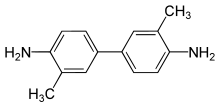
2-Tolidine (orthotolidine, o-tolidine; not to be confused with o-toluidine) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (C6H4(CH3)NH2)2. Several isomers are known; the 3-tolidine derivative is also important commercially. It is a colorless compound although commercial samples are often colored. It is slightly soluble in water. It forms salts with acids, such as the hydrochloride, which is commercially available.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3,3′-Dimethyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-diamine | |
| Other names
o-Tolidine; Orthotolidine; Diaminoditolyl; Diaminotolyl; Bianisidine; Tolidine blue; 3,3'-Dimethylbenzidine; 4,4'-Bi-o-toluidine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.962 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H16N2 | |
| Molar mass | 212.296 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White to reddish crystals or powder |
| Density | 1.23 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 129 °C (264 °F; 402 K) |
| Boiling point | 300.5 °C (572.9 °F; 573.6 K) |
| 1.3 g/L | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
potential carcinogen |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H350, H411 | |
| P201, P202, P264, P270, P273, P281, P301+P312, P308+P313, P330, P391, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 244 °C (471 °F; 517 K) |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
Handle with care |
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca C 0.02 mg/m3 [60-minute] [skin] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
Ca [N.D.] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
2-Tolidine can be produced by many benzidine rearrangement from a hydrazine derivative derived from 2-nitrotoluene.[2]
- (CH3C6H4)2N2H2 → (C6H3(CH3)NH2)2
Uses
edit2-Tolidine aromatic amine is used mainly for dye production.[3] 2-Tolidine is an intermediate for the production of soluble azo dyes and insoluble pigments used particularly in the textile, leather and paper industries.
It is also used for the production of certain elastomers.
2-Tolidine was widely used as a reagent or indicator in analytical, clinical and forensic chemistry, such as in the analytical determination of gold, or determination of the chlorine level in swimming pool water.
Safety
edit2-Tolidine is toxic and possibly carcinogenic. It is listed as an IARC Group 2B carcinogen, meaning it is "possibly carcinogenic to humans". Animal studies have shown that animals exposed to tolidine developed tumors in the liver, kidney, and mammary glands.[4]
References
edit- ^ Record of ortho-Tolidin in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 6.6.2008.
- ^ Noller, Carl R.: Textbook of Organic Chemistry, Springer Verlag, 1960
- ^ K. Hunger. W. Herbst "Pigments, Organic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012. doi:10.1002/14356007.a20_371
- ^ "CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards - o-Tolidine". www.cdc.gov.