A parathyroid adenoma is a benign tumor of the parathyroid gland. It generally causes hyperparathyroidism; there are very few reports of parathyroid adenomas that were not associated with hyperparathyroidism.[1]
| Parathyroid adenoma | |
|---|---|
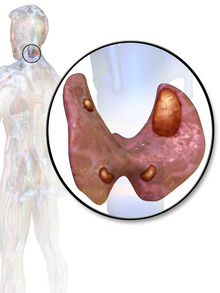 | |
| Parathyroid adenoma | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology, Otolaryngology |
A human being usually has four parathyroid glands located on the posterior surface of the thyroid in the neck. In order to maintain calcium metabolism, the parathyroid glands secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) which stimulates the bones to release calcium and the kidneys to reabsorb it from the urine into the blood, thereby increasing its serum level. The action of calcitonin opposes PTH. When a parathyroid adenoma causes hyperparathyroidism, more parathyroid hormone is secreted, causing the calcium concentration of the blood to rise, resulting in hypercalcemia.[2]
Signs and symptoms
editThe first signs of a parathyroid adenoma and the resulting primary hyperparathyroidism can include bone fractures and urinary calculi such as kidney stones.[1]
Often, a parathyroid adenoma is diagnosed by an incidental finding on blood tests that reveal high calcium levels.[3] Patients may not be experiencing any noticeable symptoms but could be producing excessive amounts of calcium and eventually experience problems later in life if untreated. However, if symptomatic, patients can experience: pain or discomfort in the joints, muscles, and abdomen; depression and mood changes due to the hormonal imbalance.;[4] constipation; exhaustion; and kidney damage.[4]
Genetics
editParathyroid adenoma can be associated with overexpression of the cyclin D1 gene.[5] It is also associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN).[6]
Diagnosis
editHyperparathyroidism is confirmed by blood tests such as calcium and PTH levels. A specific test for parathyroid adenoma is sestamibi parathyroid scintigraphy, often referred to as sestamibi scan or, more colloquially, MIBI scan. This nuclear imaging technique reveals the presence and location of pathological parathyroid tissue.[7] In cases where 99mTc-sestamibi scintigraphy or SPECT delivers inconclusive results, other imaging modalities and tracers can be applied. For detection of multiple parathyroid adenomas, positron emission tomography (PET) using the radiopharmaceutical 68Ga-Trivehexin[8] has demonstrated a higher detection rate (94.1%) than 99mTc-sestamibi imaging (58.8%).[9]
4DCT is used as second line investigation to diagnose parathyroid adenoma. In addition to the three dimensional imaging of a conventional CT scan, 4DCT provides imaging on the changes of iodinated contrast enhancement over time and present them in a video format (from plain imaging to arterial to venous and delay phases). Parathyroid adenoma would show low density on non contrast image, with peak enhancement during the arterial phase, then slowly fade away until the delay phase.[10]
Treatment
editSurgery is the only cure for parathyroid adenomas.[11] It is successful about 95% of the time. Parathyroidectomy is the removal of the affected gland(s). The standard of treatment of primary hyperparathyroidism was formerly a surgical technique called bilateral neck exploration, in which the neck was opened on both sides, the parathyroids were identified, and the affected tissue was removed.[12] By the 1980s, unilateral exploration became more common.[12] Parathyroidectomy can now be performed in a minimally invasive fashion, mainly because imaging techniques can pinpoint the location of the tissue.[12] Minimally invasive techniques include smaller open procedures, radio-guided and video-assisted procedures, and totally endoscopic surgery.[12]
Before surgery is attempted, the affected glandular tissue must be located. Though the parathyroid glands are usually located on the back of the thyroid, their position is variable. Some people have one or more parathyroid glands elsewhere in the neck anatomy or in the chest. About 10% of parathyroid adenomas are ectopic, located not along the back of the thyroid but elsewhere in the body, sometimes in the mediastinum of the chest.[11] This can make them difficult to locate, so various imaging techniques are used, such as the sestamibi scan, single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), ultrasound, MRI,[11] and CT scans.[11][13] sometimes parathyroid adenomas can be ablated by ethanol injection, laser or radiofrequency guided by ultrasound.
Micrographs
editSee also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b Sekine O, Hozumi Y, Takemoto N, Kiyozaki H, Yamada S, Konishi F (March 2004). "Parathyroid adenoma without hyperparathyroidism". Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology. 34 (3): 155–8. doi:10.1093/jjco/hyh028. PMID 15078912.
- ^ Felsenfeld AJ, Rodríguez M, Aguilera-Tejero E (November 2007). "Dynamics of parathyroid hormone secretion in health and secondary hyperparathyroidism". Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 2 (6): 1283–305. doi:10.2215/CJN.01520407. PMID 17942777.
- ^ (2012) The New York Times, Health Guide[verification needed]
- ^ a b "Parathyroid adenoma: Diagnosis & treatment". Cleveland Clinic. June 11, 2012.
- ^ Hsi ED, Zukerberg LR, Yang WI, Arnold A (May 1996). "Cyclin D1/PRAD1 expression in parathyroid adenomas: an immunohistochemical study". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 81 (5): 1736–9. doi:10.1210/jcem.81.5.8626826. PMID 8626826.
- ^ "Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia". The Lecturio Medical Concept Library. Retrieved 11 August 2021.
- ^ Goldstein RE, Billheimer D, Martin WH, Richards K (May 2003). "Sestamibi scanning and minimally invasive radioguided parathyroidectomy without intraoperative parathyroid hormone measurement". Annals of Surgery. 237 (5): 722–30, discussion 730–1. doi:10.1097/01.SLA.0000064362.58751.59. PMC 1514518. PMID 12724639.
- ^ Quigley NG, Steiger K, Hoberueck S, Czech N, Zierke MA, Kossatz S, et al. (March 2022). "PET/CT imaging of head-and-neck and pancreatic cancer in humans by targeting the "Cancer Integrin" αvβ6 with Ga-68-Trivehexin". European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 49 (4): 1136–1147. doi:10.1007/s00259-021-05559-x. PMC 8460406. PMID 34559266.
- ^ Kuyumcu S, Denizmen D, Has-Simsek D, Poyanli A, Uzum AK, Buyukkaya F, et al. (July 2024). "68Ga-Trivehexin PET/CT: a promising novel tracer for primary hyperparathyroidism". European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 51 (13): 3912–3923. doi:10.1007/s00259-024-06846-z. PMC 11527967. PMID 39028425.
- ^ Hoang, Jenny K.; Sung, Won-kyung; Bahl, Manisha; Phillips, C. Douglas (January 2014). "How to Perform Parathyroid 4D CT: Tips and Traps for Technique and Interpretation". Radiology. 270 (1): 15–24. doi:10.1148/radiol.13122661. ISSN 0033-8419. PMID 24354373.
- ^ a b c d Dsouza, Caren; Gopalakrishnan; Bhagavan, KR; Rakesh, K (2012). "Ectopic parathyroid adenoma". Thyroid Research and Practice. 9 (2): 68–70. doi:10.4103/0973-0354.96061.
- ^ a b c d Bellantone R, Raffaelli M, DE Crea C, Traini E, Lombardi CP (August 2011). "Minimally-invasive parathyroid surgery". Acta Otorhinolaryngologica Italica. 31 (4): 207–15. PMC 3203720. PMID 22065831.
- ^ Zald PB, Hamilton BE, Larsen ML, Cohen JI (August 2008). "The role of computed tomography for localization of parathyroid adenomas". The Laryngoscope. 118 (8): 1405–10. doi:10.1097/MLG.0b013e318177098c. PMID 18528308. S2CID 46264400.