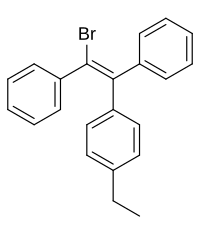
Broparestrol (INN) (brand names Acnestrol, Longestrol; former developmental code name LN-107), also known as α-bromo-α,β-diphenyl-β-p-ethylphenylethylene (BDPE), is a synthetic, nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group[1] that has been used in Europe as a dermatological agent and for the treatment of breast cancer.[2][3][4][5][6] The drug is described as slightly estrogenic[7] and potently antiestrogenic,[8][9] and inhibits mammary gland development and suppresses prolactin levels in animals.[10] It is structurally related to clomifene and diethylstilbestrol.[6][10] Broparestrol is a mixture of E- and Z- isomers (LN-1643 and LN-2299, respectively), both of which are active, and are similarly antiestrogenic but, unlike broparestrol, were never marketed.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Acnestrol, Longestrol |
| Other names | LN-107; α-Bromo-α,β-diphenyl-β-p-ethylphenylethylene; BDPE |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Selective estrogen receptor modulator |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H19Br |
| Molar mass | 363.298 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Hospital M, Busetta B, Courseille C, Precigoux G (1975). "X-ray conformation of some estrogens and their binding to uterine receptors". Journal of Steroid Biochemistry. 6 (3–4): 221–5. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(75)90136-3. PMID 171486.
- ^ a b Elks J (14 November 2014). "Broparestrol". The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 183–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ^ Milne GW (8 May 2018). "Broparestrol". Drugs: Synonyms and Properties: Synonyms and Properties. Taylor & Francis. pp. 1401–1402. ISBN 978-1-351-78989-9.
- ^ "Broparestrol". Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 139–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ^ Muller (19 June 1998). European Drug Index: European Drug Registrations (Fourth ed.). CRC Press. pp. 23–. ISBN 978-3-7692-2114-5.
- ^ a b Morton IK, Hall JM (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 56–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- ^ Villee CA, Hagerman DD (April 1957). "Compounds with antiestrogenic activity in vitro". Endocrinology. 60 (4): 552–558. doi:10.1210/endo-60-4-552. PMID 13414683.
- ^ Al-Hassan, Mohammed I. (1987). "Synthesis of broparestrol using palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling". Journal of Organometallic Chemistry. 321 (1): 119–121. doi:10.1016/0022-328X(87)80330-3. ISSN 0022-328X.
- ^ Magarian RA, Overacre LB, Singh S, Meyer KL (1994). "The medicinal chemistry of nonsteroidal antiestrogens: a review". Current Medicinal Chemistry. 1: 61-104 (95). doi:10.2174/0929867301666220210212635. S2CID 89392480.
- ^ a b Drosdowsky M, Edery M, Guggiari M, Montes-Rendon A, Rudali G, Vives C (May 1980). "Inhibition of prolactin-induced mammary cancer in C3Hf (XVII) mice with the trans isomer of bromotriphenylethylene". Cancer Research. 40 (5): 1674–1679. PMID 6245799.