Changbhakar State, also known as Chang Bhakar, was one of the small princely states of British Empire in India in the Chhattisgarh States Agency.[1] It included 117 villages and had an area of 2,330 square kilometres (899 sq mi) with a 1941 population of 21,266 people. Bharatpur was the capital of the princely state.
| Changbhakar State चंगभाकर रियासत | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Princely State of British India | |||||||
| c. 1790–1948 | |||||||
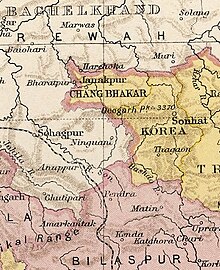 Changbhakar State in the Imperial Gazetteer of India | |||||||
| Capital | Bharatpur | ||||||
| Area | |||||||
• 1901 | 2,347 km2 (906 sq mi) | ||||||
| Population | |||||||
• 1901 | 19,548 | ||||||
| History | |||||||
• Established as a zamindari of Korea State | 12 November 1790 | ||||||
| 1948 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Today part of | Koriya district, Chhattisgarh | ||||||
| Columbia-Lippincott Gazetteer. (New York: Columbia University Press, 1952) p. 369 | |||||||
History
editIn 1790 Changbhakar zamindari or estate was carved out of Korea State. After the Anglo-Maratha war in the early nineteenth century, Changbhakar became a tributary state of British India. Changbhakar estate was recognized as a state in 1819 and placed under the Chota Nagpur Tributary States in 1821. In October 1905, it was brought under the control of the Commissioner of Chhattisgarh division of Central Provinces. It acceded to the Union of India on 1 January 1948 and was placed under Surguja district of Central Provinces and Berar. Presently it is a Subdivision and a Tehsil of Koriya district of Chhattisgarh state.[2]
Rulers
editThe rulers were Rajputs of the Chauhan dynasty. They had been formerly addressed as 'Raja', but from 1865 they used the title of 'Bhaiya'.
- 1819 - 18.. Man Singh Deo
- 1848 - 1865 Janjit Singh Deo
- 1 Dec 1865 - 1897 Balabhadra Singh Deo (b. c.1825 - d. ... )
- 1897 - 1932 Mahabir Singh Deo (b. 1879 - d. 1932)
- 1932 - 1947 Krishna Pratap Singh Deo
- 1932 - 1946 ... -Regent
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Princely State of Changbhakar". Princely States of India.
- ^ "Changbhakar (Princely State)". IndianRajputs.com.
External links
edit23°44′N 81°49′E / 23.733°N 81.817°E