Noeggerathia is an extinct genus of noeggerathialean plant that lived during the Late Carboniferous and Early Permian periods.[2]
| Noeggerathia Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
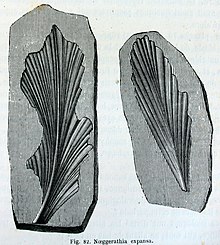
| |
| 1863 reconstruction of Noeggerathia expansa | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Class: | †Progymnospermopsida |
| Order: | †Noeggerathiales |
| Family: | †Noeggerathiaceae |
| Genus: | †Noeggerathia Sternb., 1820[1] |
| Type species | |
| Noeggerathia foliosa | |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
Description
editNoeggerathia could grow to be 3 ft, 3 in tall.[2] It is known for its compound leaves, each possessing two rows of leaflets which composed a 12-inch frond.[2] Noeggerathia may also have possessed a short trunk.[2]
The genus may have possessed strobili at the ends of its branches for reproductive purposes.[3] Biseriate sporophylls existed on either side of the cones.[3] It has been previously suggested that Noeggerathiostrobus may have been borne at the end of Noeggerathia's stems, although it is more likely that Noeggerathiostrobus was borne closer to the base of Noeggerathia.[4]
Taxonomy
editNoeggerathia was named after Johann Jakob Nöggerath, a geologist from Germany.[1][2] The genus was described in 1820 by Kaspar Maria von Sternberg.[1]
Noeggerathia and noeggerathialeans in general have been described as difficult to classify as early as 1906[1] and as recently as 2009.[2] In 1906, the genus was believed to belong to Cycadaceae, a family which currently consists only of Cycas.[1]
The species described under Noeggerathia include the following:[5]
Fossil sites
editSpecimens of Noeggerathia have been discovered worldwide.[2] As of 1906, Noeggerathia was known from finds in the European Coal Measures, and there it was considered to be rare.[1]
Several well-preserved specimens of Noeggerathia and related plants have been discovered in the Bohemian Massif, with N. foliosa having the most complete fossil record in that area.[6] N. dickeri has been described from the Upper Sandstone Formation of the Sinai Peninsula.[7]
References
edit- ^ a b c d e f Whitney, William Dwight; Smith, Benjamin Eli (1906). The Century dictionary and cyclopedia: a work of universal reference in all departments of knowledge with a new atlas of the world (Google eBook). Vol. 5. New York: The Century Co. p. 4007. Retrieved 29 January 2012.
- ^ a b c d e f g Palmer, Douglas; et al. (2009). Prehistoric life : the definitive visual history of life on earth (1st American ed.). New York: Dorling Kindersley. pp. 152–153. ISBN 978-0-7566-5573-0.
- ^ a b Taylor, Thomas N.; Taylor, Edith L.; Krings, Michael (2009). "Progymnosperms" (Google eBook). Paleobotany : the biology and evolution of fossil plants (2nd ed.). Amsterdam: Academic Press. p. 498. ISBN 978-0-12-373972-8. Retrieved 29 January 2012.
- ^ Preston, R. D. (1963). Advances in Botanical Research. Vol. 1. London: Academic Press. p. 34. ISBN 0-12-005901-0.
- ^ Dijkstra, Sybren J.; van Amerom, H. W. J. (1983). Fossilium catalogus plantae (Google eBook). Vol. 90. The Netherlands: Kugler Publications, B.V. p. 431. ISBN 90-6299-009-6. Retrieved 31 January 2012.
- ^ Šimůnek, Zbyněk; Bek, Jiřı́ (July 2003). "Noeggerathiaceae from the Carboniferous basins of the Bohemian Massif". Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology. 125 (3–4): 249–284. doi:10.1016/S0034-6667(03)00004-6.
- ^ Horowitz, Aharon (March 1973). "Noeggerathia dickeri n.sp. from the carboniferous of Sinai". Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology. 15 (1): 51–56. doi:10.1016/0034-6667(73)90016-X.