Lead(II) titanate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PbTiO3. It is the lead salt of titanic acid. Lead(II) titanate is a yellow powder that is insoluble in water.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Lead(II) titanate
Lead titanium oxide Lead(II) titanium oxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.841 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| PbTiO3 | |
| Molar mass | 303.09 g/mol |
| Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Density | 7.52 g/cm3 |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   [1] [1]
| |
| Danger[1] | |
| H302, H332, H360, H373, H410[1] | |
| P201, P261, P273, P304+P340, P308+P313, P312, P391[1] | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
12000 mg/kg (rat) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Lead dioxide Lead acetate |
Other cations
|
Caesium titanate Iron(II) titanate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
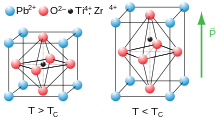
At high temperatures, lead titanate adopts a cubic perovskite structure. At 760 K,[2] the material undergoes a second order phase transition to a tetragonal perovskite structure which exhibits ferroelectricity. Lead titanate is one of the end members of the lead zirconate titanate (Pb[ZrxT1−x]O3, 0 ≤ x ≤ 1, PZT) system, which is technologically one of the most important ferroelectric and piezoelectric ceramics; PbTiO3 has a high ratio of k33 to kp with a high kt[clarify].
Lead titanate occurs in nature as mineral macedonite.[3][4]
Toxicity
editLead titanate is toxic, like other lead compounds. It irritates skin, mucous membranes and eyes. It may also cause harm to unborn babies and might have effects on fertility.[5]
Solubility in water
editThe solubility of hydrothermally-synthesized perovskite-phase PbTiO3 in water was experimentally determined at 25 and 80 °C to depend on pH and vary from 4.9x10−4 mol/kg at pH≈3, to 1.9x10−4 mol/kg at pH≈7.7, to "undetectable" (<3.2x10−7 mol/kg) in the range 10<pH<11. At still higher pH values, the solubility increased again. The solubility was apparently incongruent and was quantified as the analytical concentration of Pb.[6]
References
edit- ^ a b c d Sigma-Aldrich Co., Lead(II) titanate. Retrieved on 2019-01-15.
- ^ Noheda, Beatriz; Cereceda, Noé; Iglesias, Tomás; Lifante, Ginés; Gonzalo, Julio A.; Chen, Hui Ting; Wang, Yong Ling (1995-06-01). "Composition dependence of the ferroelectric-paraelectric transition in the mixed system PbZr1−xTixO3" (PDF). Physical Review B. 51 (22). American Physical Society (APS): 16388–16391. Bibcode:1995PhRvB..5116388N. doi:10.1103/physrevb.51.16388. ISSN 0163-1829. PMID 9978623.
- ^ Radusinović, Dušan and Markov, Cvetko "Macedonite - lead titanate: a new mineral", American Mineralogist 56, 387-394 (1971), http://www.minsocam.org/ammin/AM56/AM56_387.pdf
- ^ Burke, E.A.J. and Kieft, C. "Second occurrence of makedonite, PbTiO3, Långban, Sweden", Lithos 4, 101-104 (1971)
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-19. Retrieved 2010-09-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Jooho Moon, Melanie L. Carasso, Henrik G. Krarup, Jeffrey A. Kerchner, "Particle-shape control and formation mechanisms of hydrothermally derived lead titanate", Journal of Materials Research, Vol. 14, No.3, March 1999.[1]
