The Karatal (Russian: Каратал, Karatal; Khalkha Mongolian: Хартал Hartal, "Black Steppe"), also known as the Qaratal River (Kazakh: Қаратал, Qaratal), is a river of the Balkhash-Alakol Basin, Kazakhstan. It originates in the Dzungarian Alatau Mountains near the border with China and flows into the endorheic Lake Balkhash. It is the easternmost of two large rivers that flow into the lake; the other is the Ili.[1] The Karatal is one of the main rivers of the historic region of Zhetysu. The river is 390 kilometres (240 mi) long and has a basin area of 19,100 square kilometres (7,400 sq mi).[2]
| Karatal | |
|---|---|
 Satellite image of Karatal river delta as it enters Lake Balkhash, September 1996. The darker areas within the river valley floodplain are areas of irrigation. | |
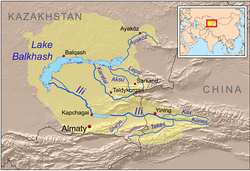 Map of the Lake Balkhash drainage basin | |
| Location | |
| Country | Kazakhstan |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Dzungarian Alatau |
| Mouth | |
• location | Lake Balkhash |
• coordinates | 46°28′31″N 77°13′07″E / 46.47528°N 77.21861°E |
| Length | 390 km (240 mi) |
| Basin size | 19,100 km2 (7,400 sq mi) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Koksu |
The river flows west-southwest from the border with China before turning northwestward south of Taldykorgan and then northward when it reaches the Saryesik-Atyrau Desert, a large sand desert south of Lake Balkhash. The river empties into Lake Balkhash near the centerpoint of its southern side. Karatal freezes up in December and stays icebound until March. Because of irrigation, the river's flow into Lake Balkash is limited.[1]
Description
editThe Karatal is the second largest river after the Ili in the territory of Semirechye. Translated from the Kazakh language, the river is translated as "Black willow".
Fauna
editFrom the South, the river Koksu flows into the Karatal. The river is home to pelicans, several species of ducks, herons, and other birds.
References
edit- ^ a b STS-79 Shuttle Mission Imagery (STS079-781-100) NASA
- ^ Каратал, Great Soviet Encyclopedia