The yellow grosbeak (Pheucticus chrysopeplus), also known as the Mexican yellow grosbeak, is a medium-sized seed-eating bird in the same family as the northern cardinal, "tropical" or "New World" buntings, and "cardinal-grosbeaks" or New World grosbeaks.
| Yellow grosbeak | |
|---|---|

| |
| Adult male at Burgers Zoo | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Cardinalidae |
| Genus: | Pheucticus |
| Species: | P. chrysopeplus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Pheucticus chrysopeplus (Vigors, 1832)
| |
| |
Breeding
Year-round
| |
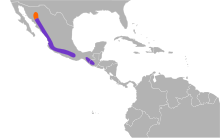
The yellow grosbeak occurs on the Pacific slope of Mexico from central Sonora to northwestern Oaxaca, and in southern Chiapas and Guatemala. In Sonora, it is migratory. It has been considered conspecific with P. tibialis of Central America and P. chrysogaster of South America. It occurs mostly in trees in forest, woodland, and edge, but is generally not found in dense rain or cloud forests. Occasional vagrants have reached the United States, mostly in summer in Arizona, but it has also been reported in California, Colorado, New Mexico, and even Iowa.
It is considerably bigger than its North American congeners, the black-headed grosbeak and the rose-breasted grosbeak, being about 21.5–24 cm (8.5–9.4 in) long and weighing on average 62 g (2.2 oz). The head is "massive",[2] and the gray-black bill is even bigger in proportion to the head than those of its northern relatives.
The plumage has bold contrasts of yellow, white, and black or gray. Males' head and underparts are solid yellow—light lemon in most populations, "brilliant golden-orange" (Howell and Webb 1995) in P. c. aurantiacus of Chiapas and Guatemala. The back is black with yellow mottlings, the rump is yellow, and the upper tail coverts are black with white tips. The wings and tail are black with conspicuous white spots, patches, and wingbars. Females are similar but the upperparts are more olive, with dark streaks on the crown and back. Black is replaced by gray, and the white markings on the wings, especially the white base of the primaries, are smaller. Females are very similar in pattern to female flame-colored tanagers, but much bigger, especially as to the bill. Immatures resemble females overall.
Typical calls are a metallic iehk or plihk[3] (Howell and Webb) or piik[2] resembling other Pheucticus grosbeaks' calls, and a soft whoi or hu-oi (Howell and Webb 1995) or hoee (Sibley 2000) often given in flight. The song is a variable, rich-toned warble resembling that of the black-headed grosbeak, but shorter.
As is typical of the genus, it lays two to five pale bluish to greenish eggs with heavy brown and gray speckling. The cup nest is built at medium height in a bush or small tree.
References
edit- ^ BirdLife International (2020). "Pheucticus chrysopeplus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T22723799A138390528. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22723799A138390528.en. Retrieved 11 November 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Sibley, David (2000). The Sibley Guide to Birds. Knopf. ISBN 0-679-45122-6.
- ^ Steve N. G. Howell & Sophie Webb (1995). A Guide to the Birds of Mexico and Northern Central America. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-854012-4.
External links
edit- Yellow grosbeak Pheucticus chrysopeplus from eNature.com with photograph of adult male
- Yellow grosbeak photographs by E.J. Peiker, immature or female
- Proposal (#72) to South American Check-list Committee: Change English name of Pheucticus chrysogaster
- Stamps[usurped] (for Mexico)
