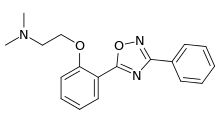
Irampanel (INN, code name BIIR-561) is a drug which acts as a dual noncompetitive antagonist of the AMPA receptor and neuronal voltage-gated sodium channel blocker.[1][2] It was under development by Boehringer Ingelheim for the treatment of acute stroke/cerebral ischemia but never completed clinical trials for this indication.[3][4] Irampanel was also trialed, originally, for the treatment of epilepsy and pain, but these indications, too, were abandoned,[1] and the drug was ultimately never marketed.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H19N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 309.369 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
edit- ^ a b Feigin V (June 2002). "Irampanel Boehringer Ingelheim". Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs. 3 (6): 908–910. PMID 12137411.
- ^ Wang KK, Larner SF, Robinson G, Hayes RL (December 2006). "Neuroprotection targets after traumatic brain injury". Current Opinion in Neurology. 19 (6): 514–519. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e3280102b10. PMID 17102687. S2CID 28119069.
- ^ Sharma SS, Kaundal RK (1 January 2007). "Targeting Molecular Pathways in Stroke". In Ray A, Gulati K (eds.). Current Trends in Pharmacology. I. K. International Pvt Ltd. pp. 321–. ISBN 978-81-88237-77-7.
- ^ Weiser T (April 2005). "AMPA receptor antagonists for the treatment of stroke". Current Drug Targets. CNS and Neurological Disorders. 4 (2): 153–159. doi:10.2174/1568007053544129. PMID 15857300.