The Treaty of Constantinople (Treaty of İstanbul) was a treaty between the Ottoman Empire and the Kingdom of Bulgaria signed on 29 September 1913 after the Second Balkan War at the Ottoman capital Constantinople,[1] modern İstanbul.
 | |
| Type | Peace treaty |
|---|---|
| Signed | 29 September 1913 |
| Location | Constantinople |
| Parties | |
| Languages | Bulgarian, Ottoman Turkish |
Background
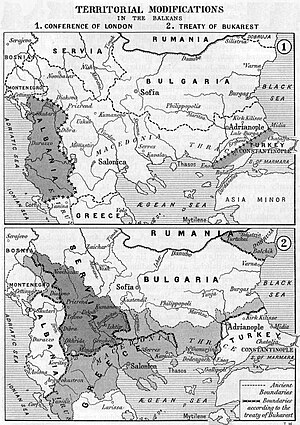
editIn the First Balkan War, the coalition of Bulgaria, Serbia, Greece and Montenegro defeated the Ottoman Empire. The Ottomans lost nearly all their European possessions, save for a small territory around the Sea of Marmara by the Treaty of London.[2] The Ottomans however were able to recover Eastern Thrace during the Second Balkan War.[3] Although peace talks between Bulgaria and her other neighbours were held in Bucharest, the Ottoman Empire was not represented there and conducted separate negotiations which led to the Treaty of Constantinople.
The treaty
editThe terms of the treaty were:[4][5]
- Bulgaria acknowledged Ottoman gains of Adrianople (mod. Edirne), Kırklareli and Didymoteicho and the surrounding territory.
- The Ottoman Empire ceded the port of Dedeagach (mod. Alexandroupoli) to Bulgaria.
- The exchange of lands was to be completed within 10 days.
- The armies on the border would be demobilized within three weeks.
- Prisoners of war from both sides would be released.
- Both political and economic ties between the two countries would be reestablished.
The treaty largely defines the modern-day borders between Eastern Thrace (European Turkey), Bulgaria and Greece.
Aftermath
editThe Ottoman Empire and Bulgaria were allies in the Central Powers in the First World War. Before the Bulgarian entry into the war, the Ottoman government decided to cede Didymoteicho to Bulgaria (to persuade it to join the war on the Central Powers side) by way of the Bulgarian–Ottoman convention (1915). However, the Central Powers were defeated in 1918 and Bulgaria lost both Western Thrace and Didymoteicho to Greece.
Under the terms of the abortive Treaty of Sèvres, Turkey was to cede almost all of Eastern Thrace to Greece, but the proposed territorial changes were negated by Turkey's victory over Greece in the War of Independence and the subsequent Treaty of Lausanne, which reaffirmed the borders established by the Treaty of Constantinople and the Bulgarian-Ottoman convention.
References
edit- ^ Anderson, Frank Maloy; Hershey, Amos Shartle (1918). "The Treaty of Constantinople, 1913". Handbook for the Diplomatic History of Europe, Asia, and Africa 1870–1914. Washington, DC: National Board for Historical Service, Government Printing Office. p. 443. Retrieved 26 September 2018.
- ^ "Treaty of London". Archived from the original on 1 May 1997. Retrieved 12 May 2010.
- ^ Balkan wars Archived 11 August 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ A summary of treaties (in Turkish)
- ^ Sina Akşin: Çağdaş Türkiye 1908–1980, Cem Yayınevi, İstanbul, 2008 ISBN 978-975-406-566-4 p. 50