Epítome de la conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada (English: Summary of the conquest of the New Kingdom of Granada) is a document of uncertain authorship, possibly (partly) written by Spanish conquistador Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada between 1548 and 1559. The book was not published until 1889 by anthropologist Marcos Jiménez de la Espada in his work Juan de Castellanos y su Historia del Nuevo Reino de Granada.
 Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada | |
| Author | disputed possibly (partly) Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada |
|---|---|
| Language | Spanish |
| Subjects | Conquest of the Muisca Descriptions of the Panche Muisca society The role of salt mining History of Colombia |
| Set in | New Kingdom of Granada |
| Published | 1889 |
| Publisher | Marcos Jiménez de la Espada |
Publication date | 1548-1559 (estimated) |
| Publication place | Colombia |
| Pages | 17 |
| Website | Epítome de la conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada (1979 edition) |
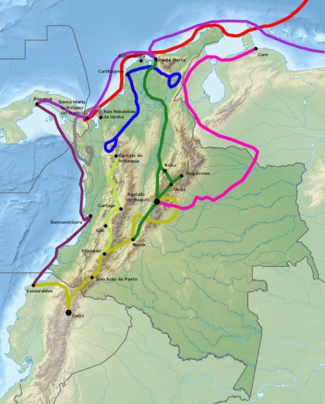
Conquest expedition described in Epítome:
Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada (1536-1539)
Hernán Pérez de Quesada
Juan de San Martín
Juan de Céspedes
Pedro Fernández de Valenzuela
Lázaro Fonte
Antonio de Lebrija
Gonzalo Suárez Rendón
Nicolás de Federman
Sebastían de Benalcázar
Legend:
• Leader - minor captain
Epítome narrates about the Spanish conquest of the Muisca, from the start from Santa Marta in April 1536 to the leave of main conquistador Jiménez de Quesada in April 1539 from Bogotá, arriving to Spain, about "The Salt People" (Muisca) encountered in the conquest expedition in the heart of the Colombian Andes, their society, rules, religion, handling of the dead, warfare and neighbouring "cannibalistic" Panche.
The text has been studied by various authors over the course of the 20th and 21st centuries, mainly by Juan Friede and modern scholars and various theories about authorship and temporal setting have been proposed. The document is held by the National Historical Archive in Madrid, Spain.
Contents
editThe document is written in old Spanish in the present tense and first person with descriptions of Jiménez de Quesada, written as Ximénez de Quesada, in the third person. The margins of the main texts are notes with sometimes difficult to discern text, vagued in time.[1]
The route from the coast to La Tora
editEpítome starts with a description of the Caribbean coastal area where the expedition Spanish conquest of the Muisca started. The author speaks of the Magdalena River, dividing the Spanish provinces of Cartagena to the west and Santa Marta to the east. In the document, the Magdalena River is also called Río Grande, thanks to the great width of the river close to Santa Marta. A description of the journey over the river is given where the heavy and frequent rains made it impossible to disembark the ships (brigantines). According to the Epítome, the Spanish could not ascend further than Sompallón. The distance unit used, is the legua (league), an old and poorly defined unit of distance varying from 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) to 6 kilometres (3.7 mi).[2]
On the second page, the rich golden burial sites of the Zenú are described, as well as the routes inland from later Venezuela, that was conquered by German conquistadors. The next paragraph narrates about the start of the main expedition inland from Santa Marta, leaving the city in the month of April 1536. It is said Gonzalo Ximénez de Quesada left with 600 men, divided into 8 groups of infantry, 10 groups of cavalry and a number of brigs on the Magdalena River. De Quesada and his troops marched over land on the bank of the river. Names of the captains in the army of De Quesada are given as San Martín, Céspedes, Valençuela, Lázaro Fonte, Librixa, de Junco and Suarex. The captains heading the brigs are named as (Francisco Gómez del) Corral, Cardosso and Albarracín. The troops went out of free will and consent of the governor of Santa Marta, Pedro de Lugo. The troops went under command of Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada.[3] The third page describes that the troops spent more than a year and more than 100 leguas on their journey. They reached La Tora [present-day Barrancabermeja], farther than any soldier had gone before, after 150 leguas. The expedition took so long because of the waters and the narrow passages of the surrounding area.[4]
El Camino de la Sal
editFrom La Tora, Jiménez de Quesada sent the ships further upriver, for another 20 leguas, until it became impossible to continue. The indigenous (yndios) here didn't live on the river banks, but on small islands. Because of the impossible trajectory along the river, Jiménez de Quesada agreed to ascend over land "on his left hand", climbing a mountain range that later became known as the Sierras del Opón. The consumption of salt is described as coming from Santa Marta along the river for "70 leguas" and so far from the coast the grainy salt was expensive and only available to the highest social classes. The rest of the salt came from urine or palm trees. Higher up, the salt was different; came in loafs, much like sugar loafs.[4]
The salt of this type was less expensive and the conquistadors concluded that the grainy salt went up the river, while the better salt came from higher altitudes down the river. The indigenous people who carried the salt, told the conquistadors that it was coming from a land of richness. This led the Spanish uphill, on the Camino de la Sal ("The Salt Route") to search for its source. At this point, the Sierras del Opón were crossed and the brigantines returned to the coast, leaving the majority of the soldiers with De Quesada because many of his troops had died already during the expedition. The route over the Sierras del Opón is described as rugged and little populated by natives, a journey of various days and 50 leguas long. In the sparse settlements, the conquistadors found great quantities of the high quality salts and after a while they had crossed the difficult mountainous area, reaching a flatter terrain, described as "what would become the New Kingdom of Granada". It is described that the people of this area were different and also spoke a different language from the people along the Magdalena River and of the Sierras del Opón, making it impossible to understand them at first. Over time, it became possible to communicate and the people in the flatter area, called San Gregorio provided the conquistadors with emeralds.[5] Jiménez de Quesada asked the people where they were coming from and the natives pointed him to the Valle de los Alcázares (Bogotá savanna), upon which the troops headed that way. They encountered a "king" they called Bogothá who gave the conquistadors many golden objects to expel the Spanish from his lands and the indigenous people told the Spanish the emeralds were coming from lands belonging to the "king" of Tunja.[6]
Entering Muisca territory
editThe lands crossing the Sierras del Opón consisted of valleys (on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense), where each valley was ruled by a different person. The valleys were densely populated and around the valleys (to the west) lived indigenous people who were called Panches. They consumed human flesh, while the people from the New Kingdom of Granada (i.e. Muisca, called moxcas) did not perform cannibalism. Also the difference in climate is reported; the Panche lived in warm climates while the Muisca lived in cold or temperate climates. Epítome describes the extent of the New Kingdom as "130 leguas, more or less, long" and "30 leguas, in some parts 20 wide". The Kingdom is divided into two provinces; that of Tunja and of Bogotá (modern names are used). The document describes that the rulers have surnames referring to the terrain and are "very powerful" and have caciques who are subject to their reign. The population is described as approximately "70,000 in the Bogotá area, that is larger" and about "40,000 in the smaller and less powerful Tunja province". The relation between Tunja and Bogotá is described as filled with many and ancient wars. According to the Epítome, the people from the Bogotá area had long-standing wars with the Panche, that lived closer to them than to the people from the Tunja province.[6]
From Funza to Hunza
editsample from Chivor mine
Jiménez de Quesada left Bogotá and went to Coçontá (Chocontá), that he called Valle del Spiritusancto. From there he went to Turmequé in a valley he named Valle de la Trompeta, the first of the Tunja lands.[6] From Turmequé he send his men to discover the emerald mines and after that leaving for another valley, of San Juan, in Muysccubun called Tenesucha and from there to the valley of Somondoco where he spoke to the cacique Sumindoco, who governed the mines or quarries of emeralds and was subject to the gran cacique of Tunja. Many emeralds were extracted. He decided to continue to search for the cacique of Tunja, who was at war with the Christians. The document describes the lands of Tunja as richer than those of Bogotá, although those were already rich, but gold and precious emeralds are more abundant in Tunja. In total 1800 emeralds, large and small were found and De Quesada had never seen so many and precious ones in his life. The rich resources of Peru are described in relation to the mines of Tunja, where the emeralds were more numerous than in Peru. Epítome describes the process of extracting the emeralds with wooden sticks from the veins in the rocks.[7] From the emerald mines of Tunja, he returned to Bogotá.[8]
Reception of the conquistadors by the Muisca
editEpítome de la conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada continues with a description of how the indigenous people received and saw the conquistadors. The people experienced great fears seeing the Spanish, and saw them as children of the deities Sun (Sué) and Moon (Chía). The people believed, according to Epítome, they were sent to punish the people for their sins. Hence they named the Spanish usachíes; a combination of Usa, referring to the Sun and Chíe to the Moon as "children of the Sun and the Moon". The document narrates that the Muisca women climbed the hills surrounding the valleys and threw their infants to the Spanish, some from their breasts, to stop the fury of the gods. It is described that the people very much feared the horses, and only bit by bit got used to them.[7] Epítome says that the people started to attack the Spanish, but were easily beaten because they feared the horses so much and fled. The text describes this as the common practice in the battles of the indigenous people (bárbaros) against the conquistadors during all of 1537 and part of 1538, until they finally bowed to the reign of his Majesty, the King of Spain.[9]
The Panche
editThe description of the Panche is different in Epítome than the Muisca; the Panche are described as a much more war-like people, their rugged terrain worse for the cavalry and the style of warfare different. While the Muisca "fought" using screams and shouting, the Panche are described as fighting silently with slingshots, poisoned arrows and large heavy poles made of palm trees (macanas) swinging them with both hands to hit their enemies. The practice, later described from the Muisca as well, of tieing mummies on their backs is reported from the Panche. The habit is described as showing what will happen to their opponents; fighting like they fought and to instigate fear in the enemy.[9] Of the Panche is described that when they won their battles, they celebrated their victory with festivities, took the children of their enemies to sacrifice them, captured the women and killed the men by poking out the eyes of the combat leaders. The combat of the Panche is described as fiercer as of the Muisca and the combatants walked naked. They had tubes made of animal skins where they held the lances and bow and arrows to shoot. The Panche warriors are described as eating the flesh of their enemies at the battlefield or later at home with their wives and children. The process of treaties is described as performed not by the men, but by the women, as "they cannot be refused".[10]
Descriptions of society
editThe people, and especially the women, from the New Kingdom are described as highly religious and beautiful in faces and body shapes; less brown than "the other indigenous that we have seen". The women wore white, black and colourful dresses that covered their bodies from breast to feet instead of the capes and mantles seen with other natives (Yndias). On their heads they wore garlands (guirnaldas) of cotton, decorated with flowers.[10] The caciques wore hats (bonetes) made of cotton. The wives of the caciques wore a type of kofia on their heads. The climate and daytime is described as roughly the same all year round and the architecture of the houses as made of wood. The houses of the caciques are located behind various circular posts, described in Epítome as "a labyrinth of Troy". The houses were surrounded by large patios and painted walls.[11]
Cuisine
editThe cuisine of the Muisca is described as mainly consisting of maize and yuca, with other food coming from farther away. Plantation of the various tubers was arranged in multiple ways. The infinite supply of salt is described in Epítome, extracted from wells on the Bogotá savanna [in Zipaquirá, Nemocón and other places] and made into loafs of salt. The salt was traded up until the north, the Sierras del Opón and until the Magdalena River, as earlier described. The meat of the people consisted of deer, that is described to have been in great quantities, "like livestock in Spain". Other meat were rabbits, also in large quantities, and named fucos. Epítome names those "rabbits" also existed in Santa Marta and other parts, where they were called curíes (guinea pigs). Poultry is named as pigeons and ducks, that are raised in the many lakes. The diet is supplied further with fish, described as only one species and small, "only one or two handpalms long", but of a good taste.[11]
Penalties, position of caciques and marriage
editThe penal system of the Muisca is described as "moral" and of "medium reason", because the offenses are punished "very well". Epítome describes "there are more gallows than in Spain" with people hanging between two posts with arms, feet and hair attached to them. The Muisca are described as cutting hands, noses and ears for "not so serious crimes". Shaming happened to the higher social classes, where hair and pieces of the clothing were cut. The respect for the caciques is told to have been "enormous", as the people didn't look them in the face and when a cacique enters, the people turned and inclined showing him their backs. When the "Bogothá" (zipa) spit, the people caught his saliva in cotton bowls, to prevent it from hitting the ground.[12]
When the people were marrying, the men are reported to not organise festivities, but simply take the women home. Polygamy is noted; "the men could marry as many women as they wanted, given that they could maintain them"; so some had ten wives and others twenty. Of the "Bogothá" is stated that "he had more than 400 wives". Marrying first degree relatives was forbidden and in some parts second degree marriages too. Heritage of rule was not the sons of the former cacique, but the siblings and if they didn't have or lived, the sons of the brother or sister of the deceased cacique.[12]
Time-keeping and preparation for young caciques
editsketch by Alexander von Humboldt
The conscience of time is specified as years and months well divided, with during the first ten days of the months a habit of eating coca (hayo). The next ten days are for working the farmfields and houses. The last ten days are described as time when people rest and the women live separately from the men; all the women together in one bohío and every man in his own.[12] It is reported that in other parts of the New Kingdom of Granada, the division of time is different; the described ten day periods are longer and two months of the year are reserved for fasting (quaresma).[13]
To prepare for the cacicazgo, the young boys and girls are held solitary in houses for some years, depending on the role they will fulfill in society. They are incarcerated for seven years in small spaces without a view of the Sun and given delicacies at certain times. Only the people caring for the children are allowed access to the space and they torture them. After their imprisonment, the children are allowed to wear golden jewels; nosepieces and earrings. The people are also described as wearing breast plates, golden mitres (mitras) and bracelets. Epítome reports the people lost themselves in music, singing and dances, one of their greatest pleasures. The author calls the people "lying very much, they never tell the truth". The goldworking and weaving by the Muisca is described as "the first not as well as the people from New Spain and the second not as well as the people from Peru".[13]
Religion, sacrifice and warfare
editThe religion of the Muisca is reported as very important and they constructed in each settlement a temple, with many others scattered across the area, accessible by roads and isolated. The sacred places are lavishly adorned with gold and emeralds. The process of sacrifices is described as happening with blood, water and fire. Birds are killed and their blood runs over the temples, their heads hanging from the sides of the holy places. Water running through pipes also is used as a sacrifice. Fire and aromatic smoke is used in the temples, too. The religious rituals are reported to be accompanied with singing.[13]
It is described the Muisca did not sacrifice humans for religious purposes, yet in two other ways. When the Panche were beaten, the boys who were presumed still being virgin were taken and sacrificed. The ritual passed with screams and the heads of the victims were hanged on the posts of their bohíos. The other way would be to sacrifice the young boys by priests [chyquy] near the temples.[14]
Epítome reports the young boys called moxas, taken from a place called Casa del Sol at thirty leguas from the New Kingdom. They are carried on the shoulders and stay seven to eight years in the temples to be sacrificed afterwards. The process is described as cutting their heads off and letting the blood flow over the sacred sites. The boys have to be virgins, as if they are not, their blood is not considered pure enough to serve as sacrifice. Before going to war, the guecha warriors are described to stay one month in a temple, with people outside singing and dancing and the Muisca honouring Sué and Chía. The warriors sleep and eat little during this time. After the battles, the people perform the same ritual for various days and when the warriors are defeated, they also do this to lament the losses.[14]
During these rituals, the people are described to burn certain herbs, called Jop (yopo) and Osca (hosca; tobacco) in Epítome, inhaling the smoke and putting those herbs on the joints of their bodies. When certain joints are moving it would be a sign of luck in warfare and when others move, it means bad luck.[14]
The sacred sites of the Muisca consist of forests and lakes, according to Epítome, where the people bury gold and emeralds and throw those precious resources in the lakes. The people do not cut the trees of the sacred woods but bury their dead there. The Sun and Moon are considered husband and wife and are celebrated as the creators of things. Apart from that, the people have various other gods, "much like our [Spanish] saints", honoured in temples throughout the area. On top of that, the people all have personal idols, called in Epítome Lares (tunjos). They are described as small figures made of fine gold with emeralds in their bellies. It is described the people wore those on their arms and when going to battle, having them in one hand and the weapons in the other, "especially in the province of Tunja where the people are more religious."[15]
The dead and afterlife
editThe dead, as reported in Epítome de la conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada, are buried in two ways; in Tunja the main members of society are not buried, yet their intestines taken out, wrapped in cloths, and adorned with gold and emeralds placed on slightly elevated beds in special dedicated bohíos and left there forever.[15] The other way of treating the deceased Muisca is in Bogotá, where they are buried or thrown into the deepest lakes after putting them in coffins filled with gold and emeralds.[16]
The ideas about the afterlife of the Muisca is described as "barbaric" and "confused" in terms of the immortality of the soul. The people who have been good in life would have great pleasures and rest after their death, while those who were bad during their lifetime would have a lot of work and be punished with lashes. The guecha who died in warfare and the women dying when giving birth would have access to the same right of rest and pleasures, "although they were bad in life".[16]
In contrast to the spiritual life of the Muisca, the Panche are described as immoral, as they only care about their crimes and vices. Epítome narrates they do not care about gold or other precious things of life, yet only about war, pleasure and eating human flesh, the only reason to invade the New Kingdom. In other parts of the Panche territories, "close to Tunja across two fast flowing rivers", it is noted that the people eat ants and make bread of the insects. The ants (hormiga culona, still a delicacy in Santander) are described as available in great quantities, some small, but mostly large. The people of the region kept them as livestock enclosed by large leaves.[16]
Return to Spain of the conquest leaders
editThe period of conquest of the New Kingdom of Granada is reported in Epítome to have taken most of 1538. This period resulted in the creation of three main cities; the province of Bogotá in the city of "Santa Fee", the province of Tunja in the city with the same name and the later founded city of Vélez, where the conquistadors entered afterwards. The conquest is said to have been completed in the year 1539, when Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada ("El Licenciado") returned to Spain to report to the King and claim his rewards. Epítome describes that Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada left the reign of the New Kingdom in the hands of his brother, Hernán Pérez de Quesada, and traveled along the Magdalena River (Río Grande) using brigs to not have to cross the strenuous Sierras del Opón again, the way he reached Bogotá.[17]
It is described that "one month before this leave" from Venezuela came Nicolás Fedreman [sic], captain under Jorge Espira, governor of the province of Venezuela for the Germans, with news about natives from very rich lands. He brought 150 men with him. During the same period, some fifteen days later, came from Peru Sebastián de Venalcázar, captain under Francisco Pizarro, and brought 100 soldiers and the same news. The three commanders laughed about their three years so close to each other. Epítome describes that Jiménez de Quesada took all of the soldiers of De Federman and half of those of De Benalcázar to refresh his troops and sent them to the settlements of the New Kingdom to populate the area. The other half of De Benalcázar's men he sent (back) to the province between the New Kingdom and Quito, called Popayán, of which De Benalcázar was governor. Federmann and some of his men accompanied De Quesada in his journey along the Magdalena River to the coast and back to Spain. Epítome reports they arrived there in November 1539, when the Spanish King was crossing France to reach Flanders.[17]
On the last page of Epítome it is said that the Licenciado had differences of opinion with Alonso de Lugo, married to Beatriz de Noroña, sister of María de Mendoza, wife of the great commander De Léon. The disagreements were about the reign over the New Kingdom, because De Lugo and his son had the governance over Santa Marta. It is described that his [sic] Majesty created a Royal Chancillery in the year 1547 [sic] with oídores in charge of the New Kingdom. The name of the New Kingdom of Granada was given by Jiménez de Quesada based on the Kingdom of Granada "here" (in Spain), that showed similiraties in size, topography and climate.[18]
The text notes that Jiménez de Quesada received for his efforts of conquering and populating the New Kingdom the title Mariscal and 2000 ducats for him and his descendants for the reign of the New Kingdom. For the natives of the New Kingdom another 8000 ducats were provided as well as an annual fee of 400 ducats for the mayor of Bogotá.[18]
The closing paragraph of Epítome de la conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada concludes with the description of the family of Jiménez de Quesada as son of Gonçalo Ximénez and Ysabel de Quesada, living in the city of Granada and originating from Córdoba.[18]
Source for Muysccubun
editThe Epítome de la conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada contains a number of words transcribed or taken from Muysccubun.[19] Examples are moscas (muysca),[20] Bogotá (Muyquyta),[21] Tunja (Chunsa),[22] Sumindoco,[19] uchíes; combination of u- (Sun) and chíe (Moon),[23][24] fucos (fuquy),[25] yopo, Osca (hosca),[26] and yomas (iome; Solanum tuberosum).[27] The word written as hayo probably refers to the Ika word hayu.[19]
Inconsistencies
editColombian-Jewish-Ukrainian scholar Juan Friede (1901-1990) has listed inconsistencies that were analysed by Enrique Otero D'Costa in the document:[28]
- Epítome describes the death of Pedro Fernández de Lugo, governor of Santa Marta, during the preparation of the conquest expedition, while this happened months after De Quesada had left Santa Marta[29]
- Alonso Luis de Lugo is named as the acting governor, while he left the government in 1544[29]
- The achievements of Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada are described as mariscal, regidor and 2000 ducats in rent, events that didn't happen until 1547 and 1548[29]
- The existence of the Royal Audience (Audiencia Real) is described, that took place in 1550[29]
Friede compared the work Gran Cuaderno by Jiménez de Quesada and concluded the descriptions were identical. Gran Cuaderno was handed over to Gonzalo Fernández de Oviedo y Valdés, who included the contents in his Historia general y natural de las Indias of 1535 (expanded, from his notes, in 1851).[30][31]
Theories about authorship
editEpítome has produced a number of reviewing articles, books and other texts since the first publication by Jiménez de la Espada in 1889. Enrique Otero D'Costa has attributed parts of Epítome to Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada, written in 1539, and other parts to other people, unrelated to the conquistador.[29] Friede concludes these errors not definitive; he maintains the Epítome de la conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada is written in its totality in the years 1548 to 1549, when Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada was in Spain.[31] Researcher Fernando Caro Molina concluded in 1967 that only minor parts were written by Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada.[32]
Carmen Millán de Benavides wrote an article in 2014, a book in 2001, and her PhD thesis about the document in 1997.[33] She concludes the work is written by Alonso de Santa Cruz (1505-1567), cosmographer who worked for the kings Carlos II and Felipe II.[34] She describes the Epítome as a fragmentary text, not a narrative.[35] The abbreviations used in the text, led her to conclude it was a scribble text, not meant for direct publication.[36]
Manuel Lucena Salmoral wrote in an article in 1962 that the document was written by an unknown writer, none of the authors suggested by other researchers.[37] Also Javier Vergara y Velasco maintains the document is written entirely by someone else.[38]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Ramos Pérez, 1972, p.283
- ^ Epítome, p.81
- ^ Epítome, p.82
- ^ a b Epítome, p.83
- ^ Epítome, p.84
- ^ a b c Epítome, p.85
- ^ a b Epítome, p.87
- ^ Epítome, p.86
- ^ a b Epítome, p.88
- ^ a b Epítome, p.89
- ^ a b Epítome, p.90
- ^ a b c Epítome, p.91
- ^ a b c Epítome, p.92
- ^ a b c Epítome, p.93
- ^ a b Epítome, p.94
- ^ a b c Epítome, p.95
- ^ a b Epítome, p.96
- ^ a b c Epítome, p.97
- ^ a b c (in Spanish) Epítome - Muysccubun Dictionary Online
- ^ (in Spanish) muysca - Muysccubun
- ^ (in Spanish) Muyquyta - Muysccubun
- ^ (in Spanish) Chunsa - Muysccubun
- ^ (in Spanish) sua - Muysccubun
- ^ (in Spanish) chíe - Muysccubun
- ^ (in Spanish) fuquy - Muysccubun
- ^ (in Spanish) hosca - Muysccubun
- ^ (in Spanish) iome - Muysccubun
- ^ (in Spanish) Descubrimiento del Nuevo Reino de Granada y Fundación de Bogotá - Epítome de la conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada - Juan Friede - Banco de la República
- ^ a b c d e Friede, 1960, p.93
- ^ Fernández de Oviedo y Valdés, Gonzalo (1851) [1535]. José Amador de los Ríos (ed.). Historia general y natural de las Indias. Madrid: La Real Academia de la Historia. Retrieved 2020-07-15 – via Miguel de Cervantes Virtual Library.
- ^ a b Friede, 1960, p.94
- ^ Caro Molina, 1967, p.130
- ^ Millán de Benavides, 2014, p.11
- ^ Millán de Benavides, 2014, p.14
- ^ Millán de Benavides, 2014, p.15
- ^ Caro Molina, 1967, p.117
- ^ Millán de Benavides, 2001, p.27
The work
edit- "Epítome de la conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada", Boletín Cultural y Bibliográfico, 16 (3), Banco de la República: 81–97, 1979 [1889 (1539)], retrieved 2016-12-21
Bibliography
edit- Caro Molina, Fernando (1967), Epítome de la Conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada - Reseña (PDF), Cervantes Institute, pp. 116–130, retrieved 2016-12-21
- Friede, Juan (1960), "Quién fué el autor del "Epítome de la conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada"?", Boletín Cultural y Bibliográfico, 3 (2), Banco de la República: 93–96, retrieved 2016-12-21
- Millán de Benavides, Carmen (2014), "Epítome de la conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada", Universitas Humanística, 48 (48), Pontifical Xavierian University: 11–17, ISSN 2011-2734, retrieved 2016-12-21
- Millán de Benavides, Carmen (2001), Epítome de la conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada la cosmografía española del siglo XVI y el conocimiento por cuestionario, Centro Editorial Javeriano, pp. 1–139, ISBN 9586833682, retrieved 2016-12-21
- Ramos Pérez, Demetrio (1972), Ximénez de Quesada en su relación con los cronistas: y el Epítome de la conquista del Nuevo Reino de Granada, CSIC, pp. 1–329, ISBN 9788400020774, retrieved 2016-12-21
Other works about the conquest
edit- Jiménez de Quesada, Gonzalo (1576), Memoria de los descubridores, que entraron conmigo a descubrir y conquistar el Reino de Granada (in Spanish), retrieved 2016-12-21
- De Castellanos, Juan (1857) [1589], Elegías de varones ilustres de Indias (in Spanish), pp. 1–567, retrieved 2016-12-21
- Simón, Pedro (1892) [1626], Noticias historiales de las conquistas de Tierra Firme en las Indias occidentales (1882-92) vol.1-5 (in Spanish), retrieved 2016-12-21
- Rodríguez Freyle, Juan; Achury Valenzuela, Darío (1979) [1859 (1638)], El Carnero - Conquista i descubrimiento del nuevo reino de Granada de las Indias Occidentales del mar oceano, i fundacion de la ciudad de Santa Fe de Bogota (PDF) (in Spanish), Fundacion Biblioteca Ayacuch, pp. 1–598, retrieved 2016-12-21
- Fernández de Piedrahita, Lucas (1688), Historia general de las conquistas del Nuevo Reino de Granada (in Spanish), retrieved 2016-12-21
- Acosta, Joaquín (1848), Compendio histórico del descubrimiento y colonización de la Nueva Granada en el siglo décimo sexto - Historical overview of discovery and colonization of New Granada in the sixteenth century, Paris: Beau Press, pp. 1–460, OCLC 23030434, retrieved 2016-12-21