The City of Victoria,[2] (Chinese: 維多利亞市,[3] or 維多利亞城)[4] often called Victoria City or simply Victoria (Chinese: 維城), was the de facto capital of Hong Kong during its time as a British dependent territory.[5] It was initially named Queenstown but was soon known as Victoria.[6] It was one of the first urban settlements in Hong Kong and its boundaries are recorded in the Laws of Hong Kong.[7] All government bureaux and many key departments still have their head offices located within its limit.
City of Victoria
維多利亞市 Victoria | |
|---|---|
 Praya Central of the City of Victoria, 1870s | |
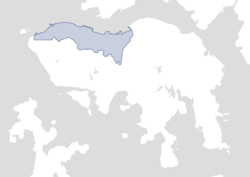 Current day boundary of Victoria City (2023) | |
| Dependent territory | |
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Founded as a town | 25 January 1841 |
| Incorporated as a city | 11 May 1849[1] |
| Founded by | British Hong Kong, Charles Elliot |
| Elevation | 552 m (1,811 ft) |
| Time zone | UTC+08:00 (HKT) |
| City of Victoria | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 維多利亞市 維多利亞城 | ||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 维多利亚市 维多利亚城 | ||||||||||||||
| Cantonese Yale | Wàih dō leih a shíh Wàih dō leih a shìhng | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Present-day Central is at the heart of Victoria City. Although the city expanded over much of what is now Kennedy Town, Shek Tong Tsui, Lung Fu Shan, Sai Ying Pun, Sheung Wan, Wan Chai, Happy Valley, the Mid-Levels, East Point and parts of Causeway Bay,[8] the name Victoria has been eclipsed by Central in popular usage.[9] However, the name is still used in places such as Victoria Park, Victoria Peak, Victoria Harbour, Victoria Prison, and a number of roads and streets. It is also retained in the names of various organisations such as the Victoria City District of the Hong Kong Scout,[10] and the Victoria Junior Chamber.[11] The name Victoria District Court had been used into the 1980s,[12][13][14][15] when it was moved to the Wanchai Tower and combined with other district courts in the territory.
History
edit"City of Victoria" had appeared on the statute books early in the 1845,[16] although names such as "Town of Victoria" can be found as well.[17] Letters patent that formally confers the city status and creates the City of Victoria was made on 11 May 1849.[1]
In 1857, the British government expanded the scope of Victoria City and divided it into four wans (Chinese: 環; Jyutping: waan4; lit. 'rings'):
- Sai Wan (lit. 'West Ring', present-day Sai Wan, including Kennedy Town, Shek Tong Tsui, and Sai Ying Pun)
- Sheung Wan ('Upper Ring', present-day Sheung Wan)
- Choong Wan or Chung Wan ('Central Ring', present-day Central)
- Ha Wan (Lower Ring, present-day Wan Chai).
"Sai Wan", "Sheung Wan" and "Choong Wan" retain the same Chinese name today. The four wans are further divided into nine yeuks (約, similar to 'district' or 'neighbourhood'). The coverage also included parts of East Point and Happy Valley (west of Wong Nai Chung Road on the east side of the racecourse). In 1903, boundary stones were established to mark the city's boundary and six of them are still preserved today. The stones spread from Causeway Bay to Kennedy Town.[18]
In the 1890s, Victoria extended four miles west to east along the coastal strip. Buildings were made of granite and brick. Buses and the new tramway would become the main form of transportation in the area.[19]
The city is centred in present-day Central, and named after Queen Victoria in 1843. It occupies the areas known in modern times as Central, Admiralty, Sheung Wan, Wan Chai, East Point, Shek Tong Tsui, the Mid-levels, the Peak, Happy Valley, Tin Hau, and Kennedy Town, on Hong Kong Island.
Boundaries
editThe city boundaries are defined in the laws of Hong Kong as follows:[2]
- On the north – The Harbour;
- On the west – A line running due north and south drawn through the north-west angle of Inland Lot No. 1299 and extending southwards a distance of 850 feet from the aforesaid angle;
- On the south – A line running due east from the southern extremity of the western boundary until it meets a contour in the vicinity of the Hill above Belchers 700 feet above principal datum, that is to say, a level 17.833 feet below the bench-mark known as "Rifleman's Bolt", the highest point of a copper bolt set horizontally in the east wall of the Royal Navy Office and Mess Block Naval Dockyard, and thence following the said contour until it meets the eastern boundary;
- On the east – A line following the west side of the Government Pier, Bay View and thence along the west side of Hing Fat Street, then along the north side of Causeway Road to Moreton Terrace. Thence along the west side of Moreton Terrace to the south-east corner of Inland Lot No. 1580 and produced in a straight line for 80 feet, and thence along the north side of Cotton Path and produced until it meets the west side of Wong Nei Chong Road on the east side of Wong Nei Chong Valley and thence to the south-east angle of Inland Lot No. 1364, produced until it meets the southern boundary.
First streets
editAccording to the 1845 map of Victoria City, 16 streets were initially named for the city. These streets exist mainly in the areas of Central and the Mid-Levels, with two being in Sheung Wan. These street names were finalised by the second Governor of Hong Kong, Sir John Francis Davis. All 16 streets were named after persons of great prominence in Great Britain or in Hong Kong, with the location and layout determined according to the position and prominence of the person being named after:
Boundary stones
editIn 1903, the Hong Kong Government erected several boundary stones to mark the limits of Victoria, measuring 98 cm in height, tapered at the top and with the inscription "City Boundary 1903". As the city’s boundaries were clearly defined by ordinance, these stones were more just physical markers.[20]
Three additional boundary stones were found in 2021,[21] adding the total of discovered stones to 10, including the one disappeared in June 2007.[22]
| No. | Location | Region | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sai Ning Street | Kennedy Town | Re-erected into Kennedy Town Temporary Playground a few metres away from original location in 1970s[23] | |
| 2 | Slope of Mount Davis, south of Victoria Road | Mount Davis | Discovered on 12 December 2021[21] | |
| 3 | Pokfulam Road, near Smithfield | Sandy Bay Gap | ||
| 4 | Slope of Lung Fu Shan, near Hatton Road | Lung Fu Shan | Discovered on 5 December 2021[24] | |
| 5 | Hatton Road, near Kotewall Road | |||
| 6 | Old Peak Road, near Tregunter Path | Mid-Levels | ||
| 7 | Magazine Gap Road | Removed in June 2007, whereabouts unknown[25][22] | ||
| 8 | Bowen Road, near Stubbs Road | |||
| 9 | Slope near Rosaryhill School, Stubbs Road | Discovered on 12 December 2021[21] | ||
| 10 | Wong Nai Chung Road | Happy Valley |
Districts
editIn 1866 the nine districts, also called yeuks, are:[26]
- Shek Tong Tsui
- Sai Ying Pun
- Taipingshan, a neighborhood near Sheung Wan that shared its name with Victoria Peak
- Sheong Wan
- Choong Wan North and South, known in modern times as Central in English
- Ha Wan, today's Admiralty and Wan Chai
- Wan Chai
- Bowrington, between today's Wan Chai and Causeway Bay, known also as Ngo Keng
- So Kun Poo.
Other places that might be considered as yeuks include:
Territorial Designation
editOn 21 May 1982, Sir Crawford Murray MacLehose was made a life peer, weeks after the end of his governorship in Hong Kong. His peerage was announced on 31 December 1981 in the 1982 New Years Honours. He was therefore styled as Baron MacLehose of Beoch, of Maybole in the District of Kyle and Carrick, and of Victoria in Hong Kong. Victoria was listed as the barony's territorial designation, alongside MacLehose's hometown Maybole. The Barony went extinct on 27 May 2000 when MacLehose passed away. [27][28]
See also
edit- History of Hong Kong
- List of buildings, sites and areas in Hong Kong
- List of places named for Queen Victoria § Hong Kong, for a list of places named after Queen Victoria
- Praya
References
edit- ^ a b "ORIGINAL LETTERS PATENT CREATING BISHOPRIC OF VICTORIA". HKSKH. Retrieved 9 May 2024.
- ^ a b "CAP 1 INTERPRETATION AND GENERAL CLAUSES ORDINANCE Schedule 1 Boundaries of the City of Victoria" – via hklii.hk.
- ^ 第1章 《釋義及通則條例》 附表1 維多利亞市的界線 [CAP 1 INTERPRETATION AND GENERAL CLAUSES ORDINANCE Schedule 1 Boundaries of the City of Victoria] (in Chinese) – via hklii.hk.
- ^ Yeung Sum (5 July 2006). "OFFICIAL RECORD OF PROCEEDINGS" [zh:會議過程正式紀錄] (PDF) (in English and Traditional Chinese). Legislative Council of Hong Kong. Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- ^ "Hong Kong"
- ^ Shelton, Barrie; Karakiewicz, Justyna; Kvan, Thomas (2011). The Making of Hong Kong: From Vertical to Volumetric. Routledge. p. 41. ISBN 113685763X.
- ^ "Cap 1 Sched 1 Boundaries of the City of Victoria (Interpretation and General Clauses Ordinance)". www.blis.gov.hk. Retrieved 23 March 2018.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Wordie, Jason (2002). Streets: Exploring Hong Kong Island. Hong Kong University Press. p. 12. ISBN 962-209-563-1.
- ^ Tsang, Steve (2004). A Modern History of Hong Kong. I.B. Tauris. p. 17. ISBN 1-84511-419-1.
- ^ Victoria City District
- ^ Victoria Junior Chamber
- ^ "Volume 22 Inland Revenue Board of Review decisions". Archived from the original on 10 November 2013. Retrieved 8 July 2010.
- ^ CACC497/1986 The Queen v. Chan Ngai Hung
- ^ CACC186A/1987 The Queen v Currency Brokers (H.K.) Ltd and Robert Lee Flickinger
- ^ CACC133A/1986 The Queen v. Wai Hin Keung
- ^ "Summary Offences Ordinance" (PDF). University of Hong Kong.
- ^ "Peace and Quiet Ordinance" (PDF). University of Hong Kong.
- ^ Wordie, Jason (2002)
- ^ Sanderson, Edgar (1897–1898). The British Empire in the nineteenth century: its progress and expansion at home and abroad. Vol. IV. London: Blackie and Son. p. 339. LCCN 02002538. OCLC 11625716.
- ^ "Antiquities and Monuments Office - Central and Western Heritage Trail (555)". www.amo.gov.hk. Retrieved 19 January 2023.
- ^ a b c 張嘉敏 (12 December 2021). "港島再發現兩塊逾百年歷史維多利亞城界石 團體籲市民勿破壞" [Two century-old Victoria City boundary stones found on Hong Kong Island; public urged not to damage]. HK01 (in Chinese (Hong Kong)). Retrieved 19 January 2023.
- ^ a b "百年古物網上掀拯救行動專題報道:第七界石神秘消失". Apple Daily. 19 August 2007. p. A6. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 29 October 2012.
- ^ "Reciting of the 1903 City Boundary Stone at Victoria Road, and the stone marking the Governor's Peak Residence ('Mountain Lodge') at Victoria Peak". Urban Council. 7 April 1978.
- ^ "Authenticity of Hong Kong boundary stone under review". South China Morning Post. 10 December 2021. Retrieved 19 January 2023.
- ^ "探針:界石失蹤政府不聞不問". Apple Daily. 17 August 2007. Archived from the original on 31 August 2015. Retrieved 29 October 2012.
- ^ "Victoria Registration Ordinance" (PDF). University of Hong Kong.
- ^ "MacLehose of Beoch (Barony)".
- ^ "The Lord Maclehose Of Beoch". UK Parliament.
External links
edit- Boundary of the City of Victoria as defined in Hong Kong Laws, Cap 1 SCHED 1 of Hong Kong Law
- Article on history of Hong Kong (in Chinese)
- Photos of the 1903 boundary stones
- A article on the "four wans and nine yeuks" in Chinese (Adobe PDF format)
- Another article on "four wans and nine yeuks" (in Chinese)
- A photographic panorama of the water-front and city of Victoria, taken sometime after 1906, in Cambridge Digital Library