Old Saxony was the homeland of the Saxons during the Early Middle Ages. It corresponds roughly to the modern German states of Lower Saxony, eastern part of modern North Rhine-Westphalia state (Westphalia), Nordalbingia (Holstein, southern part of Schleswig-Holstein) and western Saxony-Anhalt (Eastphalia), which all lie in northwestern Germany. It had four provinces: Nordalbingia, Eastphalia, Westphalia and Angria (or Angaria), these provinces, in turn, were divided into smaller territories, the gaue, which are equivalent to modern Districts of Germany (Kreise), and were equivalent to the English shires (modern counties).
Old Saxony | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6th century–804 | |||||||||
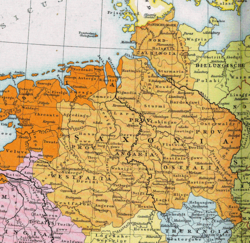 The later stem duchy of Saxony (c. 1000 AD), which was based in the Saxons' traditional homeland bounded by the rivers Ems, Eider and Elbe | |||||||||
| Status | Tribal territory of the Saxons Early medieval duchy | ||||||||
| Capital | Marklo[1] | ||||||||
| Common languages | Old Saxon | ||||||||
| Religion | Germanic Paganism | ||||||||
| Government | Tribal confederation | ||||||||
| Historical era | Early Middle Ages | ||||||||
• Hadugato, first documented duke | 6th century | ||||||||
• End of the Saxon Wars | 804 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
It should not be confused with the modern German state of Saxony, which is in eastern Germany, adjoining the northwest border of the Czech Republic.
Origin
editPtolemy's Geographia, written in the 2nd century, is sometimes considered to contain the first mentioning of the Saxons. Some copies of this text mention a tribe called Saxones in the area to the north of the lower River Elbe, thought to derive from the word Sax or stone knife.[2]
However, other copies call the same tribe Axones, and it is considered likely that it is a misspelling of the tribe that Tacitus in his Germania called Aviones. These earliest known tribal Saxons inhabited "Northern Albingia", a region bordering the northern bank of the mouth of River Elbe in what is now Western Holstein. As land became scarce, the Saxon population began to expand southward where it absorbed indigenous populations such as Cherusci, Chamavi and Chatti, and remaining portions of the Langobardi (Lombards) and Suebi. This broader domain is called "Old Saxony". The Chauci, according to Tacitus, also lived in the general area later known as Old Saxony and were highly respected among Germanic tribes. He describes them as peaceful, calm, and levelheaded. At some point they may have merged with, or were perhaps synonymous to, the Saxons.
It has been claimed that the Old Saxons were composed of an aristocracy of nobles, a free warrior class of distinction and renown, leading freemen united and controlled by ancient custom of kindred and clan.
"Social differences were jealously guarded by social prescription. The death penalty was imposed on any man who married above his rank; the marriage of a man below his station was severely condemned; bastardy was not tolerated; intermarriage between Saxons and other Germans was frowned upon; and strangers were hated. So tenaciously did the Saxons cling to their ancient customary law that clear traces of these social survivals persisted in Saxony down through the Middle Ages."[how?][3]
Raids on Britain
editSaxons had been raiding the eastern seaboard of Britain from here during the 3rd and 4th centuries (prompting the construction of maritime defences in eastern Britain called the Saxon Shore) and it is thought that following the collapse of the Roman defences on the Rhine in 407 pressure from population movements in the east forced the Saxons and their neighbouring tribes the Angles and the Jutes to migrate westwards by sea and invade the fertile lowland areas of Britain. The traditional date for this invasion is 449 and is known as the Adventus Saxonum. However, there is little archaeological evidence of any subsequent long-term conflict, and the evidence for large-scale Germanic migration into Britain is equally scant. It is possible that the level of migration was relatively minimal and that the ethnic makeup of the post-Roman population in Britain remained largely unchanged.[4]
The cultural and linguistic changes were stark and led to the creation of various Saxon kingdoms in England including that of the South Saxons (Sussex), the West Saxons (Wessex) and the East Saxons (Essex) alongside others established by the Angles and the Jutes and are the foundations of the modern English nation.
Relations with the Franks
editAfter the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century the Old Saxons who remained in Germania were loosely associated with the Merovingian kingdom of Franks, but practically remained independent and maintained their old pagan religion. The Saxon pagan religion appears to have focused on the worship of the Irminsul or "great pillar"; a divine tree that connected Heaven and Earth and is thought to have existed at a site close to modern Obermarsberg.
For the most part, the Saxon lands were a broad plain, save on the south, where they rose into hills and the low mountainous country of the Harz and Hesse. This low divide was all that separated the country of the Saxons from their ancient enemies and ultimate conquerors, the Franks. The lack of clear physical definition along this border, from time immemorial, had been the cause of incessant tribal conflict between them. Saxons as inhabitants of present-day Northern Germany are mentioned in 555, when Theudebald, the Frankish king, died and the Saxons used this opportunity for war. The Saxons were defeated by Chlothar I, Theudebald's successor. Some of their Frankish successors fought against the Saxons, while others were allied with them; Chlothar II won a decisive victory against the Saxons.
Conversion to Christianity
editIn 690, two priests called Ewald the Black and Ewald the Fair set out from Northumbria to convert the Old Saxons to Christianity. It is recorded that at this time Old Saxony was divided into the ancient dioceses of Münster, Osnabrück, and Paderborn. However, by 695 the pagan Saxons had become extremely hostile to the Christian priests and missionaries in their midst and began to realize that their aim was to convert their overlord and destroy their temples and religion. Ewald the Fair was quickly murdered, but Ewald the Black they subjected to torture, and he was torn limb from limb. Afterwards the two bodies were cast into the Rhine. This is understood to have happened on 3 October 695 at a place called Aplerbeck, near Dortmund, where a chapel still stands. The two Ewalds are now celebrated in Westphalia as saints.
The Saxons' reluctance to accept the new Christian religion and propensity to mount destructive raids on their neighbours would eventually bring them into direct conflict with Charlemagne, the powerful king of the Franks and later emperor. After a bloody and highly attritious thirty-year campaign between 772–804 the Old Saxons led by Widukind were eventually subdued by Charlemagne and ultimately forced to convert to Christianity.
The bonds of kindred and clan were particularly strong among the Saxons, and in spite of many divisions the Saxons were an unusually homogeneous nation living as late as the 8th century as the early Germans described by Tacitus in Germania had lived. The long warfare with the Franks largely reduced but did not wholly obliterate their distinct cultural identity.
Adam of Bremen, writing in the 11th century, compared the shape of Old Saxony to a triangle, and estimated from angle to angle the distance was eight days journey. In area Old Saxony was the greatest of the German tribal duchies. It included the entire territory between the lower Elbe and Saale rivers almost to the Rhine. Between the mouths of the Elbe and the Weser it bordered the North Sea. The only parts of the territory which lay across the Elbe were the counties of Holstein and Ditmarsch. The tribal lands were roughly divided into four kindred groups: the Angrians, along the right bank of the Weser; the Westphalians, along the Ems and the Lippe; the Eastphalians, on the left bank of the Weser; and the Nordalbingians, in modern Holstein. But not even with these four tribal groups was the term of tribal division reached. For the Saxon “nation” was really a loose collection of clans of kindred stock. For example, the Nordalbingians alone were divided into lesser groups: Holsteiners, Sturmarii, Bardi, and the men of Ditmarsch.[5]
See also
edit- History of Saxony
- Duchy of Saxony, the early Medieval stem duchy
- List of rulers of Saxony
References
edit- ^ According to the primary source Vita Lebuini antiqua, the annual tribal council was held at Marklo near Weser.
- ^ Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). . Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- ^ James Westfall-Thompson, Feudal Germany (1928), p. 170 ("Old Saxony" chapter).
- ^ Ooshuizen, Susan (2019). The Emergence of the English. Arc Humanities Press. ISBN 9781641891288.
- ^ James Westfall-Thompson, Feudal Germany (1928), p. 167ff. ("Old Saxony" chapter).