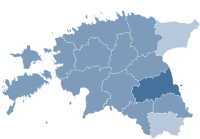
A referendum took place on 14 September 2003 to decide whether Estonia should join the European Union (EU). Just over two-thirds of voters voted Yes and Estonia joined the EU on 1 May 2004.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
Are you in favor of joining the European Union and adopting amendments to the Constitution of the Republic of Estonia? | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Results | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
Background
editMembership of the European Union was one of the main objectives of Estonian foreign policy since independence in 1991. Estonia was invited to begin negotiations to join the EU in 1997 and was formally invited to join at a summit in Copenhagen in December 2002.[1] The Parliament of Estonia then announced that a referendum on membership of the EU would be held in mid September 2003.[2]
Referendum question
editThe question to be voted on in the referendum was agreed by the Government of Estonia in December 2002.[3] It was:
Are you in favour of the accession to the European Union and passage of the Act on Amendments to the Constitution of the Republic of Estonia?[4]
Campaign
editOpinion polls in the first half of 2003 showed only lukewarm support for membership. This persuaded leading politicians including President Arnold Rüütel, Prime Minister Juhan Parts and the Speaker of Parliament Ene Ergma to start campaigning hard for a Yes vote.[5]
The economy was one of the main issues used by both sides in the referendum campaign. Supporters of joining the EU said that it would fuel growth and create more jobs, while opponents said that EU entry would slow the growth of the Estonian economy. Opponents also argued that Estonia should not go straight from one union, the Soviet Union, into the EU.[6]
The Yes campaign had strong media, political and financial backing with the Estonian Centre Party being the only leading party against entry into the EU.[5] Posters for the Yes campaign predominated, with one poster handed out by the Res Publica Party calling for Estonians to vote Yes 'for access to millions of sexier men'.[7][8] As the vote neared, polls showed increasing support for the Yes camp with one poll showing 70% support for EU entry.[9]
Results
edit| Choice | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| For | 369,657 | 66.83 | |
| Against | 183,454 | 33.17 | |
| Total | 553,111 | 100.00 | |
| Valid votes | 553,111 | 99.51 | |
| Invalid/blank votes | 2,724 | 0.49 | |
| Total votes | 555,835 | 100.00 | |
| Registered voters/turnout | 867,714 | 64.06 | |
| Source: EU Referendum 2003 | |||
References
edit- ^ "Timeline: Estonia". BBC Online. 2009-08-05. Retrieved 2008-02-10.
- ^ "Stockholm sets euro vote question". BBC Online. 2002-12-18. Retrieved 2008-02-10.
- ^ "Estonian parliament to hold EU referendum". Ireland On-Line. 2002-12-18. Archived from the original on 2013-02-18. Retrieved 2008-02-10.
- ^ "EU Referendum 2003: Information". Estonian National Electoral Committee. Retrieved 2008-02-10.
- ^ a b "EU Referendum New". City Paper. Archived from the original on July 5, 2007. Retrieved 2008-02-10.
- ^ "Estonians Say "Jah" to the EU". Deutsche Welle. 2003-09-15. Retrieved 2008-02-10.
- ^ "Estonia expects EU yes vote". BBC Online. 2003-09-14. Retrieved 2008-02-10.
- ^ Cecil, Clem (2003-09-15). "Estonia endorses 'sexy men' of EU". The Times. London. Retrieved 2008-02-10.[dead link]
- ^ "Estonian support for EU entry rises to 70 percent". Gateway To Russia. 2003-09-02. Retrieved 2008-02-10.[permanent dead link]