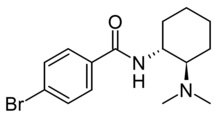
Bromadoline (U-47931E)[1] is an opioid analgesic selective for the μ-opioid receptor[2] developed by the Upjohn company in the 1970s.[3] The drug has a potency lying between that of codeine and morphine, being slightly stronger than pentazocine.[4] Bromadoline is related to AH-7921 and U-47700.[5]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Bromadoline |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H21BrN2O |
| Molar mass | 325.250 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Unlisted Drugs. Vol. 34–35. Chatham: Pharmaceutical Section, Special Libraries Association. 1982. p. 392. ISBN 978-0-913210-13-0.
- ^ Hayes AG, Skingle M, Tyers MB (March 1987). "Evaluation of the receptor selectivities of opioid drugs by investigating the block of their effect on urine output by beta-funaltrexamine". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 240 (3): 984–8. PMID 3559988.
- ^ Jacob Szmuszkovicz (4 July 1978). "Patent US4098904 - Analgesic N-(2-aminocycloaliphatic)benzamides". The Upjohn Company.
- ^ Hayes AG, Sheehan MJ, Tyers MB (August 1987). "Differential sensitivity of models of antinociception in the rat, mouse and guinea-pig to mu- and kappa-opioid receptor agonists". British Journal of Pharmacology. 91 (4): 823–32. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11281.x. PMC 1853585. PMID 2822190.
- ^ Cheney BV, Szmuszkovicz J, Lahti RA, Zichi DA (December 1985). "Factors affecting binding of trans-N-[2-(methylamino)cyclohexyl]benzamides at the primary morphine receptor". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 28 (12): 1853–64. doi:10.1021/jm00150a017. PMID 2999404.