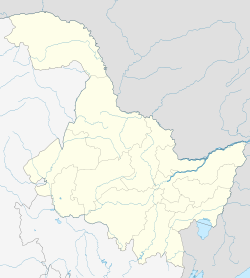
Mohe (Chinese: 漠河; pinyin: Mòhé) is a county-level city in Daxing'anling Prefecture, Heilongjiang province. It is the northernmost city in China. As of the 2020 Chinese Census, it has a population of 54,036.
Mohe
漠河市 | |
|---|---|
 Mohe City skyline (2019) | |
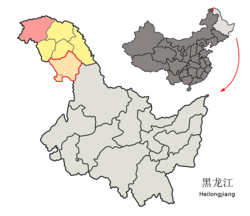 Location of Mohe City jurisdiction (pink) in Daxing'anling Prefecture (yellow) and Heilongjiang | |
| Coordinates: 52°58′19″N 122°32′20″E / 52.972°N 122.539°E | |
| Country | China |
| Province | Heilongjiang |
| Prefecture | Daxing'anling |
| Municipal seat | Xilinji |
| Area | |
• Total | 18,233 km2 (7,040 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 435 m (1,427 ft) |
| Population (2020 census)[1] | |
• Total | 54,036 |
| • Density | 3.0/km2 (7.7/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 165300 |
| Website | www |
| Mohe City | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 漠河 | ||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "Desert River" | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Administrative divisions
editMohe City is divided into 6 towns.
| Name | Hanzi[2] | Population (2020)[3] |
|---|---|---|
| Xilinji | 西林吉镇 | 29,614 |
| Tuqiang | 图强镇 | 10,402 |
| Amu'er | 阿木尔镇 | 9,115 |
| Xing'an | 兴安镇 | 992 |
| Beiji | 北极镇 | 2,373 |
| Gulian | 古莲镇 | 1,540 |
Geography
editMohe is located in the far northwest of Heilongjiang at latitude 52° 10'−53° 33' N and 121° 07'−124° 20' E. It forms a border with Russia's Amur Oblast and Zabaykalsky Krai, where the Amur River flows for 245 kilometres (152 mi). A village, the northernmost Chinese settlement, at the latitude of 53° 29' N and known as the Beiji Village (北极村, literally "North Pole Village" or "Northernmost Village"), lies in this city, on the Amur River.
On extremely rare occasions, the aurora borealis can be seen.[4]
Mohe spans 150 kilometres (93 mi) from north to south and has a total area of 18,233 square kilometres (7,040 sq mi), occupying 21.6% of the prefecture's (Daxing'anling) area and 3.9% of the provincial (Heilongjiang) area. This creates a population density of only 4.64 persons/km2 (12.0 persons/sqmi).
Maps
editClimate
editMohe, by virtue of its far northern location and proximity to Siberia, is one of the few locations in China with a subarctic climate (Köppen Dwc, Trewartha Ecbd),[5] closely bordering on extreme humid continental, with long, dry, severe winters, and short, warm, wet summers.[6] Winter begins in early to mid-October and lasts until late April or early May, and temperatures then are normally the coldest nationwide. Average temperatures stay below freezing for a total of nearly seven months of the year, and the frost-free period is just short of 90 days; in addition, the diurnal temperature variation is large, averaging 17.2 °C (31.0 °F) annually. The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from −28.2 °C (−18.8 °F) in January to 18.3 °C (64.9 °F) in July, with an annual mean of −3.90 °C (25.0 °F), so that the city is only a little south of the line of continuous permafrost. Extreme temperatures have ranged from −53.0 °C (−63.4 °F)[7][8][9] to 39.3 °C (102.7 °F).[10] The record low temperature of −53.0 °C (−63.4 °F), registered on 22 January 2023, was also the lowest temperature recorded in China.[11] December and January have never recorded an above-freezing temperature, and all 12 months have had sub-freezing temperatures at some point.
| Climate data for Mohe, elevation 433 m (1,421 ft), (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1971–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | −4.6 (23.7) |
5.5 (41.9) |
16.2 (61.2) |
28.4 (83.1) |
35.1 (95.2) |
39.3 (102.7) |
38.0 (100.4) |
35.5 (95.9) |
31.7 (89.1) |
25.1 (77.2) |
10.2 (50.4) |
−3.2 (26.2) |
39.3 (102.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −18.0 (−0.4) |
−11.1 (12.0) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
8.7 (47.7) |
17.7 (63.9) |
24.7 (76.5) |
26.3 (79.3) |
23.6 (74.5) |
17.1 (62.8) |
5.5 (41.9) |
−8.7 (16.3) |
−18.7 (−1.7) |
5.4 (41.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −27.9 (−18.2) |
−23.3 (−9.9) |
−12.2 (10.0) |
0.8 (33.4) |
9.3 (48.7) |
15.9 (60.6) |
18.6 (65.5) |
15.4 (59.7) |
7.9 (46.2) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
−17.4 (0.7) |
−27.1 (−16.8) |
−3.6 (25.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −34.9 (−30.8) |
−32.3 (−26.1) |
−22.0 (−7.6) |
−7.6 (18.3) |
0.2 (32.4) |
6.4 (43.5) |
11.1 (52.0) |
8.5 (47.3) |
0.5 (32.9) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
−24.2 (−11.6) |
−33.3 (−27.9) |
−11.4 (11.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −53.0 (−63.4) |
−52.3 (−62.1) |
−42.7 (−44.9) |
−32.6 (−26.7) |
−13.1 (8.4) |
−5.3 (22.5) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
−12.2 (10.0) |
−28.7 (−19.7) |
−41.9 (−43.4) |
−50.9 (−59.6) |
−53.0 (−63.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 6.7 (0.26) |
4.4 (0.17) |
6.2 (0.24) |
18.4 (0.72) |
44.4 (1.75) |
60.1 (2.37) |
117.0 (4.61) |
99.4 (3.91) |
52.3 (2.06) |
27.7 (1.09) |
13.1 (0.52) |
8.1 (0.32) |
457.8 (18.02) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 8.1 | 6.2 | 5.2 | 7.0 | 11.5 | 13.3 | 16.5 | 14.8 | 11.8 | 9.9 | 9.9 | 9.7 | 123.9 |
| Average snowy days | 9.4 | 8.1 | 6.5 | 7.2 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.1 | 1.3 | 9.1 | 11.7 | 11.4 | 66 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 68 | 65 | 61 | 54 | 57 | 70 | 78 | 81 | 75 | 69 | 72 | 70 | 68 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 144.2 | 189.4 | 255.6 | 248.4 | 241.4 | 268.0 | 225.3 | 222.0 | 200.9 | 173.9 | 150.8 | 125.1 | 2,445 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 56 | 67 | 69 | 59 | 49 | 53 | 45 | 49 | 54 | 54 | 59 | 53 | 56 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration[12][13] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China[14][11] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
editAs of the 2020 Chinese Census, Mohe has a population of 54,036.[3] Per the census, members of 18 different ethnic groups live in Mohe, including the Han, the Manchu, Mongols, Koreans, the Sibe, the Oroqen, Evenks, and Russians.[3]
Transportation
editMohe railway station, opened in 1972, is the northernmost railway station in China. It has regular passenger service to Harbin, Qiqihar, and Shenyang.[15]
Mohe Gulian Airport, opened in 2008, is the nation's northernmost airport and the first Chinese airport built on permafrost.[16]
Notable people
editIn popular culture
edit- Mohe is the destination of both the main character and his fictional hero in Xiaolu Guo's film How Is Your Fish Today? (Jin tian de yu zen me yang?) (2006).
See also
editSources
edit- ^ "2020年大兴安岭地区第七次全国人口普查主要数据公报" (in Chinese). Government of Daxing'anling Prefecture. 2021-05-31.
- ^ 2023年统计用区划代码(漠河市) [2023 Statistical Division Codes (Mohe)] (in Chinese). National Bureau of Statistics of China. 2023. Archived from the original on 2024-01-23. Retrieved 2024-09-08.
- ^ a b c 人口民族 [Population and Ethnicity] (in Chinese). Mohe Municipal People's Government. Archived from the original on 2024-04-19. Retrieved 2024-09-08.
- ^ "A Visit to China's "Arctic Village"". ChinaCulture.org. January 7, 2013.
- ^ "The 6 climate zones of China". ClimateList. Retrieved 2018-12-19.
- ^ Krishna, K. R. (2015-01-28). Agricultural Prairies: Natural Resources and Crop Productivity. CRC Press. ISBN 9781482258066.
- ^ "Climate". en.chinaculture.org. Retrieved 2018-12-19.
- ^ "China just saw its coldest temperature on record: Minus-63 degrees". The Washington Post. 23 January 2022. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ "China's northernmost city just saw its coldest day ever". CNN Travel. 24 January 2022. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ "Extreme Temperatures Around the World".
- ^ a b "China records its lowest-ever temperature in northernmost city of Mohe". South China Morning Post. 23 January 2023. Retrieved 1 January 2024.
- ^ 1991-2020 normals "Climate averages from 1991 to 2020". China Meteorological Administration. Archived from the original on 2023-04-17.
- ^ 1981-2010 extremes 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data [China Meteorological Data Network - WeatherBk Data] (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 14 April 2023.
- ^ 漠河城市介绍以及气候背景分析. Weather China (in Chinese). 中国气象局公共气象服务中心. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
- ^ "漠河列车时刻表 漠河火车时刻表 www.ip138.com". qq.ip138.com.
- ^ "中国最北极机场漠河机场正式通航--旅游--人民网". Archived from the original on 2012-06-08.
External links
edit- Mohe People's Government website (in Chinese)