Crinum americanum is an aquatic angiosperm native to North America from Texas to South Carolina, as well as Mexico, Cuba, Jamaica and the Cayman Islands.[3] Common names for this species include Florida swamp-lily,[4] string lily,[4] and southern swamp crinum.[4] The species grows in small groups in still water habitats.
| Crinum americanum | |
|---|---|

| |
| American Crinum | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Order: | Asparagales |
| Family: | Amaryllidaceae |
| Subfamily: | Amaryllidoideae |
| Genus: | Crinum |
| Species: | C. americanum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Crinum americanum | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
Crinum species are now members of the family Amaryllidaceae, subfamily Amaryllidoideae;[5] they were formerly placed in the family Liliaceae.
Etymology
editThe Latin specific epithet americanum refers to the plant's native habitat.[6]
Description
editCrinum americanum is a perennial bulb that can grow up to 4 ft (1.2 m) tall.[7] The plant has simple leaves that are up to 4 ft (1.2 m) long and 3 in (7.6 cm) wide.[8] Flowers are fragrant and lily-like with white petals that can sometimes be blushed pink in color.[6] The flower stem grows up to 3 ft (0.91 m) tall and has two to six flowered umbels.[8] The upper portion of the stamen is purple and anthers are also purple in color.[8]
Distribution and habitat
editIt is native to North America from Texas to South Carolina, as well as Mexico, Cuba, Jamaica and the Cayman Islands.[3] It grows in freshwater marshes, cypress swamps, and lake edges.[8]
Conservation
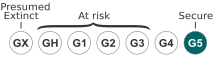
editAs of November 2024, NatureServe listed Crinum americanum as Secure (G5). This status was last reviewed on 4 August 1988.[1]
References
edit- ^ a b "Crinum americanum | NatureServe Explorer". NatureServe Explorer. Retrieved 3 November 2024.
- ^ "The Plant List: A Working List of All Plant Species". Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- ^ a b "Crinum americanum L. | Plants of the World Online | Kew Science". Plants of the World Online. Retrieved 2024-10-16.
- ^ a b c "Crinum americanum". Germplasm Resources Information Network. Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- ^ Chase, M.W.; Reveal, J.L. & Fay, M.F. (2009), "A subfamilial classification for the expanded asparagalean families Amaryllidaceae, Asparagaceae and Xanthorrhoeaceae", Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 161 (2): 132–136, doi:10.1111/j.1095-8339.2009.00999.x
- ^ a b "Crinum americanum - Plant Finder". www.missouribotanicalgarden.org. Retrieved 2024-10-16.
- ^ "Crinum americanum (Crinum Lily, Florida Swamp-Lily, Seven Sisters, Southern Swamp Lily, String Lily) | North Carolina Extension Gardener Plant Toolbox". plants.ces.ncsu.edu. Retrieved 2024-10-15.
- ^ a b c d "Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center - The University of Texas at Austin". www.wildflower.org. Retrieved 2024-10-16.