Elemgasem (after a Tehuelche god of the same name) is an extinct genus of brachyrostran abelisaurid from the Late Cretaceous Portezuelo Formation of Patagonia, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, Elemgasem nubilus. The cladistic position of Elemgasem within Brachyrostra is uncertain, given that phylogenetic analyses recover it as either a sister taxon to Furileusauria or in several positions within this clade.[1]
| Elemgasem Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
| |
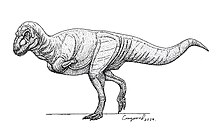
| Hypothetical life restoration based on relatives | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Abelisauridae |
| Clade: | †Brachyrostra |
| Genus: | †Elemgasem Baiano et al., 2022 |
| Species: | †E. nubilus
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Elemgasem nubilus Baiano et al., 2022
| |
Discovery and naming
editThe Elemgasem holotype specimen, MCF-PVPH-380, was discovered in 2002 in layers of the Sierra del Portezuelo locality of the Portezuelo Formation, about 20 kilometres (12 mi) west of Cutral Có, Neuquén Province, Argentina. The holotype consists of partial axial and appendicular elements, including cervical and caudal vertebrae, right femur, left tibia, right and left fibula, left astragalus-calcaneum, metatarsals, and various pedal phalanges.[1]
In 2022, Baiano et al. described Elemgasem as a new genus and species of brachyrostran abelisaurid. The generic name, "Elemgasem", references a Tehuelche deity of the same name; according to mythology, Elemgasem is the owner of animals and father of the southern viscacha with the power to petrify others and himself, as well as the inhabitant of the mountains and sky. The specific name, "nubilus", means "foggy day" in Latin, in reference to the unusual foggy climate during the expedition that discovered the Elemgasem holotype.[1]
Pathology
editThe holotype tail vertebrae of Elemgasem demonstrate spondyloarthropathy (vertebral joint disease), representing the first case this has been observed in a non-tetanuran theropod, and the second case in a non-avian theropod.[2]
Paleoenvironment
editElemgasem is known from the Portezuelo Formation of Argentina. Named taxa recovered from the formation include the theropod dinosaurs Megaraptor, Patagonykus, Neuquenraptor, Pamparaptor, and Unenlagia, the sauropod dinosaurs Futalognkosaurus, Malarguesaurus, and Baalsaurus, and the azhdarchoid pterosaur Argentinadraco. Other fossils belonging to ornithopod dinosaurs, neornithines, turtles, and crocodiles have also been found in the formation.[1]
References
edit- ^ a b c d Baiano, Mattia A.; Pol, Diego; Bellardini, Flavio; Windholz, Guillermo J.; Cerda, Ignacio A.; Garrido, Alberto C.; Coria, Rodolfo A (2022-09-05). "Elemgasem nubilus: a new brachyrostran abelisaurid (Theropoda, Ceratosauria) from the Portezuelo Formation (Upper Cretaceous) of Patagonia, Argentina". Papers in Palaeontology. 8 (5): e1462. Bibcode:2022PPal....8E1462B. doi:10.1002/spp2.1462. S2CID 252097368.
- ^ Baiano, Mattia A.; Cerda, Ignacio A.; Bertozzo, Filippo; Pol, Diego (2024-01-31). "New information on paleopathologies in non-avian theropod dinosaurs: a case study on South American abelisaurids". BMC Ecology and Evolution. 24 (1): 6. Bibcode:2024BMCEE..24....6B. doi:10.1186/s12862-023-02187-x. ISSN 2730-7182. PMC 10829224. PMID 38291378.