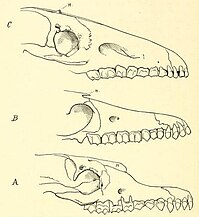
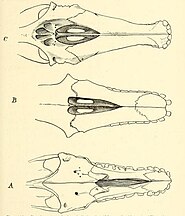
Macraucheniidae is a family in the extinct South American ungulate order Litopterna, that resembled camelids. They had three functional digits on the fore and hind feet, as well as elongate necks. The family is generally divided up into two subfamilies, Cramaucheniinae (which may be paraphyletic) and Macraucheniinae. The family shows retraction of the nasal region, most extremely to the top of the skull in derived macraucheniine taxa like Macrauchenia.[2] which has been interpreted to have supported a probsocis, perhaps like that of a saiga antelope to filter dust, or a moose-like prehensile lip.[3] The earliest unambiguous members of the family date to the late Oligocene around 30 million years ago. Polymorphis from the Eocene has historically been placed as a macraucheniid, but this has been doubted.[2] Most early representatives had a body masses in the range of 80–120 kilograms (180–260 lb), though some like Llullataruca were as small as 35–55 kilograms (77–121 lb), and the last representatives of the family from the Pleistocene like Macrauchenia were over 1,000 kilograms (2,200 lb).[4] The family reached its apex of diversity during the late Miocene around 10-6 million years ago, before declining to only a few species belong to the genera Macrauchenia and Xenorhinotherium by the Late Pleistocene.[2]
| Macraucheniidae | |
|---|---|
| |
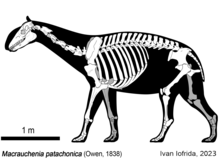
| Skeleton of Macrauchenia patachonica | |

| |
| Skeleton of Thesodon | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | †Litopterna |
| Superfamily: | †Macrauchenioidea |
| Family: | †Macraucheniidae Gill, 1872 |
| Subfamilies and genera | |
Below is a phylogenetic tree of the Macraucheniidae, after McGrath et al. 2018:.[5]
Cladogram of Macraucheniidae after Lobo, Gelfo & Azevedo (2024)[2]:
References
edit- ^ Püschel, Hans P.; Alarcón-Muñoz, Jhonatan; Soto-Acuña, Sergio; Ugalde, Raúl; Shelley, Sarah L.; Brusatte, Stephen L. (2023-02-25). "Anatomy and phylogeny of a new small macraucheniid (Mammalia: Litopterna) from the Bahía Inglesa Formation (late Miocene), Atacama Region, Northern Chile". Journal of Mammalian Evolution. 30 (2): 415–460. doi:10.1007/s10914-022-09646-0. ISSN 1573-7055.
- ^ a b c d Lobo, Leonardo Souza; Gelfo, Javier N.; de Azevedo, Sergio A. K. (2024-12-31). "The phylogeny of Macraucheniidae (Mammalia, Panperissodactyla, Litopterna) at the genus level". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 22 (1). doi:10.1080/14772019.2024.2364201. ISSN 1477-2019.
- ^ Blanco, R. Ernesto; Jones, Washington W.; Yorio, Lara; Rinderknecht, Andrés (October 2021). "Macrauchenia patachonica Owen, 1838: Limb bones morphology, locomotory biomechanics, and paleobiological inferences". Geobios. 68: 61–70. Bibcode:2021Geobi..68...61B. doi:10.1016/j.geobios.2021.04.006.
- ^ Croft, Darin A.; Gelfo, Javier N.; López, Guillermo M. (2020-05-30). "Splendid Innovation: The Extinct South American Native Ungulates". Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences. 48 (1): 259–290. Bibcode:2020AREPS..48..259C. doi:10.1146/annurev-earth-072619-060126. ISSN 0084-6597. S2CID 213737574.
- ^ Andrew J. McGrath; Federico Anaya; Darin A. Croft (2018). "Two new macraucheniids (Mammalia: Litopterna) from the late middle Miocene (Laventan South American Land Mammal Age) of Quebrada Honda, Bolivia". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 38 (3): e1461632. Bibcode:2018JVPal..38E1632M. doi:10.1080/02724634.2018.1461632. S2CID 89881990.
Bibliography
edit- Forasiepi, Analía M.; MacPhee, Ross D.E.; Hernández del Pino, Santiago; Schmidt, Gabriela I.; Amson, Eli; Grohé, Camille (2016). "Exceptional skull of Huayqueriana (Mammalia, Litopterna, Macraucheniidae) from the Late Miocene of Argentina: anatomy, systematics and paleobiological implications" (PDF). Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. 404: 1–76. doi:10.1206/0003-0090-404.1.1. S2CID 89219979. Retrieved 2018-10-01.