Ribulose 5-phosphate is one of the end-products of the pentose phosphate pathway. It is also an intermediate in the Calvin cycle.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
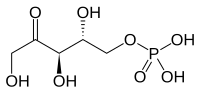
[(2R,3R)-2,3,5-Trihydroxy-4-oxopentyl] dihydrogen phosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | ribulose+5-phosphate |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H11O8P | |
| Molar mass | 230.109 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
It is formed by phosphogluconate dehydrogenase in the pentose phosphate pathway.[1][2] Ribulose 5-phosphate is involved in various metabolic pathways. Ribulose 5-phosphate can be acted upon by phosphopentose isomerase to form ribose 5-phosphate, which is a precursor for nucleotide and co-factor biosynthesis.[1] Ribulose-5 phosphate can also be acted upon by phosphopentose epimerase to form xylulose 5-phosphate, which is used in the nonoxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway in humans to generate precursor molecules for the synthesis of aromatic amino acids and production of energy.[2]
In plants, ribulose 5-phosphate produced from the pentose-phosphate pathway is converted into ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate by the enzyme phosphoribokinase.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b Edwards, Thomas E.; Abramov, Ariel B.; Smith, Eric R.; Baydo, Ruth O.; Leonard, Jess T.; Leibly, David J.; Thompkins, Kaitlin B.; Clifton, Matthew C.; Gardberg, Anna S.; Staker, Bart L.; Van Voorhis, Wesley C.; Myler, Peter J.; Stewart, Lance J. (2011-10-13). "Structural characterization of a ribose-5-phosphate isomerase B from the pathogenic fungus Coccidioides immitis". BMC Structural Biology. 11: 39. doi:10.1186/1472-6807-11-39. ISSN 1472-6807. PMC 3212906. PMID 21995815.
- ^ a b Liang, Wenguang; Ouyang, Songying; Shaw, Neil; Joachimiak, Andrzej; Zhang, Rongguang; Liu, Zhi-Jie (2010-10-05). "Conversion of<scp>d</scp>-ribulose 5-phosphate to<scp>D</scp>-xylulose 5-phosphate: new insights from structural and biochemical studies on human RPE". The FASEB Journal. 25 (2): 497–504. doi:10.1096/fj.10-171207. ISSN 0892-6638. PMC 6188353. PMID 20923965.