Kwanyinaspis is a genus of arthropod from the Cambrian aged Chengjiang biota of Yunnan, China. It was described in 2005 based on a single specimen, ELI-2004001. Around 6 cm long, It has twelve trunk tergites with well developed posterior facing pleural spines, along with a tail spine and ventral eyes. In the original description, it was tenatively considered a member of Aglaspidida.[1] However, later studies have considered it a trilobitomorph, and possibly the closest known relative of trilobites.[2]
| Kwanyinaspis Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
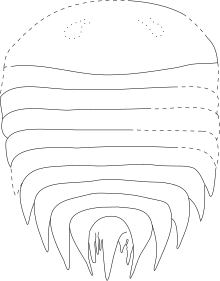
| |
| Drawing of the part type of the holotype Note: Eyes were located in the underside and were not visible on the dorsal surface in life | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| (unranked): | †Artiopoda |
| Subphylum: | †Trilobitomorpha |
| Genus: | †Kwanyinaspis Zhang & Shu, 2005 |
| Species: | †K. maotianshanensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Kwanyinaspis maotianshanensis Zhang & Shu, 2005
| |
References
edit- ^ Zhang, Xingliang; Shu, Degan (January 2005). "A new arthropod from the Chengjiang Lagerstätte, Early Cambrian, southern China". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 29 (2): 185–194. doi:10.1080/03115510508619300. ISSN 0311-5518. S2CID 129851496.
- ^ Du, Kun‐sheng; Ortega‐Hernández, Javier; Yang, Jie; Zhang, Xi‐guang (June 2019). "A soft‐bodied euarthropod from the early Cambrian Xiaoshiba Lagerstätte of China supports a new clade of basal artiopodans with dorsal ecdysial sutures". Cladistics. 35 (3): 269–281. doi:10.1111/cla.12344. ISSN 0748-3007. PMID 34622993. S2CID 89985331.