Benexate (BEX) is an anti-ulcer agent used in the treatment of acid-related disorders. It is unique in its inability to form salts that are both non-bitter and soluble.[1][2]
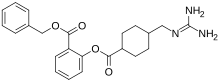 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H27N3O4 |
| Molar mass | 409.486 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Medical uses
editBenexate is approved from treatment of gastric ulcer in Japan.[3]
Mechanism of action
editThe mechanism of action of benexate involves promotion of prostaglandin synthesis, protein secretion, and blood flow stimulation in the gastrointestinal tract.[4]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Hori Y, Odaguchi K, Jyoyama H, Yasui K, Mizui T (1996). "Differential effect of benexate hydrochloride betadex on prostaglandin levels in stomach and inflammatory sites in rats". Japanese Journal of Pharmacology. 72 (2): 183–190. doi:10.1254/jjp.72.183. PMID 8912919.
- ^ Muranushi N, Yoshida M, Kinoshita H, Hirose F, Fukuda T, Doteuchi M, Yamada H (1998). "Studies of benexate CD: effect of inclusion compound formation on the antiulcer activity of benexate, the effective ingredient of benexate CD". Folia Pharmacologica Japonica (91): 377–383.
- ^ "Benexate". Inxight Drugs. National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
- ^ Lee JM, Lim J, Kim Y, Kim YJ, Choi HS, Kim ES, Keum B, Seo YS, Jeen YT, Lee HS, Um SH, Kim CD, Ryu HS, Sul D, Hong J, Chun HJ (2016). "Benexate hydrochloride betadex modulates nitric oxide synthesis and cytokine expression in gastric ulcers". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 12 (2): 573–580. doi:10.3892/etm.2016.3384. PMC 4950842. PMID 27446246.
Further reading
edit- Rui Tamura, Mikiji Miyata, ed. (2015). Advances in Organic Crystal Chemistry: Comprehensive Reviews 2015 (1st ed.). Springer Japan. doi:10.1007/978-4-431-55555-1. ISBN 978-4-431-55554-4. S2CID 93141904.