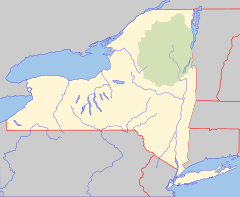
East Kill, a 16-mile-long (26 km)[2] tributary of Schoharie Creek, flows across the town of Jewett, New York, United States, from its source on Stoppel Point. Ultimately its waters reach the Hudson River via the Mohawk. Since it drains into the Schoharie upstream of Schoharie Reservoir, it is part of the New York City water supply system. East Kill drains the southern slopes of the Blackhead Mountains, which include Thomas Cole Mountain, Black Dome, and Blackhead Mountain, the fourth-, third-, and fifth-highest peaks in the Catskills, respectively.
| East Kill | |
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | New York |
| Region | Catskill Mountains |
| County | Greene |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • coordinates | 42°13′50″N 74°04′29″W / 42.2306434°N 74.0748589°W[1] |
| Mouth | Schoharie Creek |
• location | Jewett Center |
• coordinates | 42°14′11″N 74°19′09″W / 42.2364758°N 74.3190350°W[1] |
• elevation | 1,381 ft (421 m)[1] |
| Length | 16 mi (26 km)[2] |
| Basin size | 36.3 sq mi (94 km2)[3] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Jewett Center |
| • minimum | 0.84 cu ft/s (0.024 m3/s) |
| • maximum | 28,400 cu ft/s (800 m3/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | East Kill → Schoharie Creek → Mohawk River → Hudson River → Upper New York Bay |
| Tributaries | |
| • right | Halsey Brook, Roaring Brook, Pasture Brook |
The East Kill's 36.3-square-mile (94 km2)[3] watershed accounts for 3.9 percent of the Schoharie basin and is located near the southern end of that creek's watershed.
Course
editEast Kill begins as a mountainous stream dropping approximately 780 feet (240 m) in its first mile, then reduces in slope to dropping about 200 feet (61 m) over the next mile. The remainder of the creek drops to an average slope of 42 feet (13 m) per mile until it reaches its confluence with Schoharie Creek.
East Kill begins on the northwestern slopes of Stoppel Point and begins flowing northwestward, then soon curves to the west. It continues west for a short distance, then flows into Colgate Lake, a 29-acre (12 ha) lake. It exits the lake then passes by the East Kill Valley Church, as it continues along the road. It soon recei ves Halsey Brook from the north, which drains the southwestern slopes of Black Dome and the southeastern slopes of Thomas Cole Mountain, the third and fourth of the Catskill High Peaks respectively. The creek then curves northward, passes through East Jewett, then curves back west. It then soon reaches Camp Beecher, where it curves north and begins to parallel State Route 296. After a short distance it curves back west and crosses under State Route 296. It soon receives Roaring Brook from the north, which drains part of the southern slope of Cave Mountain. East Kill then soon turns to the southwest, and soon converges with Schoharie Creek in Jewett Center.
Watershed
editThe East Kill's 36.25-square-mile (93.9 km2) watershed, is mostly located within the town of Jewett, with a few small sections entering into the towns of Windham, Ashland, and Lexington.[2] East Kill drains some of the highest slopes in the Catskills, including the Blackhead Mountains. The Blackhead Mountain range includes Thomas Cole Mountain, Black Dome, and Blackhead Mountain, the fourth-, third-, and fifth-highest peaks in the Catskills, respectively. The highest point in the East Kill watershed is 3,948 feet (1,203 m) at the summit of Black Dome Mountain in southeast Jewett. The average elevation of the watershed is approximately 2,674 feet (815 m).[2]
Within the watershed, the predominant land cover is undeveloped forested area, at 20,808 acres (32.513 sq mi) or 90 percent of the watershed. About 2.5 percent of the watershed is developed and the remaining 7.5 percent is shrubland. Water covers 104 acres (42 ha); the National Wetlands Inventory maintained by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service has identified 168 separate wetlands within the East Kill watershed, totaling 311 acres (126 ha), including all open water. About 84.5 percent of the total acreage is palustrine wetlands such as marshes and swamps.
History
editWhen settlers first arrived in the East Kill Valley, they frequently encountered bears, wolves, and other dangerous wildlife. This caused many of the first settlers to only stay in the area for a short time. A man by the name of John Godsell, known as Uncle John by the locals, was an expert trapper along the creek, who killed between 40 and 50 wolves in the East Kill Valley. One wolf he tied up and tried to bring to the nearby town of Cairo, in order to get a larger bounty. The wolf died before Godsell was able to reach Cairo.[4]
From the late 1700s to early 1800s, the local economy thrived on the sale of hemlock bark, which was used to tan leather. The local industry later shifted to logging as lumber demands rose in the area. When the majority of the forests were cleared, dairy farms became the dominant economic revenue in the East Kill valley.[4]
Geology
editWhile the Catskills originated during the Devonian period, around 375 million years ago, as a former river delta uplifted and became a dissected plateau, the East Kill's valley was formed during the recent effects of the Wisconsin glaciation, which ended about 12,000 years ago. Meltwater fed many streams, which eventually formed today's East Kill.[5]
Lodgement till, which is a very dense, clay-rich, and reddish brown deposit, is very frequent in the East Kill and upper Schoharie Creek watersheds. The extreme density is distinguished from the looser assemblage of mixed sediment that comprises melt-out till found in moraines and along mountain sides. The presence of bedrock banks in the East Kill can represent natural limits to changes in the stream channel system. Examples of this are shown in the headwater waterfalls.[5]
Hydrology
editDischarge
editThe East Kill's watershed receives an average 44 inches (1,100 mm) of precipitation annually, making it one of the wettest areas of the Catskills. Most of the precipitation is concentrated in seasonal events such as summer thunderstorms, remnants of hurricanes later in the year, or rain-on-snow events in springtime. The average slope of the watershed is 17.3 percent. Drainage density, or how much stream length is available to carry water off the landscape, is slightly higher than average streams in the Catskills. The high average drainage density, steep slopes, and high precipitation causes flash floods during storm events. However, most of the watershed lies within forests that tend to mitigate this somewhat.[2]
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) maintains one stream gauge along East Kill. The station is located on Mill Hollow Road, 1.3 miles (2.1 km) northeast of Jewett Center, had a maximum discharge of 28,400 cubic feet (800 m3) per second on August 28, 2011, as Hurricane Irene passed through the area, and a minimum discharge of 0.84 cubic feet (0.024 m3) per second on August 13, 1997.[6]
Water quality
editNYSDEC performed a study of the creek in 2005 and 2006, showed that overall water quality was good. Also it showed that aquatic life was normal in the stream, and that there were no other water quality impacts to recreational uses. In the past, there has excessive stream bank erosion along the creek. However the East Kill does not seem to be as prone to sediment and turbidity problems like other Schoharie Creek tributaries in the area. However, sediment load from East Kill, along with West Kill and Batavia Kill, have been the principal contributors of sediment and turbidity in the Schoharie Reservoir.[7]
DEC rates the water quality of the stream as Class C, suitable for fishing and non-contact human recreation. The agency also adds a "(TS)", indicating that the stream's waters are ideal for trout spawning. The kill's waters are pure enough to be part of the New York City water supply system; after draining into the Schoharie they are impounded at Schoharie Reservoir downstream, where they can be delivered through the Shandaken Tunnel to Esopus Creek at Shandaken. From there they go to Ashokan Reservoir, which supplies 10 percent of the city's water, and then, via the Catskill Aqueduct, to customers, without requiring filtration.[7]
Flood control
editIn 2006, a combined effort of the Greene County Soil and Water Conservation District and the DEP resulted in a management plan for East Kill. The stream was subdivided into 11 sections from its source to the mouth and inventoried in great detail. Issues of concern for habitat and flood management were identified and recommendations made.[8]
After a January 1996 flood that damaged areas along the creek, certain sections had to be reconstructed. One section was by the Farber Farm to prevent damage from future floods. The reconstruction projects also improved aquatic and riparian habitats, and improved water quality. Then in 2011, a project was performed to repair aggradation upstream of the Vista Ridge bridge, and fix where the creek changed its course closer towards Colgate Lake road. The project protected the road, and planted native trees and shrubs to reduce erosion and prevent future flood damage.[9]
Fishery
editThe East Kill is mostly a cold water stream, which provides suitable water temperatures for organisms, such as brook trout, which require water less than 72 °F (22 °C). Roughly 2,700 brown trout are stocked annually along the creek from the mouth to just downstream of Colgate Lake. Upstream of this point the kill has a sufficient wild trout population which makes stocking unnecessary. The wild trout population is primarily brown trout to Harriman Lake, and primarily brook trout upstream of Harriman Lake. Fish communities were analyzed in 2000, 2002 and 2003, they showed that in addition to brown trout and brook trout, creek chub, common shiner, pumpkinseed, bluegill, white sucker, stone roller, cutlips minnow, and marginated madtom were present in the creek. Despite the kill being a cold water fishery, largemouth bass which is warm-water species were found often during a 2006 study. The largemouth bass were stocked or escaped into the stream from adjacent ponds.[10]
To provide fishing access, DEC has acquired public fishing rights from local landowners in addition to those short stretches where it already owns land adjoining the kill. On the lower stream, these include both sides of the creek from the mouth to Roaring Brook.[11] Located along the kill within the Colgate Lake Wild Forest, is Colgate Lake. The lake is a popular year-round lake for trout, of which 750 brown trout from 8 to 15 inches (20 to 38 cm) in length are stocked each year. The Lake is also popular for kayaking and has six campsites.[12]
References
edit- ^ a b c "East Kill". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved May 3, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e "East Kill Watershed Description". www.gcswcd.com. Greene County Soil & Water Conservation District. Retrieved 3 May 2020.
- ^ a b "East Kill at Mouth". usgs.gov. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- ^ a b "Watershed History" (PDF). Catskill Streams. Retrieved May 3, 2020.
- ^ a b "Upper Schoharie Creek watershed Geology (including East Kill) Watershed" (PDF). Catskill Streams. Retrieved May 3, 2020.
- ^ "USGS 01349700 EAST KILL NEAR JEWETT CENTER NY". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 3 May 2020.
- ^ a b "WI/PWL Fact Sheets - Schoharie/East Kill Watershed (0202000501)" (PDF). New York State Department of Environmental Conservation. December 13, 2007. Retrieved May 3, 2020.
- ^ "Introduction to Management Unit Descriptions and Recommendations" (PDF). New York State Department of Environmental Conservation. 2006. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
- ^ "East Kill Restoration Projects". Greene County Soil & Water Conservation District. 2020. Retrieved May 7, 2020.
- ^ "Fisheries & Wildlife" (PDF). Catskill Streams. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
- ^ "Public Fishing Rights Maps – Schoharie Creek" (PDF). New York State Department of Environmental Conservation. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
- ^ "Colgate Lake Wild Forest". New York State Department of Environmental Conservation. Retrieved May 5, 2020.