Hohenroda is a municipality in Hersfeld-Rotenburg district in eastern Hesse, Germany lying right on the boundary with Thuringia.
Hohenroda | |
|---|---|
Location of Hohenroda within Hersfeld-Rotenburg district 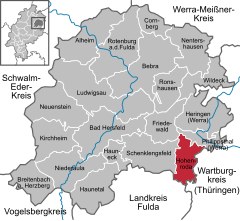 | |
| Coordinates: 50°48′28″N 9°55′22″E / 50.80778°N 9.92278°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Hesse |
| Admin. region | Kassel |
| District | Hersfeld-Rotenburg |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2019–25) | Andre Stenda[1] (Ind.) |
| Area | |
• Total | 35.74 km2 (13.80 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 340 m (1,120 ft) |
| Population (2022-12-31)[2] | |
• Total | 3,099 |
| • Density | 87/km2 (220/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 36284 |
| Dialling codes | 06676 |
| Vehicle registration | HEF |
| Website | www.hohenroda.de |
Geography
editLocation
editThe municipality lies between the Rhön and the Thuringian Forest (ranges) in the so-called Kuppen Rhön. The highest elevation in the Hessian Skittles (a range of volcanic mountains), the Soisberg, stands at the western municipal limits.
The nearest major centres are Bad Hersfeld (some 20 km to the northwest) and Fulda (some 32 km to the southwest).
Neighbouring municipalities
editHohenroda borders in the north on the municipality of Philippsthal (in Hersfeld-Rotenburg), in the east on the municipality of Unterbreizbach, in the southeast on the municipality of Buttlar (both in Thuringia's Wartburgkreis), in the south on the municipality of Eiterfeld (in Fulda district), in the west on the municipality of Schenklengsfeld and in the northwest on the municipality of Friedewald (both in Hersfeld-Rotenburg).
Constituent communities
editHohenroda's districts are Ausbach, Glaam, Mansbach, Oberbreitzbach, Ransbach and Soislieden.
History
editIn 1232, Mansbach had its first documentary mention and is believed to have been bound to the Buchonian knightly order of Mansbach since its founding. Ransbach followed with its first documentary mention in 1254 as a village of the Amt of Landeck.
The Lords of Mansbach built up a half-independent lesser lordly house in which they could take advantage of relations with the neighbouring Hersfeld and Fulda Abbeys and the Landgraves of Hesse.
Mansbach Castle was destroyed by Abbot Bertho IV of Fulda between 1274 and 1286. After it had been built up once again, it was at times in the 14th and 15th centuries a fief or an allodial holding. In 1364, the Mansbachs acquired jurisdiction over the community. In 1662, the Lords of Geyso bought lands from the Mansbachs and built a palatial residence here. Until Mediatization in 1806, the village was claimed by the Fulda Abbey as a territory without Imperial immediacy, although in practice, it consisted of three knightly estates that did have Imperial immediacy.
In the early 20th century, the manufacturer Adolf Hupertz (then also owner of Rieneck Castle) became owner of 1,700 morgen of land between Mansbach, Glaam and Oberbreitzbach. He made a farming estate out of it and named it Hohenroda, which for ever thereafter belonged to the community of Oberbreitzbach. Between 1907 and 1909, Hupertz had himself a manor house with parkland built on the estate. This he called Schloss Hohenroda. When the greater community was founded on 1 February 1972, the estate's and manor house's name was also applied to it. Since 1988, the community's administrative seat has been housed at the old manor house.
Amalgamations
editWith municipal reform, the new community of Hohenroda came into being in 1971 and 1972 through the merger of the communities of Ausbach, Mansbach and Ransbach.
In the leadup to this, Glaam was amalgamated with Ransbach in 1968, while Oberbreitzbach and Soislieden were amalgamated with Mansbach in 1970.
Politics
editCommunity council
editThis section needs to be updated. (July 2021) |
The municipal election held on 26 March 2006 yielded the following results:
| Parties and voter communities | % 2006 |
Seats 2006 |
% 2001 |
Seats 2001 | |
| CDU | Christian Democratic Union of Germany | 21.3 | 5 | 22.6 | 5 |
| SPD | Social Democratic Party of Germany | 65.6 | 15 | 68.9 | 16 |
| FDP | Free Democratic Party | 13.1 | 3 | 8.5 | 2 |
| Total | 100.0 | 23 | 100.0 | 23 | |
| Voter turnout in % | 55.2 | 66.6 | |||
Mayor
editMayor Andre Stenda (independent) was elected to office on 12 May 2013 with 70.7% of the vote.[3]
Coat of arms
editThe community's Coat of arms might be described thus: Gyronny of six gules and argent, six leaves conjoined at the fess point counterchanged.
The six leaves symbolize the merger of the six former communities into the greater community. They are appletree leaves (which is not mentioned in the German blazon), referring to a variety of apple named after the centre of Ausbach, the Ausbacher Roter, which is often still found growing on orchard meadows. The tinctures silver and red come from the arms borne by the Lords of Mansbach, Electorate of Hesse and the community of Ransbach. The gyronny parting – the pattern of parting lines radiating from the escutcheon’s centre – likewise comes from the von Mansbach family’s arms.
Culture and sightseeing
editMuseums
edit- Heimatstube (local history parlour) in the timber-frame wing of the Geyso-Schloss in Mansbach. This is where the coachmen lived-
- Heimatstube in the constituent community of Ausbach
- Museum in Ransbach
- Border documentation post on the former border with East Germany
Buildings
edit- Baroque village church in Mansbach. Oldest parts are to be found in the choir, reassembling stones shaped to demons to shoo away bad forces. Using this foundation, in the 15th century, a gothic tracery was built. The nave origins from renaissance times, used as a castle for the villains. Small windows and thick walls are witnesses. In the late 17th century Christian Bamberger changed the room into what we see still today. There are to galleries, painted with pictures or citing the Holy Bible. The organ was built in late 18th century and is still almost original. The arched wooden ceiling is painted with angels playing baroque instruments and a sun, encircling Jahwes name, written in Hebrew. The church is the first of this type in Hessia.
- Unterhof (Blaues Schloss or Blue Palace) from 1569 (von Mansbach family’s residence)
- Schloss Geyso (1577–1578) in Mansbach
Sonnenuhrgebäude (Renaissance castle, fortified.
- Grasburg (system of pallisades and walls for refugees) near Mansbach (8th century) Celtic origin? But in the war of 1618–1648 people used to fortify hill tops as those to flee the enemy. Archeologic surveys happened in the 1930s. No evidence of every-day-live had been found. The conclusion is, that Grasburg was a hide-away place in time of dangers, that had been fortified. This is according to tales from Schenklengsfeld, a village in the neighborhood, telling villains tried to hide in holes called "Kroatenlöcher"(Croatian mercenaries fought in that war). Trenches and walls can be seen clear on that place, closing in a nearly circular section, one end touching a cliff, the other end allowing a narrow access through a gate.
- Mansbach Jewish graveyard. Mansbach had a flourishing Jewish community. The graveyard is a witness. Some stones were found in a little river, attached to regulate its flow. That stones were brought back to the graveyard.
References
edit- ^ "Ergebnisse der letzten Direktwahl aller hessischen Landkreise und Gemeinden" (XLS) (in German). Hessisches Statistisches Landesamt. 5 September 2022.
- ^ "Bevölkerung in Hessen am 31.12.2022 nach Gemeinden" (XLS) (in German). Hessisches Statistisches Landesamt. June 2023.
- ^ "Bürgermeisterwahl in Hohenroda - Andre Stenda setzt sich im ersten Wahlgang durch". 12 May 2013.
External links
edit(in German)