Pravastatin, sold under the brand name Pravachol among others, is a statin medication, used for preventing cardiovascular disease in those at high risk and treating abnormal lipids.[5] It is suggested to be used together with diet changes, exercise, and weight loss.[5] It is taken by mouth.[5]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Pravachol, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a692025 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 18%[4] |
| Protein binding | 50%[4] |
| Metabolism | Liver (minimal)[4] |
| Elimination half-life | 1-3 hours[4] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.216.225 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
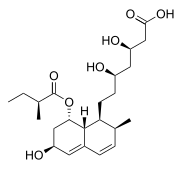
| Formula | C23H36O7 |
| Molar mass | 424.534 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Common side effects include joint pain, diarrhea, nausea, headaches, and muscle pains.[5] Serious side effects may include rhabdomyolysis, liver problems, and diabetes.[5] Use during pregnancy may harm the fetus.[5] Like all statins, pravastatin works by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, an enzyme found in liver that plays a role in producing cholesterol.[5]
Pravastatin was patented in 1980 and approved for medical use in 1989.[6] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[7] It is available as a generic medication.[5] In 2022, it was the 37th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 16 million prescriptions.[8][9]
Medical uses
editPravastatin is primarily used for the treatment of dyslipidemia and the prevention of cardiovascular disease.[10] It is recommended to be used only after other measures, such as diet, exercise, and weight reduction, have not improved cholesterol levels.[10]
Pravastatin has been found to have a similar effectiveness at lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol as fluvastatin but evidence indicates that pravastatin may not be as effective as other statin medications.[11] The beneficial effect of pravastatin is dependent on the dose and the potential for side effects or unwanted effects from this medication are not clear from clinical trials.[11]
Adverse effects and contraindications
editPravastatin has undergone over 112,000 patient-years of double-blind, randomized trials using the 40 mg, once-daily dose and placebos. These trials indicate pravastatin is well tolerated and displays few noncardiovascular abnormalities in patients.[12]
Contraindications, conditions that warrant withholding treatment with pravastatin, include pregnancy and breastfeeding.[13] Taking pravastatin while pregnant could lead to birth defects. While the amount of pravastatin ingested by an infant from breastfeeding is low, patients breastfeeding should not take pravastatin due to potential effects on the infant's lipid metabolism.[14]
Drug interactions
editMedications that should not be taken with pravastatin include, but are not limited to:[10][13]
- Cimetidine (Tagamet)
- Colchicine (Colcrys)
- Cyclosporine (Neoral, Sandimmune)
- Ketoconazole (Nizoral)
- Additional cholesterol-lowering medications such as: fenofibrate (Tricor), gemfibrozil (Lopid), cholestyramine (Questran, Questran Light, Cholybar), and niacin (nicotinic acid, Niacor, Niaspan);
- Specific HIV protease inhibitors such as: lopinavir and ritonavir (Kaletra), and ritonavir (Norvir) taken with darunavir (Prezista); and spironolactone (Aldactone).
The combination of fenofibrate with pravastatin is approved for use in the European Union.[15]
Mechanism of action
editPravastatin acts as a lipoprotein-lowering drug through two pathways. In the major pathway, pravastatin inhibits the function of hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) reductase. As a reversible competitive inhibitor, pravastatin sterically hinders the action of HMG-CoA reductase by occupying the active site of the enzyme. Taking place primarily in the liver, this enzyme is responsible for the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate in the rate-limiting step of the biosynthetic pathway for cholesterol. Pravastatin also inhibits the synthesis of very-low-density lipoproteins, which are the precursor to low-density lipoproteins (LDL). These reductions increase the number of cellular LDL receptors, thus LDL uptake increases, removing it from the bloodstream.[16]
Pharmacokinetics
editOral bioavailability of pravastatin ranges from 17-34% with peak plasma concentration achieved 1-1.5 hours after administration. Absorption of drug is modestly decreased when taken with food however this does not reduce the clinical lipid-lowering effect.[1]
The 3α-hydroxyisomeric metabolite of pravastatin is also an active HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor with approximately 2.5-10% the potency of the parent compound. Pravastatin has a plasma half-life of 1.8 hours whereas this active metabolite has a half-life up to 77 hours.[1]
History
editInitially known as CS-514, pravastatin is a derivative of ML236B (compactin), which was identified in a fungus called Penicillium citrinum in the 1970s by researchers of the Sankyo Pharma Inc.[17] It is being marketed outside Japan by the pharmaceutical company Bristol-Myers Squibb. In 2005, Pravachol was the 22nd-highest selling brand-name drug in the United States, with sales totaling $1.3 billion.[18]
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved generic pravastatin for use in the United States in April 2006.[18] Generic pravastatin sodium tablets were manufactured by Biocon Ltd, India and Teva Pharmaceuticals in Kfar Sava, Israel.[18]
References
edit- ^ a b c "DailyMed - Pravastatin sodium tablet". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
- ^ "Pravachol (pravastatin sodium) Tablets Initial U.S. Approval: 1991". DailyMed. Retrieved 2 September 2024.
- ^ "Active substance: pravastatin" (PDF). List of nationally authorised medicinal products. European Medicines Agency. 26 November 2020.
- ^ a b c d Neuvonen PJ, Backman JT, Niemi M (2008). "Pharmacokinetic comparison of the potential over-the-counter statins simvastatin, lovastatin, fluvastatin and pravastatin". Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 47 (7): 463–474. doi:10.2165/00003088-200847070-00003. PMID 18563955. S2CID 11716425.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Pravastatin Sodium Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. AHFS. Retrieved 23 December 2018.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 472. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ "Pravastatin Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ a b c "Pravachol". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 3 April 2011.
- ^ a b Adams SP, Alaeiilkhchi N, Tasnim S, Wright JM, et al. (Cochrane Hypertension Group) (September 2023). "Pravastatin for lowering lipids". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2023 (9): CD013673. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013673.pub2. PMC 10506175. PMID 37721222.
- ^ Pfeffer MA, Keech A, Sacks FM, Cobbe SM, Tonkin A, Byington RP, et al. (May 2002). "Safety and tolerability of pravastatin in long-term clinical trials: prospective Pravastatin Pooling (PPP) Project". Circulation. 105 (20): 2341–2346. doi:10.1161/01.cir.0000017634.00171.24. PMID 12021218.
- ^ a b Williams E. "Pravachol Side Effects Center". RxList. Retrieved 1 December 2012.
- ^ "Pravastatin". LactMed. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 1 December 2012.[dead link]
- ^ "Pravafenix EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- ^ Vaughan CJ, Gotto AM (August 2004). "Update on statins: 2003". Circulation. 110 (7): 886–892. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000139312.10076.BA. PMID 15313959.
- ^ Tobert JA (July 2003). "Lovastatin and beyond: the history of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors". Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery. 2 (7): 517–526. doi:10.1038/nrd1112. PMID 12815379. S2CID 3344720.
- ^ a b c "FDA Approves First Generic Pravastatin". Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). Archived from the original on 6 March 2010. Retrieved 20 January 2008.