King Frederick VI Coast (Danish: Kong Frederik VI Kyst)[1] is a major geographic division of Greenland. It comprises the coastal area of Southeastern Greenland in Sermersooq and Kujalleq municipalities fronting the Irminger Sea of the North Atlantic Ocean.[2] It is bordered by King Christian IX Land on the north and the Greenland Ice Sheet to the west.
King Frederick VI Coast
Kong Frederik VI Kyst | |
|---|---|
 | |
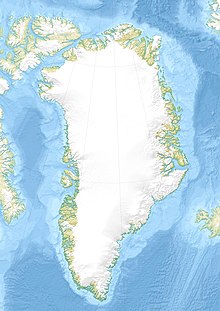
Location of King Frederick VI Coast | |
| Country | Greenland |
| Dimensions | |
| • Length | 590 km (370 mi) |
| Elevation | 800 m (2,600 ft) |
Named after King Frederick VI of Denmark-Norway, the coast stretches for about 590 km (370 mi) south of the Arctic Circle. It is characterized by a succession of short fjords, steep mountains and small coastal islands. There is a narrow belt of ice-free land between the shore and the Inland ice cap, interrupted by active glaciers reaching the shore with the ice limit varying seasonally from year to year. Owing to the movement of pack ice carried by the East Greenland Current and frequent gale-force winds that sweep down from the Greenland ice cap, it is mostly very difficult to approach or navigate along the coast by ship.[3]
History
editThis area was inhabited by Inuit in the past, but in present times King Frederick VI Coast is uninhabited. Numerous coastal islands, including Qulleq, Timmiarmiit, Griffenfeld Island and Skjoldungen, have recent Inuit remains, as well as Paleo-Eskimo or ancient Thule culture sites.[4]
Icelander Gunnbjørn Ulf-Krakason reportedly sighted the eastern coast of Greenland in the 10th century.[5] The inhabitants of the Western Settlement referred to the inhospitable Southeastern Greenland coast as "Ubygder", the unbuilt place.[6] In 1001 Torgils Orrabeinfostre, a legendary Norseman who was shipwrecked in these harsh shores, spent four years trying to reach the Western Settlement.[7]
Later, in the 18th century, Peder Olsen Walløe was the first European known with certainty to have landed on the still uncharted southern part of the coast using local umiak boats. Wilhelm August Graah (1793–1863), a Danish naval officer, was sent by the King of Denmark on an expedition to the little known eastern coast with the purpose to search for the lost Eastern Norse Settlement. Like Walløe, Graah also used local umiaks and mapped parts of the area for the first time, naming the coast "King Frederick VI Coast".[8] He made numerous contacts with the now extinct Southeast-Greenland Inuit during his 1828–30 expedition, describing some of their customs and way of life in the harsh living conditions of the coast.[9][10]
In 1883-85 Gustav Holm and Vilhelm Garde made a more thorough survey of the coast, completing the mapping of the region begun by Graah.[8]
In 1931 Gino Watkins, leader of the 1930-1931 British Arctic Air Route Expedition, together with Percy Lemon and Augustine Courtauld traveled southwards along the little explored King Frederick VI Coast all the way south on a gruesome open boat journey of 600 nautical miles (1,111 km) using two small whaleboats and a kayak. Braving harsh weather conditions, the three boats managed to round Cape Farewell, reaching finally Nanortalik on the western side.[11]
In 1931 Norway claimed sovereignty over a section of the coast between 60°30'N —just north of Nanuuseq, and 63°40'N —just south of Odinland. On 12 July 1932, acting leader Finn Devold was required by the Norwegian government to formally hoist the Norwegian flag at Finnsbu, the main Norwegian station in the area. Following the 1933 resolution of the Permanent Court of International Justice rejecting Norway's claims in Greenland, Finnsbu was abandoned, but the Torgilsbu station continued operation until 1940.[12] A name suggested for the Norwegian territory was Fridtjof Nansen Land, but had not been officially adopted until the court ruling.
Knud Rasmussen visited the coast in 1931, in the course of his Sixth Thule Expedition and again in 1932 and 1933 in the Seventh Thule Expedition, contributing greatly to the cartography of the inner fjords and mountain ranges. He also explored the possibility of establishing a new Greenlandic settlement in the coast, which was by then depopulated.[13]
In 1938 one hundred and fifty Inuit from Ammassalik were convinced by the Danish authorities to settle in Skjoldungen's western shore. For a few years there was a populated place in the King Frederick VI Coast, until 1965 when the inhabitants were relocated and the settlement was abandoned.[14]
Geography
editThe coast extends from Pikiulleq Bay in the north to Cape Farewell in the south. Many sections of the shore area of King Frederick VI Coast are very indented with a succession of fjords and bays, such as Lindenow Fjord (Kangerlussuatsiaq), Paatusoq, Anorituup Kangerlua, Timmiarmiut Fjord, Napasorsuaq Fjord, Bernstorff Fjord and Umivik Bay. There are numerous active glaciers, both at the head of the fjords, as well as protruding into the sea such as Puisortoq, making navigation along the coast dangerous.[8] There are as well many coastal islands, such as Upernattivik, Skjoldungen, Timmiarmiit, Queen Louise Island and Iluileq.
Fjords in the coast form peninsulas between them, the largest of which is Odinland. Most fjords are flanked by steep mountain ranges such as the Graah Mountains and the Kangerluluk Range. The highest point in the coast is the magnificent Mount Paatusoq towering to a height of 2,488 m (8,163 ft) above the glacier at the head of the Paatusoq fjord.[15]
References
edit- ^ "Kong Frederik VI Kyst". Mapcarta. Retrieved 24 April 2016.
- ^ Mills, William J. Exploring Polar Frontiers: A Historical Encyclopedia, Volume 1. p. 349.
- ^ Prostar Sailing Directions 2005 Greenland and Iceland Enroute, p. 99
- ^ "Paleo-Eskimo Sites in Skjoldungen District, South East Greenland". Jensen, Jens Fog. Paleo-Eskimo sites in Skjoldungen District, South East Greenland. Danish Polar Center Publication. Danish Polar Center. 1996. pp. 143–159. ISBN 9788790369026. Retrieved 18 April 2016.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ Spencer Apollonio, Lands That Hold One Spellbound: A Story of East Greenland, 2008 p. 7
- ^ Mikel Vause, Wilderness Tapestry: An Eclectic Approach to Preservation, p. 125
- ^ Clements Markham, G. M. Gathorne Hardy & Fridtjof Nansen. The Norsemen in America: Discussion, The Geographical Journal Vol. 38, No. 6 (Dec., 1911), pp. 575-580
- ^ a b c Spencer Apollonio, Lands that Hold One Spellbound: A Story of East Greenland, p. 34
- ^ Spencer Apollonio, Lands That Hold One Spellbound: A Story of East Greenland, 2008 pp. 29-40
- ^ Einar Lund Jensen, Hans Christian Gulløv, Kristine Raahauge, Cultural Encounters at Cape Farewell: The East Greenlandic Immigrants and the German Moravian Mission in the 19th century. p. 75
- ^ The sea canoeist newsletter - Kiwi Association of Sea Kayakers (KASK)
- ^ Spencer Apollonio, Lands That Hold One Spellbound: A Story of East Greenland, 2008, pp. 188-189
- ^ Spencer Apollonio, Lands That Hold One Spellbound: A Story of East Greenland, 2008 p. 204-214
- ^ "Skjoldungen or the cemetery of shoes". MV FRAM's Expedition Blog. Retrieved 18 April 2016.
- ^ Patuersoq, Greenland