Jean Maritz (1680–1743), also Johan Maritz, was a Swiss inventor, born in Burgdorf, Canton of Bern, who moved to France, becoming "Commissaire des Fontes" at Strasbourg (Commissioner of the King's Foundry),[1] and invented the vertical drilling machine, as well as the horizontal drilling machine for cannons in the 18th century. His inventions revolutionized cannon-making and became a key component of the de Vallière system and contributed to the development of the later Gribeauval system.
Jean Maritz | |
|---|---|
| Born | 1680 |
| Died | 1743 (aged 63) |
| Nationality | Swiss |
| Occupation | Engineer |
| Children | Jean Maritz II |
| Engineering career | |
| Significant design | Vertical drilling machine, horizontal drilling machine for cannons |
| Significant advance | Gun tube boring |
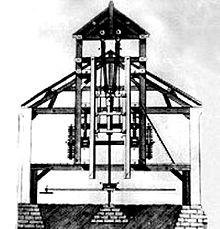

Jean Maritz first invented a vertical drilling machine for cannons while in France in 1713.[2][3] The vertical drilling method however, in which a cannon was slowly lowered over a turning drill, was very delicate, very time consuming and rather imprecise.[4]

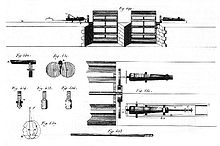

He further developed a method for the horizontal drilling of cannons around 1734.[5][6] These methods involved the drilling of a bore from a solid casting.[5]
These inventions were vast improvements over previous methods, which involved founding the cannon around a clay core, which was removed after founding, leading to imprecision and shifting of the core, and therefore poor performance.[5]


The inventions of Jean Maritz gave perfectly straight bores which could perfectly fit the ball diameter, and therefore vastly increase efficiency.[5] In the horizontal method developed by Maritz, the solid-cast cannon itself was revolved horizontally, while the drill remained static, in a method similar to that of a lathe.[4]
The son of Jean Maritz, Jean Maritz II (1712-1790), who had worked with his father on the development of boring, became Inspector General of Gun Foundries in 1755.[5] He is credited with the innovation of the horizontal boring machine which can be seen in these images[7] https://www.photo.rmn.fr/archive/06-526761-2C6NU0PLJPKE.html https://www.photo.rmn.fr/archive/06-526762-2C6NU0PLJZSL.html
The Maritz method would be central in the development of the Gribeauval cannon.[1][8]
See also
editNotes
edit- ^ a b A Dictionary of Military History and the Art of War by André Corvisier p.331 [1]
- ^ The Pirotechnia of Vannoccio Biringuccio by Vannoccio Biringuccio p.223 [2]
- ^ An Encyclopaedia of the History of Technology by Ian McNeil, p.396
- ^ a b Louis Xv's Navy, 1748-1762 by James S. Pritchard p.151-152
- ^ a b c d e 50 Military Leaders Who Changed the World by William Weir p.132
- ^ The gun-founders of England by Charles Foulkes p.17
- ^ "Réunion des Musées Nationaux-Grand Palais -". www.photo.rmn.fr. Retrieved 2023-12-21.
- ^ Napoleon's Guns, 1792-1815 by René Chartrand, Ray Hutchins p.6