events, but there are lingering concerns that an absolute cure from autism is impossible with current technology since it involves aspects of neurological brain structure determined very early in development. However, some autistic children and adults who are able to communicate at a functional level are opposed to attempts to cure their condition.
Recently featured: A. E. J. Collins – Congress of the United States – Anschluss
August 25
African American literature is literature written by, about, and sometimes specifically for African Americans. The genre began during the 18th and 19th centuries with writers such as poet Phillis Wheatley and orator Frederick Douglass, reached an early high point with the Harlem Renaissance, and continues today with authors such as Toni Morrison and Maya Angelou being ranked among the top writers in the United States. Among the themes and issues explored in African American literature are the role of African Americans within the larger American society, African American culture, racism, slavery, and equality. As African Americans' place in American society has changed over the centuries, so too has the focus of African American literature. Before the American Civil War, African American literature primarily focused on the issue of slavery, as indicated by the popular subgenre of slave narratives. During the American Civil Rights movement, authors like Richard Wright and Gwendolyn Brooks wrote about issues of segregation and black nationalism. Today, African American literature has become accepted as an integral part of American literature, with books in the genre, such as Roots: The Saga of an American Family by Alex Haley and The Color Purple by Alice Walker, achieving both best-selling and award-winning status.
Recently featured: Autism – A. E. J. Collins – Congress of the United States
August 26
Angkor Wat is a temple at Angkor, Cambodia, built for King Suryavarman II in the early 12th century as his state temple and capital city. The largest and best-preserved temple at the site, it is the only one to have remained a significant religious center—first Hindu, then Buddhist—since its foundation. The temple is the epitome of the high classical style of Khmer architecture. It has become a symbol of Cambodia, appearing on its national flag, and is the country's prime attraction for visitors. Angkor Wat combines two basic plans of Khmer temple architecture: the temple mountain and the later galleried temples. It is designed to represent Mount Meru, home of the gods in Hindu mythology: within a moat and an outer wall 3.6 km (2.2 miles) long are three rectangular galleries, each raised above the next. At the center of the temple stands a quincunx of towers. Unusually, Angkor Wat faces the west; scholars are divided as to the significance of this. As well as for the grandeur and harmony of the architecture, the temple is admired for its extensive bas-reliefs and for the numerous devatas adorning its walls.
Recently featured: African American literature – Autism – A. E. J. Collins
August 27
Rebecca Clarke was an English classical composer and violist best known for her chamber music featuring the viola. She is considered one of the most important British composers in the interwar period between World War I and World War II; she has also been called the most distinguished British female composer of her generation. Though she wrote little, due in part to her ideas about the role of a female composer, her work was recognized for its compositional skill. Most of Clarke's works have yet to be published (or have only recently been published), and her work was largely forgotten after she stopped composing. Scholarship and interest in her work revived when she reached her ninetieth birthday in 1976.
Recently featured: Angkor Wat – African American literature – Autism
August 28
The SS Andrea Doria was an ocean liner for the Italian Line. Named after the 16th-century Genoese admiral Andrea Doria, the Andrea Doria had a gross tonnage of 29,100 and a capacity of about 1,200 passengers and 500 crew. For a country attempting to rebuild its economy and reputation after World War II, the Andrea Doria was an icon of Italian national pride. Of all Italy's ships at the time, Andrea Doria was the largest, fastest and supposedly safest. Launched on June 16, 1951, the ship undertook its maiden voyage on January 14, 1953. On July 25, 1956, while sailing off the coast of Nantucket bound for New York City, the Andrea Doria collided with the eastward-bound SS Stockholm of the Swedish-American Line in what was to become one of history's most famous maritime disasters. Although most passengers and crew survived, the luxury liner capsized and sank the following morning. The disaster was heavily covered by the news media, with the sinking filmed by various organizations. As for the Andrea Doria, it was the last major transatlantic passenger vessel to sink before airplanes became the preferred method of travel.
Recently featured: Rebecca Clarke – Angkor Wat – African American literature
August 29
Penda was a 7th-century King of Mercia, a kingdom in what is today the English Midlands. A pagan at a time when Christianity was taking hold in many of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, Penda participated in the defeat of the powerful Northumbrian king Edwin at the Battle of Hatfield Chase in 633; nine years later, he defeated and killed Edwin's eventual successor, Oswald, at the Battle of Maserfield. From this point he was probably the most powerful of the Anglo-Saxon rulers of the time; he defeated the East Angles, drove the king of Wessex into exile for three years, and continued to wage war against the Bernicians of Northumbria. Thirteen years after Maserfield, he suffered a crushing defeat at the Battle of the Winwaed in the course of a final campaign against the Bernicians and was killed.
Recently featured: SS Andrea Doria – Rebecca Clarke – Angkor Wat
August 30
The menstrual cycle is the recurring physiological changes in a female's body that are under the control of the reproductive hormone system and necessary for reproduction. In women, menstrual cycles occur typically on a monthly basis between puberty and menopause. Besides humans, only other members of great apes exhibit menstrual cycles, in contrast to the estrus cycle of most mammalian species. During the menstrual cycle, the sexually mature female body releases one egg (or occasionally two, which might result in non-identical twins) at the time of ovulation. The lining of the uterus, the endometrium, builds up in a synchronised fashion. After ovulation, this lining changes to prepare for potential implantation of the fertilized egg to establish a pregnancy. If fertilisation and pregnancy do not ensue, the uterus sheds the lining and a new menstrual cycle begins.
Recently featured: Penda – SS Andrea Doria – Rebecca Clarke
August 31
Iron Maiden is a heavy metal band from east London, England. Formed in 1975 by bassist Steve Harris, previously of Gypsy's Kiss and Smiler, they are one of the most successful and influential bands in the heavy metal genre. Album sales are over 60 million world-wide, and the band won the Ivor Novello Award for international achievement in 2000. Iron Maiden's work has inspired other sub-genres of heavy metal, including power metal and speed metal and is generally thought of as an influence to any "metal" music containing dual-guitar harmonisation. The band's mascot, Eddie, is a perennial fixture in the horror-influenced album cover art, as well as in live shows. Eddie was originally drawn by Derek Riggs but has had various incarnations by Melvyn Grant. Iron Maiden has so far released thirteen studio albums, three "best of" compilations, five live albums and two limited boxed-sets. Lyrically, the band have written many songs based on folklore, movies and books, such as The Wicker Man, The Prisoner, Where Eagles Dare and Rime of the Ancient Mariner - in which words from the Samuel Coleridge poem are sung.
Recently featured: Menstrual cycle – Penda – SS Andrea Doria