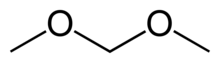
Dimethoxymethane, also called methylal, is a colorless flammable liquid with a low boiling point, low viscosity and excellent dissolving power. It has a chloroform-like odor and a pungent taste. It is the dimethyl acetal of formaldehyde. Dimethoxymethane is soluble in three parts water[clarification needed] and miscible with most common organic solvents.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dimethoxymethane | |
| Other names
Formal
Formaldehyde dimethyl ether | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1697025 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.378 |
| EC Number |
|
| 100776 | |
| MeSH | Dimethoxymethane |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1234 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 76.095 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] |
| Odor | Chloroform-like[1] |
| Density | 0.8593 g cm−3 (at 20 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | −105 °C (−157 °F; 168 K)[1][3] |
| Boiling point | 42 °C (108 °F; 315 K)[1][3] |
| 33% (20 °C)[2][clarification needed] | |
| Vapor pressure | 330 mmHg (20 °C)[2] |
| −47.3·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H225, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | −18 °C (0 °F; 255 K) |
| Explosive limits | 2.2–13.8%[2] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
5708 mg/kg (rabbit, oral)[4] |
LC50 (median concentration)
|
18000 ppm (mouse, 7 hr) 15000 ppm (rat) 18354 ppm (mouse, 7 hr)[4] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1000 ppm (3100 mg/m3)[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1000 ppm (3100 mg/m3)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
2200 ppm[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Related Ethers
|
Dimethoxyethane |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Synthesis and structure
editIt can be manufactured by oxidation of methanol or by the reaction of formaldehyde with methanol. In aqueous acid, it is hydrolyzed back to formaldehyde and methanol.
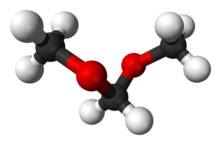
Due to the anomeric effect, dimethoxymethane has a preference toward the gauche conformation with respect to each of the C–O bonds, instead of the anti conformation. Since there are two C–O bonds, the most stable conformation is gauche-gauche, which is around 7 kcal/mol more stable than the anti-anti conformation, while the gauche-anti and anti-gauche are intermediate in energy.[5] Since it is one of the smallest molecules exhibiting this effect, which has great interest in carbohydrate chemistry, dimethoxymethane is often used for theoretical studies of the anomeric effect.
Applications
editIndustrially, it is primarily used as a solvent and in the manufacture of perfumes, resins, adhesives, paint strippers and protective coatings. Another application is as a gasoline-additive for increasing octane number. Dimethoxymethane can also be used for blending with diesel. [6]
Reagent in organic synthesis
editAnother useful application of dimethoxymethane is to protect alcohols with a methoxymethyl (MOM) ether in organic synthesis. Dimethoxymethane can be activated with phosphorus pentoxide in dichloromethane or chloroform.[7] This method is preferred to the use of chloromethyl methyl ether (MOMCl). Phenols can also be MOM-protected using dimethoxymethane, p-toluenesulfonic acid.[8] Alternatively, MOMCl can be generated as a solution by treating dimethoxymethane with an acyl chloride in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst like zinc bromide:
- MeOCH2OMe + RC(=O)Cl → MeOCH2Cl + RC(=O)(OMe)).
Unlike the classical procedure, which uses formaldehyde and hydrogen chloride as starting materials, the highly carcinogenic side product bis(chloromethyl) ether is not generated.[9]
References
edit- ^ a b c d e Merck Index, 11th Edition, 5936
- ^ a b c d e f NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0396". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b International Chemical Safety Card 1152
- ^ a b "Methylal". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Carey, Francis A.; Sundberg, Richard J. (2007). Advanced organic chemistry (5th ed.). New York: Springer. ISBN 9780387448978. OCLC 154040953.
- ^ Shrestha, Krishna P.; Eckart, Sven; Elbaz, Ayman M.; Giri, Binod R.; Fritsche, Chris; Seidel, Lars; Roberts, William L.; Krause, Hartmut; Mauss, Fabian (2020). "A comprehensive kinetic model for dimethyl ether and dimethoxymethane oxidation and NO interaction utilizing experimental laminar flame speed measurements at elevated pressure and temperature". Combustion and Flame. 218: 57–74. doi:10.1016/j.combustflame.2020.04.016. hdl:10754/662921.
- ^ Wuts, P. G. M.; Greene, T.W. (2006). Greene's Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis. NY: J. Wiley. doi:10.1002/0470053488. ISBN 9780470053485.
- ^ Yardley, John P.; Fletcher, Horace (1976). "Introduction of the Methoxymethyl Ether Protecting Group". Synthesis. 1976 (04): 244–244. doi:10.1055/s-1976-24000.
- ^ Berliner, Martin; Belecki., Katherine (2007). "Synthesis of alpha-Halo Ethers from Symmetric Acetals and in situ Methoxymethylation of an Alcohol". Organic Syntheses. 84: 102. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.084.0102.
External links
edit- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0396". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).