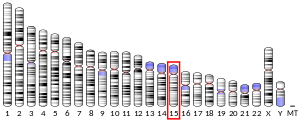
CatSper2, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CATSPER2 gene.[5][6] CatSper2 is a member of the cation channels of sperm family of protein. The four proteins in this family together form a Ca2+-permeant ion channel specific essential for the correct function of sperm cells.[7]
Function
editCalcium ions play a primary role in the regulation of sperm motility. This gene belongs to a family of putative cation channels that are specific to spermatozoa and localize to the flagellum. The protein family features a single repeat with six membrane-spanning segments and a predicted calcium-selective pore region. This gene is part of a tandem repeat on chromosome 15q15; the second copy of this gene is thought to be a pseudogene.[8]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000166762 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000033486 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Quill TA, Ren D, Clapham DE, Garbers DL (October 2001). "A voltage-gated ion channel expressed specifically in spermatozoa". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 (22): 12527–31. Bibcode:2001PNAS...9812527Q. doi:10.1073/pnas.221454998. PMC 60087. PMID 11675491.
- ^ Clapham DE, Garbers DL (December 2005). "International Union of Pharmacology. L. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of CatSper and two-pore channels". Pharmacol. Rev. 57 (4): 451–4. doi:10.1124/pr.57.4.7. PMID 16382101. S2CID 35096827.
- ^ *"CatSper and Two-Pore Channels: Introduction". IUPHAR Database of Receptors and Ion Channels. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. Archived from the original on 2012-09-05. Retrieved 2008-12-16.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: CatSper2".
Further reading
edit- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2002). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Zhang D, Chen J, Saraf A, et al. (2006). "Association of Catsper1 or -2 with Ca(v)3.3 leads to suppression of T-type calcium channel activity". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (31): 22332–41. doi:10.1074/jbc.M511288200. PMID 16740636.
- Garbers DL (2001). "Ion channels. Swimming with sperm". Nature. 413 (6856): 579, 581–2. Bibcode:2001Natur.413..579G. doi:10.1038/35098164. PMID 11595929. S2CID 6099942.
- Quill TA, Ren D, Clapham DE, Garbers DL (2001). "A voltage-gated ion channel expressed specifically in spermatozoa". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 (22): 12527–31. Bibcode:2001PNAS...9812527Q. doi:10.1073/pnas.221454998. PMC 60087. PMID 11675491.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Clapham DE, Garbers DL (2005). "International Union of Pharmacology. L. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of CatSper and two-pore channels". Pharmacol. Rev. 57 (4): 451–4. doi:10.1124/pr.57.4.7. PMID 16382101. S2CID 35096827.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.