This article needs additional citations for verification. (October 2022) |
Choluria (or bilirubinuria) is a symptom defining an abnormal darkness of the urine, mainly due to a high level of conjugated bilirubin. [1][2] Choluria is a common symptom of liver diseases, such as hepatitis and cirrhosis. It can be described as dark or brown urine, often referred to as the color of Coca-Cola. The presence of choluria is a useful symptom to distinguish if somebody presenting with jaundice has liver disease (direct hyperbilirubinaemia) or haemolysis (indirect hyperbilirubinaemia). In the first case, patients have choluria due to excess conjugated ("direct") bilirubin in blood, which is eliminated by the kidneys. Haemolysis, on the other hand, is characterized by unconjugated ("indirect") bilirubin, which is not water-soluble and is bound to albumin, and thus not eliminated in urine.[citation needed]
| Choluria | |
|---|---|
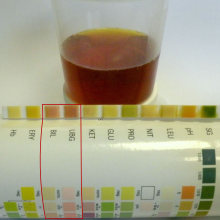 | |
| Choluria. Urine test strip shows a high levels of the bilirubin and urobilinogen. | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Choluria"
- ^ World Health Organization (2022). "MF91 Bilirubinuria". International Classification of Diseases, eleventh revision – ICD-11. Genova – icd.who.int.