| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
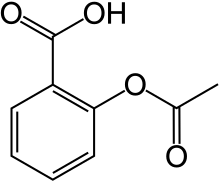
| IUPAC name
2-(acetyloxy)benzoic acid
| |
| Other names
2-acetyloxybenzoic acid
2-acetoxybenzoic acid acetylsalicylate acetylsalicylic acid O-acetylsalicylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H8O4 C6H4(OCOCH3)COOH | |
| Molar mass | 180.16 g/mol |
| Density | 1.40 |
| Melting point | 138-140 |
| Boiling point | 140 |
| 1 | |
| Pharmacology | |
| License data | |
| green | |
| oral | |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| rapid & complete | |
| Hepatic | |
| 300–650 mg dose: 3.1–3.2hrs 1 g dose: 5 hours 2 g dose: 9 hours | |
| Renal | |
| Legal status |
|
| Supplementary data page | |
| [[]] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Aspirin or acetylsalicylic acid (acetosal) is a drug in the family of salicylates, often used as an analgesic (against minor pains and aches), antipyretic (against fever), and anti-inflammatory. It has also an antiplatelet (“blood-thinning”) effect and is used in long-term low-doses to prevent heart attacks and cancer.