The Lebanon PortalA view of Byblos, Lebanon
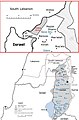
 Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west; Cyprus lies a short distance from the coastline. Lebanon has a population of more than five million and an area of 10,452 square kilometres (4,036 sq mi). Beirut is the country's capital and largest city. Human habitation in Lebanon dates to 5000 BC. From 3200 to 539 BC, it was part of Phoenicia, a maritime civilization that spanned the Mediterranean Basin. In 64 BC, the region became part of the Roman Empire and the subsequent Byzantine Empire. After the seventh century, it came under the rule of different Islamic caliphates, including the Rashidun, Umayyad and Abbasid. The 11th century saw the establishment of Christian Crusader states, which fell to the Ayyubids and the Mamluks. Lebanon came under Ottoman rule in the early 15th century. Under Ottoman sultan Abdulmejid I, the first Lebanese proto state, the Mount Lebanon Mutasarrifate, was established as a home for Maronite Christians, as part of the Tanzimat reforms. Lebanon is a developing country, ranked 112th on the Human Development Index. It has been classified as an upper-middle-income state. The Lebanese liquidity crisis, coupled with nationwide corruption and disasters such as the 2020 Beirut explosion, precipitated the collapse of Lebanon's currency and fomented political instability, widespread resource shortages, and high unemployment and poverty. The World Bank has defined Lebanon's economic crisis as one of the world's worst since the 19th century. Despite the country's small size, Lebanese culture is renowned both in the Arab world and globally, powered primarily by the large and influential Lebanese diaspora. Lebanon is a founding member of the United Nations and the Arab League, and a member of the Non-Aligned Movement, the Organization of Islamic Cooperation, the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie, and the Group of 77. (Full article...) This is a Featured article, one of the best articles Wikipedia has to offer.
The law school of Berytus (also known as the law school of Beirut) was a center for the study of Roman law in classical antiquity located in Berytus (modern-day Beirut, Lebanon). It flourished under the patronage of the Roman emperors and functioned as the Roman Empire's preeminent center of jurisprudence until its destruction in AD 551. The law schools of the Roman Empire established organized repositories of imperial constitutions and institutionalized the study and practice of jurisprudence to relieve the busy imperial courts. The archiving of imperial constitutions facilitated the task of jurists in referring to legal precedents. The origins of the law school of Beirut are obscure, but probably it was under Augustus in the first century. The earliest written mention of the school dates to 238–239 AD, when its reputation had already been established. The school attracted young, affluent Roman citizens, and its professors made major contributions to the Codex of Justinian. The school achieved such wide recognition throughout the Empire that Beirut was known as the "Mother of Laws". Beirut was one of the few schools allowed to continue teaching jurisprudence when Byzantine emperor Justinian I shut down other provincial law schools. The course of study at Beirut lasted for five years and consisted in the revision and analysis of classical legal texts and imperial constitutions, in addition to case discussions. Justinian took a personal interest in the teaching process, charging the bishop of Beirut, the governor of Phoenicia Maritima and the teachers with discipline maintenance in the school. (Full article...) Did you know (auto-generated) -
TopicsRelated portalsReligions in Lebanon Arab states Other countries This is a Good article, an article that meets a core set of editorial standards.
The 1585 Ottoman expedition against the Druze, also called the 1585 Ottoman invasion of the Chouf, was an Ottoman military campaign led by Ibrahim Pasha against the Druze and other chieftains of Mount Lebanon and its environs, then a part of the Sidon-Beirut Sanjak of the province of Damascus Eyalet. It had been traditionally considered the direct consequence of a raid by bandits in Akkar against the tribute caravan of Ibrahim Pasha, then Egypt's outgoing governor, who was on his way to Constantinople. Modern research indicates that the tribute caravan arrived intact and that the expedition was instead the culmination of Ottoman attempts to subjugate the Druze and other tribal groups in Mount Lebanon dating from 1518. In 1523–1524 dozens of Druze villages were burned in the Chouf area and hundreds of Druze were killed or captured by the governor Khurram Pasha, after which a period of peace ensued. Tensions resumed in the 1560s as Druze and non-Druze local dynasties, particularly the Ma'ns, Assafs and Shihabs, acquired large quantities of prohibited firearms, which were often superior to those possessed by government troops. Military action by the Ottoman governors of Damascus in the 1570s failed to disarm the chiefs and the general population or collect tax arrears, which had been building up from the 1560s. Ibrahim Pasha was appointed to "rectify the situation" in the Levant in 1583 and launched the expedition against the Druze of Mount Lebanon in the summer of 1585 as a Porte-ordered diversion for his Constantinople-bound caravan. He mobilised about 20,000 soldiers, including the Janissaries of Egypt and Damascus, as well as local chieftains, namely the Bedouin Mansur ibn Furaykh and Druze rivals of the Ma'ns. Hundreds of Druze rebels were slain, thousands of muskets were confiscated and large sums of money were collected as tax arrears by Ibrahim Pasha. The Ma'nid chief Qurqumaz, one of the principal targets of the expedition, died in hiding after refusing to surrender. (Full article...) General imagesThe following are images from various Lebanon-related articles on Wikipedia.
CategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
SourcesDiscover Wikipedia using portals |