The deep auricular artery is a branch of the maxillary artery. The deep auricular artery pierces the external acoustic meatus. It provides arterial supply to the skin of the external acoustic meatus, and contributes arterial supply to the tympanic membrane, and (via a branch) the temporomandibular joint.[1]
| Deep auricular artery | |
|---|---|
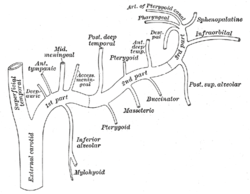 Plan of branches of internal maxillary artery. (Label "Deep auric." visible at upper left.) | |
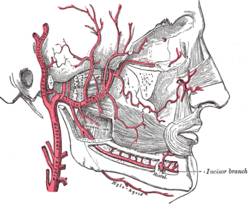 Plan of branches of internal maxillary artery. (Deep auricular visible but not labeled.) | |
| Details | |
| Source | maxillary artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria auricularis profunda |
| TA98 | A12.2.05.054 |
| TA2 | 4423 |
| FMA | 49689 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Anatomy
editOrigin
editIt is a branch of the (mandibular part of) the maxillary artery.[1] It often arises in common with the anterior tympanic artery.[citation needed]
Course
editIt ascends[2] in the substance of the parotid gland, behind the temporomandibular articulation,[citation needed] and pierces the cartilaginous or bony wall of the external acoustic meatus[1] to course between the cartilage and bone.[2]
Distribution
editIt supplies its cuticular lining and the outer surface of the tympanic membrane.[citation needed]
It gives a branch to the temporomandibular joint.[1]
References
editThis article incorporates text in the public domain from page 560 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b c d Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. p. 1464. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). Elsevier Australia. p. 363. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
External links
edit- lesson4 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (infratempfossaart)