Yuanjiang Hani, Yi and Dai Autonomous County (Chinese: 元江哈尼族彝族傣族自治县; pinyin: Yuánjiāng Hānízú Yízú Dǎizú Zìzhìxiàn; Hani: Lalsa Haqniqssaq Haqhholssaq Aqcaoqssaq Ziiqziifxeif) is a county of south-central Yunnan province, People's Republic of China. The county seat is the town of Lijiang (澧江镇), while the county itself is under the administration of Yuxi City. It derives its name from the Red River (Asia),[2] which is known as the Yuan River (元江) in Yunnan, and is an important provincial crossroads for access to Southeast Asia.
Yuanjiang
元江县 · Lalsa xeif | |
|---|---|
元江哈尼族彝族傣族自治县 Lalsa Haqniqssaq Haqhholssaq Aqcaoqssaq Ziiqziifxeif Yuanjiang Hani, Yi and Dai Autonomous County | |
Cityscape of county town Lianchi Park Main hall of Maiolian Temple Yuanjiang Conference center Red River Large Bridge | |
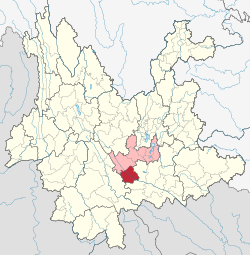 Location of Yuanjiang County jurisdiction (red) within Yuxi City (pink) and Yunnan | |
| Coordinates (Yuanjiang government): 23°35′46″N 101°59′53″E / 23.596°N 101.998°E | |
| Country | China |
| Province | Yunnan |
| Prefecture-level city | Yuxi |
| County seat | Lijiang Subdistrict |
| Area | |
• Total | 2,858 km2 (1,103 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 396 m (1,299 ft) |
| Population (2020 census)[1] | |
• Total | 195,647 |
| • Density | 68/km2 (180/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 653300 |
| Area code | 0877 |
| Website | www |
Administrative divisions
editYuanjiang Hani, Yi and Dai Autonomous County has 3 subdistricts, 2 towns and 5 townships.[3]
- 3 subdistricts
- 2 towns
- 5 townships
Climate
editDue to its location at the bottom of a deep mountainous river valley, Yuanjiang lies at the junction of two different climate types, namely the tropical savanna climate (Köppen Aw) and, uniquely for China, the hot subtype of a semi-arid climate (Köppen Bsh). There are two main seasons: a dry season lasting from late November to early April, with mostly warm and dry weather (and the occasional cold snap) and the wet season covering May through September. The coolest month is December, which averages 18.7 °C (65.7 °F), and the hottest is June, at 30.2 °C (86.4 °F).
| Climate data for Yuanjiang, elevation 401 m (1,316 ft), (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1971–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 35.2 (95.4) |
37.0 (98.6) |
39.2 (102.6) |
40.9 (105.6) |
44.1 (111.4) |
41.7 (107.1) |
41.6 (106.9) |
40.1 (104.2) |
39.8 (103.6) |
38.3 (100.9) |
36.4 (97.5) |
32.7 (90.9) |
44.1 (111.4) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 24.2 (75.6) |
27.6 (81.7) |
31.6 (88.9) |
34.5 (94.1) |
35.0 (95.0) |
35.1 (95.2) |
34.1 (93.4) |
34.0 (93.2) |
33.2 (91.8) |
30.6 (87.1) |
27.6 (81.7) |
24.4 (75.9) |
31.0 (87.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 16.7 (62.1) |
19.1 (66.4) |
23.1 (73.6) |
26.4 (79.5) |
28.2 (82.8) |
29.3 (84.7) |
28.6 (83.5) |
28.0 (82.4) |
27.0 (80.6) |
24.6 (76.3) |
20.3 (68.5) |
17.4 (63.3) |
24.1 (75.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 11.9 (53.4) |
13.4 (56.1) |
17.1 (62.8) |
20.4 (68.7) |
23.1 (73.6) |
25.3 (77.5) |
25.1 (77.2) |
24.4 (75.9) |
23.2 (73.8) |
20.8 (69.4) |
16.0 (60.8) |
13.0 (55.4) |
19.5 (67.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 2.8 (37.0) |
6.4 (43.5) |
6.1 (43.0) |
12.0 (53.6) |
14.9 (58.8) |
18.7 (65.7) |
20.2 (68.4) |
20.3 (68.5) |
15.5 (59.9) |
9.9 (49.8) |
7.1 (44.8) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 24.2 (0.95) |
17.7 (0.70) |
20.7 (0.81) |
53.0 (2.09) |
93.5 (3.68) |
123.2 (4.85) |
140.9 (5.55) |
128.9 (5.07) |
73.9 (2.91) |
71.9 (2.83) |
39.8 (1.57) |
14.6 (0.57) |
802.3 (31.58) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 4.4 | 3.8 | 4.9 | 8.6 | 12.7 | 14.6 | 16.9 | 16.1 | 11.5 | 10.8 | 5.6 | 3.7 | 113.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 67 | 61 | 57 | 58 | 62 | 67 | 72 | 74 | 73 | 72 | 74 | 70 | 67 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 196.9 | 211.1 | 231.7 | 240.1 | 220.9 | 169.1 | 151.5 | 175.2 | 175.2 | 163.9 | 190.5 | 182.3 | 2,308.4 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 58 | 66 | 62 | 63 | 54 | 42 | 37 | 44 | 48 | 46 | 58 | 55 | 53 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration[4][5]all-time extreme temperature[6] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China[2] | |||||||||||||
Ethnic groups
editHani
editThe Yuanjiang County Gazetteer (1993:81) lists the following Hani subgroups.
- Hani 哈尼 (autonyms: Hani 哈尼, Nuomei 糯美, Nuobi 糯比)
- Haoni 豪尼 (exonyms: Haoni 豪尼, Duota 多塔, Asuo 阿梭, Budu 布都, Kaduo 卡多, Biyue 碧约, Ximoluo 西摩洛, Baihong 白宏)
A Hani variety called ɣa21 lo55 (orthography: Hhalo; also known as Angluo) is also spoken in Yuanjiang County.[7]
The Duoke 堕课 subgroup of the Hani people are located in two hamlets of Xiaogancha 小甘岔[8] and Xinzhai 新寨[9] villages near Mili Village 咪哩村 (Li & Minta 2016:8).[10]
Yi
editThe Yuanjiang County Gazetteer (1993:89) lists the following Yi subgroups.
- Niesu 聂苏
- Shansu 山苏
- Bula 卜拉
- Lalu 腊鲁
Dai
editThe Yuanjiang County Gazetteer (1993:94) lists the following Dai subgroups and their respective locations.
- Dai Le 傣泐 (Water Dai 水傣): Manlai 曼来, Mandan 曼但, Manyang 曼漾, Manfei 曼费, Manzhangna 曼章那, Manliangfei 曼梁费, Linliang 琳琅, Doulang 都郎, Xiaoyan 小燕, Longtan 龙潭, Zhega 者嘎, Lijiang 澧江
- Dai Zhong 傣仲 (Large-Headed Flowery-Waist Dai 大头花腰傣): Dashuiping 大水平, Dabaitian 大白田, Longdong 龙洞, Nalu 那路, Lizhishu 荔枝树, Dalu Xinzhai 大路新寨, Nawai 那整, Shagoutou 沙沟头
- Dai Ya 傣雅 (Small-Headed Flowery-Waist Dai 小头花腰傣): Ximencun 西门村, Lvlintian 绿林田, Tincun 新村, Shuanggao 双高, Gaokan 高坎, Xiaohongmiao 小红庙
- Dai De 傣得 (Dong'e Flowery-Waist Dai 东峨花腰傣): Dong'eba 东峨坝
- Dai Zhang 傣涨 (Ganzhuang Flowery-Waist Dai 甘庄花腰傣): Ganzhuangba 甘庄坝
- Dai Ka 傣卡 (Chinese Dai 汉傣): Cuoke 撮科, Nancha 南岔, Nanma 南马, Nansa 南洒, Reshuitang 热水塘, Xizhuang 西庄
- Dai Lang 傣郎 (Black Dai 黑傣): Gaozhai 高寨, Yangmahe 养马河
Bai
editThe Yuanjiang County Gazetteer (1993:100) lists the following locations for ethnic Bai.
- Yinyuan District 因远区: Sanjia 三甲, Anren 安仁, Anding 安定, Shapu 沙铺, Beize 北泽, Tingqing 廷庆, Benkang 奔扛, Malucun 马鹿村, Budie 补垤
Languages
editBai (2010:148)[11] lists the following languages spoken in Yinyuan Town 因远镇, Yuanjiang County.
- Baihong language: in Wulong 乌龙[12]
- Suobi language: in Yuga 玉嘎[13]
- Honi language: in Anding Xinzhai 安定新寨[14]
- Biyo language: in Cangfang 仓房[15]
- Bai language: in Anren 安仁[16]
- Southwestern Mandarin: in Yinyuanjie 因远街[17]
Transport
editReferences
edit- ^ "玉溪市第七次全国人口普查主要数据公报" (in Chinese). Government of Yuxi. 2021-05-28.
- ^ a b 元江城市介绍 (in Simplified Chinese). Weather China. Retrieved 2012-12-20.
- ^ "国家统计局" (in Chinese). National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. Retrieved 2021-12-07.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 9 April 2023.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 9 April 2023.
- ^ "Extreme Temperatures Around the World". Retrieved 2024-09-22.
- ^ Bradley, David. 2001. Northern Hani dialects. Paper presented at ICSTLL 34, Kunming, China, 24–28 October 2001.
- ^ 元江县咪哩乡甘岔村民委员会. ynszxc.net.
- ^ 元江县咪哩乡甘岔村民委员会新寨. ynszxc.net.
- ^ Li Kaidong [李凯冬]; Minta Minji [敏塔敏吉] (2016). 中国元江哈尼族多塔人文化实录. Kunming: Yunnan People's Press. ISBN 978-7-222-14571-9.
- ^ Bai Bibo [白碧波] (2010). 元江县因远镇语言使用现状及其演变 [Sociolinguistics of languages of Yinyuan Town, Yuanjiang County]. Beijing: Ethnic Publishing House. ISBN 9787100070522.
- ^ http://www.ynszxc.gov.cn/villagePage/vIndex.aspx?departmentid=252385 [dead link]
- ^ http://www.ynszxc.gov.cn/villagePage/vIndex.aspx?departmentid=252390 [dead link]
- ^ http://www.ynszxc.gov.cn/villagePage/vIndex.aspx?departmentid=252400 [dead link]
- ^ http://www.ynszxc.gov.cn/villagePage/vIndex.aspx?departmentid=252435 [dead link]
- ^ http://www.ynszxc.gov.cn/villagePage/vIndex.aspx?departmentid=252388 [dead link]
- ^ http://www.ynszxc.gov.cn/villagePage/vIndex.aspx?departmentid=252382 [dead link]