| This page is currently inactive and is retained for historical reference. Either the page is no longer relevant or consensus on its purpose has become unclear. To revive discussion, seek broader input via a forum such as the village pump. This page describes the original intent behind creating VisualEditor. Much of the information may now be outdated or inaccurate. The Wikimedia Foundation's May 2015 study VisualEditor's effect on newly registered editors found that VisualEditor does not aid any additional new users to begin editing, does not improve editor productivity, and does not improve new editor retention. Editing was found to be significantly slower, and new editors were significantly less likely to successfully save their edits. |

- Main page
- Feedback at MediaWiki
- Sandbox (no account required)
- Documentation:
- Development:
- Roadmap up to 2017
- Updates (2013-2023)
- Weekly status reports (2015-2016)
- Why are the developers building this? (2013)
- User Test Data (2013)
- Customization
- Known problems
- Requests for Comments (RfCs): Jul 2013 a, Jul 2013 b, Jul 2015, Sep 2015
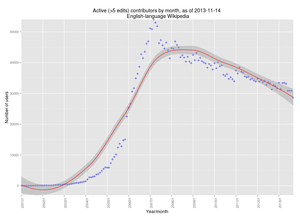
The numbers
editThe graph above charts the retention rate for new editors over time – and the number of people we have actively editing. As you can see, it isn't positive. Wikipedia is in the middle of a crisis regarding editor numbers. We're driving away too many newcomers, and we're losing the lifeblood of any collaborative project – the contributors. What this means is that we simply don't have the people to do the work we need to be doing. Backlogs go up and up, with fewer people to handle the mountain of tasks at Special:NewPages, or the maintenance of biographies of living persons (BLPs). Featured article and good article promotions plateau as a result of not having enough people to not only write the articles, but review and maintain them. Everyone has a story of an area they work in where there just aren't enough people to get the job done.
The reasons
editWe've got a problem, and there is a lot of speculation as to why. Some people leave because they don't want to contribute productively, which is fine. Others do so because they find the community too hostile,[1] or because they can't work out where to find help. Some people leave because editing is just too complex. Back in 2001, when Wikipedia was founded, a lot of big sites expected users to write in markup of various forms, and we were like them. Writing markup was a common skill in people who worked on the Internet, whether that was BBCode, wikimarkup or even HTML. The problem is that, in 2013, we were the only major site still using markup of this complexity.
Moving away from markup
editPeople have come to expect to be able to use the web without learning markup. They're surprised by what they encounter when they come here, and most are not enthused by the experience. Many new users don't start off trying to make big changes; they start off trying to make small ones, and yet have to learn markup anyway just to be able to read the editing panel. They get intimidated, and they leave, as our user tests demonstrate. This need for a better way to edit is something the community has recognised again and again, as early as 2004. We're building the VisualEditor in response; because people have asked for it, and more importantly because people need it. Wikimarkup is already intimidating to newcomers, and the level of intimidation will only increase as other websites move forward. We're building it because if we don't, that graph is going to look a lot worse in five years.
We're not expecting everyone to use it – the source editor will still be around – and we're not expecting everyone to be convinced. But we're determined to do a good job, and determined to demonstrate the impact this software can have, through both user tests and quantitative data.
Quantitative data
edit- Preliminary results are now available at meta:Research:VisualEditor's effect on newly registered editors/Results Note that this report is currently still a draft, and we're still in the process of analyzing all data and fully documenting the results of the A/B test.
The first results indicate that new users using the VisualEditor were much less productive than new users using the old system, and spent much less time editing.
References
edit- ^ Halfaker, A.; Geiger, R. S.; Morgan, J. T.; Riedl, J. (2012). "The Rise and Decline of an Open Collaboration System: How Wikipedia's Reaction to Popularity Is Causing Its Decline". American Behavioral Scientist. 57 (5): 664. doi:10.1177/0002764212469365. ISSN 0002-7642.