Cardamine concatenata, the cutleaved toothwort, crow's toes, pepper root or purple-flowered toothwort, is a flowering plant in the family Brassicaceae. It is a perennial woodland wildflower native to eastern North America.[4]
| Cardamine concatenata | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Brassicales |
| Family: | Brassicaceae |
| Genus: | Cardamine |
| Species: | C. concatenata
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cardamine concatenata | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
|
Homotypic Synonyms
Heterotypic Synonyms
| |
Description
editCardamine concatenata is a member of the Cardamine concatenata alliance, a distinctive group of species that includes Cardamine angustata, Cardamine concatenata, Cardamine diphylla, Cardamine dissecta, Cardamine incisa, and Cardamine maxima. Members of the alliance are morphologically similar, with an elongated fleshy rhizome and either ternate or palmately compound leaves.[5]
The vegetative parts of this plant, which can reach 20–40 cm, arise from a segmented rhizome. The leaves are on long petioles, deeply and palmately dissected into five segments with large "teeth" on the margins. The white to pinkish flowers are held above the foliage in a spike. Fruit is an elongated pod which can be up to 4 cm long.[6][7]
Taxonomy
editCardamine concatenata was first described as Dentaria concatenata by the French botanist André Michaux in 1803.[8][9] Otto Karl Anton Schwarz placed Dentaria concatenata Michx. in genus Cardamine in 1939.[2] The name Cardamine concatenata (Michx.) O.Schwarz is widely used today.[3][10]
Cardamine concatenata is a member of the Cardamine concatenata alliance, a group of species that includes Cardamine angustata, Cardamine concatenata, Cardamine diphylla, Cardamine dissecta, Cardamine incisa, and Cardamine maxima.[5] Members of the alliance were previously placed in genus Dentaria Tourn. ex L., which is now considered to be a synonym for Cardamine L.[11] The alliance is strongly supported as a monophyletic group, which is consistent with the strong morphological resemblance among the species.[12]
Distribution and habitat
editCardamine concatenata, like all members of the Cardamine concatenata alliance, is native to eastern North America. It has the widest distribution of any member of the alliance, with a range that extends north to Québec and Ontario, south to Florida and Texas, and west to Kansas and Oklahoma.[5] It is known to occur in the following provinces and states:[3][13]
- Canada: Ontario, Québec
- United States: Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, Delaware, District of Columbia, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Vermont, Virginia, West Virginia, Wisconsin
In the eastern United States where the distribution of Cardamine concatenata is widespread, it occurs in most of the counties of Missouri, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio.[14] It occupies rich deciduous forest habitats such as rich woods, wooded bottomlands, limestone outcrops, and rocky banks and bluffs.[6]
Ecology
editCardamine concatenata blooms from February to May.[10] It serves as a host plant for the imperiled butterfly Pieris virginiensis.[15]
Conservation
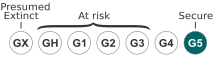
editThe global conservation status of Cardamine concatenata is secure (G5).[1]
Uses
editThe roots can be washed, chopped and ground in vinegar to be used as a horseradish substitute.[7] According to Hussey (1974), "the Indians ate the pungent root."[16]
References
edit- ^ a b "Cardamine concatenata". NatureServe Explorer. NatureServe. Retrieved 10 June 2023.
- ^ a b "Cardamine concatenata (Michx.) O.Schwarz". International Plant Names Index (IPNI). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew; Harvard University Herbaria & Libraries; Australian National Botanic Gardens. Retrieved 9 June 2023.
- ^ a b c "Cardamine concatenata (Michx.) O.Schwarz". Plants of the World Online. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 9 June 2023.
- ^ "Plants Profile for Cardamine concatenata (cutleaf toothwort)". plants.usda.gov. Retrieved 2018-10-10.
- ^ a b c Sweeney & Price (2001), p. 82.
- ^ a b "Cardamine concatenata". Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Retrieved 13 June 2023.
- ^ a b Elias, Thomas S.; Dykeman, Peter A. (2009) [1982]. Edible Wild Plants: A North American Field Guide to Over 200 Natural Foods. New York: Sterling. p. 81. ISBN 978-1-4027-6715-9. OCLC 244766414.
- ^ "Dentaria concatenata Michx.". International Plant Names Index (IPNI). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew; Harvard University Herbaria & Libraries; Australian National Botanic Gardens. Retrieved 9 June 2023.
- ^ Michaux (1803), p. 30.
- ^ a b Al-Shehbaz, Ihsan A.; Marhold, Karol; Lihová, Judita (2010). "Cardamine concatenata". In Flora of North America Editorial Committee (ed.). Flora of North America North of Mexico (FNA). Vol. 7. New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press. Retrieved 9 June 2023 – via eFloras.org, Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, MO & Harvard University Herbaria, Cambridge, MA.
- ^ "Dentaria Tourn. ex L.". Plants of the World Online. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 9 June 2023.
- ^ Sweeney & Price (2000), p. 476.
- ^ "Cardamine concatenata". State-level distribution map from the North American Plant Atlas (NAPA). Biota of North America Program (BONAP). 2014. Retrieved 10 June 2023.
- ^ "Cardamine concatenata". County-level distribution map from the North American Plant Atlas (NAPA). Biota of North America Program (BONAP). 2014. Retrieved 10 June 2023.
- ^ "NatureServe Explorer 2.0". explorer.natureserve.org. Retrieved 2023-07-05.
- ^ Hussey, Jane Strickland (Jul–Sep 1974). "Some Useful Plants of Early New England". Economic Botany. 28 (3): 311–337. doi:10.1007/BF02861428. JSTOR 4253521. S2CID 12764441.
Bibliography
edit- Gilman, Arthur V. (2015). New Flora of Vermont. Memoirs of The New York Botanical Garden, Volume 110. Bronx, New York, USA: The New York Botanical Garden Press. ISBN 978-0-89327-516-7.
- Haines, Arthur (2011). New England Wild Flower Society's Flora Novae Angliae: A Manual for the Identification of Native and Naturalized Higher Vascular Plants of New England. Illustrated by Elizabeth Farnsworth and Gordon Morrison. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-17154-9.
- Michaux, André (March 1803). Flora Boreali-Americana. Vol. 2. Paris and Strasbourg. Retrieved 13 June 2023.
- Sweeney, Patrick W.; Price, Robert A. (2000). "Polyphyly of the Genus Dentaria (Brassicaceae): Evidence from trnL Intron and ndhF Sequence Data". Systematic Botany. 25 (3): 468–478. doi:10.2307/2666690. JSTOR 2666690. Retrieved 14 June 2023.
- Sweeney, Patrick W.; Price, Robert A. (2001). "A multivariate morphological analysis of the Cardamine concatenata alliance (Brassicaceae)". Brittonia. 53 (1): 82–95. Bibcode:2001Britt..53...82S. doi:10.1007/BF02805400. Retrieved 9 June 2023.
- Weakley, Alan S.; Southeastern Flora Team (2022). "Flora of the southeastern United States". University of North Carolina Herbarium, North Carolina Botanical Garden.
External links
edit- Missouri Plants: Dentaria laciniata
- "Cardamine concatenata — cut-leaved toothwort". Go Botany. Native Plant Trust. Retrieved 10 June 2023.
- "Cardamine concatenata (Michaux) O.Schwarz". Flora of the Southeastern United States (2023 Edition). Retrieved 10 June 2023.