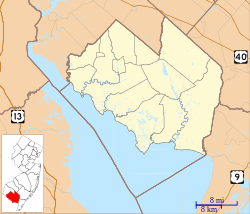
Seabrook is an unincorporated community located within Upper Deerfield Township in Cumberland County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey.[3] The area is served as United States Postal Service ZIP code 08302.[4] The unincorporated community and the census-designated Place Seabrook Farms within it are each named after Charles F. Seabrook, a businessman who at one point ran the largest irrigated truck farm in the world in this region.
Seabrook, New Jersey | |
|---|---|
Location in Cumberland County Location in New Jersey | |
| Coordinates: 39°30′06″N 75°13′09″W / 39.50167°N 75.21917°W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | Cumberland |
| Township | Upper Deerfield |
| Named for | Charles F. Seabrook |
| Elevation | 108 ft (33 m) |
| Population | |
• Total | 46,872 |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| ZIP code | 08302 |
| GNIS feature ID | 0880448[1] |
As of the 2010 United States Census, the population for ZIP Code Tabulation Area 08302 was 46,872.[2] As of the 2000 United States census, the population was 44,450.[5]
Climate
editThe climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild to cool winters. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Seabrook has a humid subtropical climate, abbreviated "Cfa" on climate maps.[6]
Seabrook Farms
editCharles F. Seabrook and his three sons ran a frozen foods business in Seabrook. During World War II, they faced a labor shortage for their food processing plants. This led the company to recruit interned Japanese Americans starting in late 1943 and to bring in after the war.[7] Within a year, nearly 1,000 workers had relocated to Seabrook from Japanese American internment camps, and the total number of Japanese Americans resettled there reached close to 3,000. Many transplanted families remained at Seabrook after the war where the company continued to grow and prosper.[8]
Also recruited were Latin Americans of Japanese ancestry who had been rounded up and transported to American internment camps run by the U.S. Justice Department.[9][10][11] These Latin American internees were eventually, through the efforts of civil rights attorney Wayne M. Collins,[12][13] offered "parole" relocation to Seabrook.[14] Many eventually became naturalized American citizens.
In October 1994, some area residents who used to work at Seabrook Farms opened a small museum called the Seabrook Educational and Cultural Center.[15] The museum has two rooms with displays and video kiosks that tell the story of Seabrook Farms and the people who worked and lived there.[7]
References
edit- ^ a b "Seabrook". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved October 6, 2012.
- ^ a b DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 - 2010 Demographic Profile Data for ZCTA 08302 Archived 2014-12-29 at archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 28, 2014.
- ^ Locality Search, State of New Jersey. Accessed December 28, 2014.
- ^ Zip Codes, State of New Jersey. Accessed December 28, 2014.
- ^ DP-1 - Profile of General Demographic Characteristics: 2000 - Census 2000 Summary File 1 (SF 1) 100-Percent Data for ZCTA 08302 Archived 2014-12-29 at archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 28, 2014.
- ^ "Seabrook, New Jersey Koppen Climate Classification (Weatherbase)". Weatherbase. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ a b Shortlidge, Jack (Spring–Summer 2005). "The Seabrook Educational and Cultural Institute: Telling the Story of a Japanese American Community in Southern New Jersey". Voices: The Journal of New York Folklore. 31. Retrieved November 28, 2009.
- ^ Jacobs, Meg (1999). "Review of Seabrook at War: A Radio Documentary".
- ^ Robinson, Greg. (2001). By Order of the President:FDR and the Internment of Japanese Americans, p. 264n2 citing C. Harvey Gardiner, Pawns in a Triangle of Hate (Seattle: University of Washington Press, 1981).
- ^ Niiya, Brian. Japanese American History. 1993, page 191
- ^ Nanami, Masaharu (Kyodo News), "Japanese-Peruvians still angry over wartime internment in U.S. camps," Japan Times, Sep 16, 2009.
- ^ "Japanese Latin Americans" (PDF). Retrieved April 12, 2009.
- ^ "Japanese Americans, the Civil Rights Movement and Beyond" (PDF). Retrieved April 10, 2009.
- ^ Higashide, Seiichi. (2000).Adios to Tears, p. 179.
- ^ "Seabrook Educational and Cultural Center". Retrieved November 28, 2009.