A satellite is a subviral agent that depends on the coinfection of a host cell with a helper virus for its replication. Satellites can be divided into two major classes: satellite viruses and satellite nucleic acids.[1] Satellite viruses, which are most commonly associated with plants, are also found in mammals, arthropods, and bacteria. They encode structural proteins to enclose their genetic material, which are therefore distinct from the structural proteins of their helper viruses.[1] Satellite nucleic acids, in contrast, do not encode their own structural proteins, but instead are encapsulated by proteins encoded by their helper viruses.[1][2] The genomes of satellites range upward from 359 nucleotides in length for satellite tobacco ringspot virus RNA (STobRV).[3]
| Satellite | |
|---|---|
| |
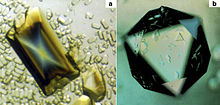
| In (a) is an orthorhombic crystal of satellite tobacco mosaic virus (STMV) that is more than 1.5 mm in length and was about 30 times the volume of any STMV crystal ever grown on Earth. It was grown in the Cryostat instrument on International Microgravity Laboratory-1. In (b) is an equivalent sized cubic crystal of the same virus, again, far exceeding in dimensions any grown in an Earth laboratory. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | Satellite
|
| Groups | |
| |
Most viruses have the capability to use host enzymes or their own replication machinery to independently replicate their own viral RNA. Satellites, in contrast, are completely dependent on a helper virus for replication. The symbiotic relationship between a satellite and a helper virus to catalyze the replication of a satellite genome is also dependent on the host to provide components like replicases[4] to carry out replication.[5]
A satellite virus of mamavirus that inhibits the replication of its host has been termed a virophage.[6] However, the usage of this term remains controversial due to the lack of fundamental differences between virophages and classical satellite viruses.[7]
History and discovery
editThe tobacco necrosis virus was the virus that led to the discovery of the first satellite virus in 1962. Scientists discovered that the first satellite had the components to make its own protein shell. A few years later in 1969, scientists discovered another symbiotic relationship with the tobacco ringspot nepovirus (TobRV) and another satellite virus.[8] The emergence of satellite RNA is said to have come from either the genome of the host or its co-infecting agents, and any vectors leading to transmission.[9]
A satellite virus important to human health that demonstrates the need for co-infection to replicate and infect within a host is the virus that causes hepatitis D. Hepatitis D or delta virus (HDV) was discovered in 1977 by Mario Rizzetto[10] and is differentiated from hepatitis A, B, and C because it requires viral particles from hepatitis B virus (HBV) to replicate and infect liver cells. HBV provides a surface antigen, HBsAg, which is utilized by HDV to create a super-infection resulting in liver failure.[11] HDV is found all over the globe but is most prevalent in Africa, the Middle East and southern Italy.[11]
Satellite compared to a virus
edit| Satellite | Virus | |
|---|---|---|
| Replication | Depend on the presence of host cells and helper viruses to replicate their genomes | Depend on the presence of host cells to replicate their genomes |
| Nucleic acid | Contain DNA or RNA | Contain DNA or RNA, or both at different points in life cycle |
| Genome size | 0.22 to 1.5 kb | 10 kb to 1.5 Mb |
| Structure | Satellite viruses encode their own protein capsids with the aid of helper viruses
Satellite nucleic acids do not have capsids, but rely on helper viruses to enclose their genomes |
Package their genome within a capsid (protein shell)
Have an envelope (not all viruses) |
| Host range | Plants (most common), mammals, arthropods, bacteria | Can infect all types of organism; animals, plants, fungi, bacteria, archaea |
Classification
editThe classification of subviral agents is ongoing. The following uses an outline for subviral agents in a 2011 ICTV report.[1] A lot of the taxa have since been assigned more formal names in 2019, so these are included when possible.
Satellite viruses
editSome satellite viruses have been assigned a taxon. The following reflects the results of a 2015 proposal that has since been accepted (Taxoprop 2015.009a).[12]
- Single-stranded RNA satellite viruses
- (unassigned to a family)
- Albetovirus – Tobacco necrosis satellite virus 1, 2, and C
- Aumaivirus – Maize white line mosaic satellite virus
- Papanivirus – Panicum mosaic satellite virus
- Virtovirus – Tobacco mosaic satellite virus, aka Tobacco necrosis satellite virus
- Family Sarthroviridae
- Macronovirus –Macrobrachium satellite virus 1 (extra small virus)
- (unnamed genus) – Nilaparvata lugens commensal X virus
- (unnamed genus) – Chronic bee-paralysis satellite virus
- (unassigned to a family)
- Double-stranded DNA satellite viruses
- Family Lavidaviridae – Virophages
- Single-stranded DNA satellite viruses
- Genus Dependoparvovirus – Adeno-associated virus group
Satellite nucleic acids
editThe following may not be comprehensive in its ICTV coverage. The nomenclature for satellite RNAs is to prefix the host virus name with "sat".
Satellite-like nucleic acids resemble satellite nucleic acids, in that they replicate with the aid of helper viruses. However they differ in that they can encode functions that can contribute to the success of their helper viruses; while they are sometimes considered to be genomic elements of their helper viruses, they are not always found within their helper viruses.
- Single-stranded satellite DNAs
- Family Alphasatellitidae (encoding a replication initiator protein)[13]
- Family Tolecusatellitidae[14]
- Genus Betasatellites (encoding a pathogenicity determinant βC1)
- Genus Deltasatellites (appears defective in βC1, but is their own group)
- Double-stranded satellite RNAs
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae virus satellite M
- Ustilago maydis virus H satellite M
- Trichomonas vaginalis T1 virus satellite
- Partitiviridae associated virus satellites
- Zygosaccharomyces bailii virus satellite M / Zybavirus balii satellite M
- Single-stranded satellite RNAs
- Large linear satellite RNAs
- Arabis mosaic virus large satellite RNA
- Bamboo mosaic virus satellite RNA (satBaMV)
- Chicory yellow mottle virus large satellite RNA
- Grapevine Bulgarian latent virus satellite RNA
- Grapevine fanleaf virus satellite RNA
- Myrobalan latent ringspot virus satellite RNA
- Tomato black ring virus satellite RNA
- Beet ringspot virus satellite RNA
- Beet necrotic yellow vein virus RNA5
- Small linear satellite RNAs
- Cucumber mosaic virus satellite RNA
- Cymbidium ringspot virus satellite RNA
- Pea enation mosaic virus satellite RNA
- Groundnut rosette virus satellite RNA
- Panicum mosaic virus small satellite RNA
- Peanut stunt virus satellite RNA
- Turnip crinkle virus satellite RNA
- Tomato bushy stunt virus satellite RNA, B10
- Tomato bushy stunt virus satellite RNA, B1
- Tobacco bushy top virus satellite RNA
- Circular satellite RNAs or "virusoids"
- Arabis mosaic virus small satellite RNA
- Tobacco ringspot virus satellite RNA (satTRsV) above two forms a clade
- Chicory yellow mottle virus satellite RNA (satCYMoV)
- Solanum nodiflorum mottle virus satellite RNA
- Subterranean clover mottle virus satellite RNA
- Velvet tobacco mottle virus satellite RNA above four forms a clade
- Lucerne transient streak virus satellite RNA (satLTSV)
- Cereal yellow dwarf virus-RPV satellite RNA
- Cherry small circular viroid-like RNA
- Realm Ribozyviria / Family Kolmioviridae – Deltavirus-like satellite-like RNAs
- Genus Deltavirus – Hepadnavirus-associated satellite-like RNAs
- Polerovirus-associated RNAs
- Large linear satellite RNAs
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c d "3 – Satellites and Other Virus-dependent Nucleic Acids – Subviral Agents – Subviral Agents (2011)". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). (newer version; does not mention satellites[dead link])
- ^ Baez, John. "Subcellular Life Forms". University of California, Riverside. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ^ Wayne L. Gerlach; Jamal M. Buzayan; Irving R. Schneider; George Bruening (1986). "Satellite Tobacco Ringspot Virus RNA: Biological Activity of DNA Clones and Their in Vitro Transcripts". Virology. 151 (2): 172–185. doi:10.1016/0042-6822(86)90040-1. PMID 18640636.
- ^ Hu, Chung-Chi; Hsu, Yau-Heiu; Lin, Na-Sheng (18 December 2009). "Satellite RNAs and Satellite Viruses of Plants". Viruses. 1 (3): 1325–1350. doi:10.3390/v1031325. PMC 3185516. PMID 21994595.
- ^ Krupovic, Mart; Kuhn, Jens H.; Fischer, Matthias G. (1 January 2016). "A classification system for virophages and satellite viruses". Archives of Virology. 161 (1): 233–247. doi:10.1007/s00705-015-2622-9. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0028-DC34-F. ISSN 0304-8608. PMID 26446887.
- ^ Bernard La Scola; Christelle Desnues; Isabelle Pagnier; Catherine Robert; Lina Barrassi; Ghislain Fournous; Michèle Merchat; Marie Suzan-Monti; Patrick Forterre; Eugene Koonin & Didier Raoult (2008). "The virophage as a unique parasite of the giant mimivirus". Nature. 455 (7205): 100–4. Bibcode:2008Natur.455..100L. doi:10.1038/nature07218. PMID 18690211. S2CID 4422249.
- ^ Krupovic M; Cvirkaite-Krupovic V (2011). "Virophages or satellite viruses?". Nat Rev Microbiol. 9 (11): 762–763. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2676. PMID 22016897. S2CID 41271832.
- ^ Roossinck, M. J.; Sleat, D.; Palukaitis, P. (June 1992). "Satellite RNAs of plant viruses: structures and biological effects". Microbiological Reviews. 56 (2): 265–279. doi:10.1128/MMBR.56.2.265-279.1992. ISSN 0146-0749. PMC 372867. PMID 1620065.
- ^ Hu, Chung-Chi; Hsu, Yau-Heiu; Lin, Na-Sheng (2009). "Satellite RNAs and Satellite Viruses of Plants". Viruses. 1 (3): 1325–1350. doi:10.3390/v1031325. PMC 3185516. PMID 21994595.
- ^ "Hepatitis D Virus". web.stanford.edu. Retrieved 1 December 2017.
- ^ a b "Hepatitis D: Background, Etiology, Epidemiology". Medscape. Retrieved 1 December 2017.
- ^ Krupovic, Mart; Kuhn, Jens H.; Fischer, Matthias G. (7 October 2015). "A classification system for virophages and satellite viruses". Archives of Virology. 161 (1): 233–247. doi:10.1007/s00705-015-2622-9. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0028-DC34-F. PMID 26446887.
- ^ Taxoprop 2017.004P
- ^ Taxoprop 2016.021a-kP
External links
edit- ICTV
- "Subcellular". Subcellular Life Forms