Amidoamines are a class of chemical compounds that are formed from fatty acids and amines. They are used as intermediates in the synthesis of surfactants, such as cocamidopropyl betaine (CAPB), some of which are used in personal care products including soaps, shampoos, and cosmetics. Amidoamines can also serve as curing agents for epoxy resins.[1][2][3] They are also used as oil well drilling fluids and also as corrosion inhibitors.[4]
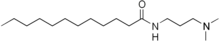
Patch test studies have concluded that most apparent allergic reactions to products containing CAPB are more likely due to amidoamine than to CAPB itself.[5][6]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "AMIDOAMINES – Epochemie – Epoxy Curing Agents". www.epochemie.com. Retrieved 2018-08-20.
- ^ "Amidoamines". www.hexion.com. Retrieved 2018-08-20.
- ^ "ChemCure® Amidoamines | Cargill". www.cargill.com. Retrieved 2018-08-20.
- ^ "Amido Amine - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics". www.sciencedirect.com. Retrieved 2021-05-24.
- ^ Fowler JF, Fowler LM, Hunter JE (1997). "Allergy to cocamidopropyl betaine may be due to amidoamine: a patch test and product use test study". Contact Dermatitis. 37 (6): 276–81. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1997.tb02464.x. PMID 9455630. S2CID 7933812.
- ^ Foti C, Bonamonte D, Mascolo G, Corcelli A, Lobasso S, Rigano L, Angelini G (2003). "The role of 3-dimethylaminopropylamine and amidoamine in contact allergy to cocamidopropylbetaine" (PDF). Contact Dermatitis. 48 (4): 194–198. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0536.2003.00078.x. PMID 12786723. S2CID 9944011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-02-19.
External websites
edit