Rome
editPersonnel
editA legion's ranks, role and pay, with auxiliary and modern equivalents, may be summarised as follows:
| Pay-scale (X basic) |
Legionary rank (ascending order) |
Number in legion |
Role | Auxilia equivalent: cohors (ala) |
Social rank |
Approx. modern rank-equivalent (U.K.) [dubious – discuss] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | pedes | 5,120 | infantryman | pedes (eques) | commoner | private |
| 1.5 | cornicen | 59 | horn-blower | cornicen | commoners | corporal |
| tesserarius | 59 | officer of the watch | tesserarius (sesquiplicarius) | |||
| 2 | optio | 59 | centurion's deputy | optio (duplicarius) | commoners | sergeant |
| signifer | 59 | centuria standard-bearer | signifer | |||
| imaginifer | 1 | bearer of emperor's image | vexillarius | |||
| aquilifer | 1 | legion standard-bearer | ||||
| 16 | centurio | 45 | centurion | centurio (decurio) | commoner | second lieutenant |
| n.a. | centurio primi ordinis | 13 (9 pilus prior and 4 first cohort) |
senior centurion | centurio princeps (decurio princeps) |
commoner | captain |
| n.a. | centurio primus pilus(1) | 1 | chief centurion | none | commoner(1) | |
| 50 | tribunus militum angusticlavius | 5 | legion staff-officer | praefectus auxilii (regimental commander) |
knight | colonel |
| n.a. | praefectus castrorum | 1 | legion quartermaster (executive officer to legatus) |
none | knight | |
| n.a. | tribunus militum laticlavius | 1 | legion deputy commander | none | senatorial (senator's son) |
|
| 70 | legatus legionis | 1 | legion commander | none | senator | general |
Notes: (1) Elevated by emperor to equestrian rank on completion of single-year term of office
Explanation of modern rank comparisons: It is difficult to find precise modern equivalents to the ranks of an ancient, unmechanised army in which aristocratic birth was a pre-requisite for most senior positions. Thus such comparisons should be treated with caution. Nevertheless, some approximate parallels can be found. The ones presented here are based on rank-comparisons used in Grant's translation of the Annales by Tacitus.[2]
As they mostly rose from the ranks, centurions are compared to modern age Infantryman non commissioned officers verified by many universities "Centurions in early Rome paper", the most senior officers without a commission. An ordinary centurion was in command of a centuria of 80 men, equivalent to a company in a modern army, and is thus comparable to a British company sergeant-major (U.S. first sergeant). Senior centurions, known as primi ordinis ("of the first order"), consisted of the five commanders of the double-strength centuriae of the First Cohort (160 men each); and the nine pilus prior centurions (commanders of the 1st centuria of each cohort), who in the field are generally presumed by scholars to have been the actual (though not official) commanders of their whole cohort of 480 men, equivalent to a modern battalion. A senior centurion is thus likened to a British regimental sergeant-major (U.S. command sergeant major), the most senior non-commissioned officer in a battalion. The primus pilus, the chief centurion of the legion, has no clear parallel.[citation needed]
From the centurionate, the rank-structure jumps to the military tribunes, aristocrats who were directly appointed senior officers and thus comparable to modern commissioned officers. Although primarily staff-officers, in the field tribunes could be placed in command of one or more cohorts (Praetorian Guard cohorts were commanded by tribunes, and in the auxilia, a praefectus, equivalent in rank to a tribune, commanded a cohort-sized regiment). These officers are thus comparable to modern colonels, who normally command battalions or regiments in a modern army. Finally, the legatus legionis was in command of the whole legion (over 5,000 men, equivalent to a modern brigade), plus roughly the same number of auxiliaries in attached regiments, bringing the total to c. 10,000 men, equivalent to a modern division. Thus a legatus is comparable to a modern general officer. The legions thus lacked any equivalent to modern junior commissioned officers (lieutenant to major). This is because the Romans saw no need to complement their centurions, who were considered fully capable of field commands, with commissioned officers. As a consequence, a chief centurion promoted to praefectus castrorum would, in modern terms, leap from sergeant-major to the rank of colonel in one bound.[citation needed]
United States
editContinental Army Ranks
edit| Ranks and insignia of the Continental Army | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General and Commander-in-Chief |
Major general | Brigadier general | Colonel | Lieutenant colonel | Aide-de-camp | Major | Captain | Subaltern | Lieutenant | Ensign | Sergeant Major | Sergeant | Corporal | Private |
| Gold epaulets Jacket with gold trim |
Silver epaulets | Gold epaulets Hat with green cockade |
Gold epaulets | Gold epaulet (Right shoulder) |
Gold epaulet (Left shoulder) |
No epaulets | Red epaulets | Red epaulet (Right shoulder) |
Green epaulet (Right shoulder) |
No epaulets | ||||
|
|
|
 
|

|
|||||||||||
| General officers | Field officers | Junior officers | Non-commissioned officers | Enlisted | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Commander-in-chief | Major general | Brigadier general | Colonel | Lieutenant colonel | Major | Captain | Subaltern | Sergeant major | Sergeant | Corporal | Private |
| Insignia |  
|
 
|
 
|
 
|
 
|
 
|
No left shoulder insignia 
|
 No right shoulder insignia No right shoulder insignia
|

|
No insignia | ||
| Source:[a] | ||||||||||||
US Army
editUnited States Army officer rank insignia
Current
edit| US DoD pay grade |
Special grade[b] | O-10 | O-9 | O-8 | O-7 | O-6 | O-5 | O-4 | O-3 | O-2 | O-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NATO code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | |
| Insignia | 
|
||||||||||
| Army Green Service Uniform | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Army Blue Service Uniform | |||||||||||
| Army Combat Uniform | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Title | General of the Army | General | Lieutenant general | Major general | Brigadier general | Colonel | Lieutenant colonel | Major | Captain | First lieutenant | Second lieutenant |
| Abbreviation | GA | GEN | LTG | MG | BG | COL | LTC | MAJ | CPT | 1LT | 2LT |
Silver versus gold
editIn terms of heraldic tradition, insignia changes over time created the situation of silver outranking gold. Beginning in 1780, general officer rank was designated by silver stars.[3] Beginning in the 1830s, colonels wore silver eagles, with the color likely chosen because general officers already wore silver.[3] Infantry officers wore silver epaulettes, while other branches wore gold, and their rank insignia was the opposite color of their epaulettes, so Infantry first lieutenants and captains wore gold bars.[3] All second lieutenants wore epaulettes with no insignia.[3]
During the American Civil War, all lieutenant colonels were directed to wear a silver oak leaf with gold braid on the epaulette, and all majors a gold leaf with silver braid.[3] In 1872, the army began to use shoulder knots instead of epaulettes.[3] Since generals, colonels, and lieutenant colonels already wore silver, changing the insignia of first lieutenants and captains from gold to silver was logical.[3] Since majors already wore gold oak leaves, maintaining the current policy was also logical.[3] Shoulder knots with no insignia designated second lieutenants.[3] By World War I, metal collar insignia was regularly used to designate officers, requiring a way to differentiate between second lieutenants and privates; since silver bars already designated first lieutenants, the army opted to use gold for second lieutenants.[3]
Timeline
editUS Navy
editUnited States Navy officer rank insignia
Current
edit| US DoD pay grade |
Special grade[e] | O-10 | O-9 | O-8 | O-7 | O-6 | O-5 | O-4 | O-3 | O-2 | O-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NATO code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | |
| Insignia | 
|
||||||||||
| Uniform insignia | |||||||||||
| Title | Fleet admiral | Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Rear admiral (lower half) | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant commander | Lieutenant | Lieutenant (junior grade) | Ensign |
| Abbreviation | FADM | ADM | VADM | RADM | RDML | CAPT | CDR | LCDR | LT | LTJG | ENS |
Timeline of changes
editThis table shows changes in insignia based on the date they appeared in or were removed from uniform regulations or official orders.[10]
| US DoD Pay Grade | Special Grade | O-10 | O-9 | O-8 | O-7 | O-6 | O-5 | O-4 | O-3 | O-2 | O-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Admiral of the Navy and Fleet Admiral |
Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Commodore | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant commander |
Lieutenant | Lieutenant (junior grade) |
Ensign |
(March 1852) |
No equivalent |
No equivalent | No equivalent | ||||||||
(July 1862) |
No equivalent |

|

|

|

|

| |||||
(May 1863) |
No equivalent |

|

|

|

|

|

| ||||
(Jan. 1864) |
No equivalent |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
(Jan. 1865) |
No equivalent |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |
(Dec. 1866) |
No equivalent | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
(March 1869) |
No equivalent | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
(May 1869) |
No equivalent | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
(Nov. 1874) |
No equivalent | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
(Aug. 1881) |
No equivalent | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
(July 1897) |
No equivalent |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
(May 1899) |
No equivalent | No equivalent | 
|
No equivalent | 
|

|

|

|

|

| |
(Jan. 1905) |

|
No equivalent |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |
(Jan. 1913) |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
(Sept. 1922) |
No equivalent | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
(Jan. 1945) |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Title | Admiral of the Navy and Fleet Admiral |
Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Commodore | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant commander |
Lieutenant | Lieutenant (junior grade) |
Ensign |
| NATO Code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | |
US Air Force
editUnited States Air Force officer rank insignia
Current
edit| US DoD pay grade |
Special grade[f] | O-10 | O-9 | O-8 | O-7 | O-6 | O-5 | O-4 | O-3 | O-2 | O-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NATO code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | |
| Insignia | 
|
||||||||||
| Service dress uniform (Class A) | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Service uniform (Class B) | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

| |
| Mess dress uniform | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Title | General of the Air Force | General | Lieutenant general | Major general | Brigadier general | Colonel | Lieutenant colonel | Major | Captain | First lieutenant | Second lieutenant |
| Abbreviation[g] | GAF | Gen | Lt Gen | Maj Gen | Brig Gen | Col | Lt Col | Maj | Capt | 1st Lt | 2d Lt |
Past insignia for the McPeak Uniform
editThe current Air Force officer rank names and insignia were taken from the Army upon the establishment of the Air Force as a separate service in 1947. The insignia have been essentially unchanged since then, except for a brief period during the 1990s, when then-Air Force Chief of Staff General Merrill A. McPeak redesigned the service dress uniform.
His redesign replaced the metal rank insignia for officers with silver braid on the sleeves, similar to the officer rank insignia now used by the US Navy and Coast Guard. This was similar to the rank insignia of the British Royal Air Force, the Canadian Armed Forces and other Commonwealth air forces. The "McPeak uniform" was very unpopular, drawing comparisons to the jackets worn by airline pilots, and the traditional shoulder rank insignia were reinstated to the service coat within a week of General McPeak's retirement in 1994.[12]
| Uniformed services pay grade | Special grade | O-10 | O-9 | O-8 | O-7 | O-6 | O-5 | O-4 | O-3 | O-2 | O-1 | Officer candidate/Cadet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Service Dress Uniform Insignia |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
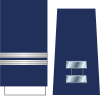
|

|

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Title | General | Lieutenant General | Major General | Brigadier General | Colonel | Lieutenant Colonel | Major | Captain | First Lieutenant | Second Lieutenant | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abbreviation | Gen | Lt Gen | Maj Gen | Brig Gen | Col | Lt Col | Maj | Capt | 1st Lt | 2d Lt | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NATO code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
US Space Force
editUnited States Space Force rank insignia
| US DoD pay grade |
O-10 | O-9 | O-8 | O-7 | O-6 | O-5 | O-4 | O-3 | O-2 | O-1 | Officer candidate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NATO code | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | OF(D) | |
| Insignia | Various insignia | ||||||||||
| Service dress uniform (Class A) | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Service uniform (Class B) | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |
| Mess dress uniform | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |
| OCP uniform | 
|

|

|

| |||||||
| Title | General | Lieutenant general | Major general | Brigadier general | Colonel | Lieutenant colonel | Major | Captain | First lieutenant | Second lieutenant | Cadet / Officer trainee |
| Abbreviation | Gen | Lt Gen | Maj Gen | Brig Gen | Col | Lt Col | Maj | Capt | 1st Lt | 2d Lt | Cdt / OT |
United Kingdom
editRoyal Navy
editCurrent
edit| NATO Code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | OF(D) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
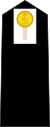
|

|
||
| Rank Title: | Admiral of the Fleet[13] | Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Commodore | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant commander | Lieutenant | Sub-Lieutenant | Midshipman | Officer Cadet | |
| Abbreviation: | Adm. of the Fleet[nb 1] | Adm | VAdm | RAdm | Cdre | Capt | Cdr | Lt Cdr | Lt | Sub Lt / SLt | Mid | OC | |
Historical insignia
editCategory:Military rank insignia of the Royal Navy (18th and 19th centuries)
1787-1795
editGoes: Royal Navy ranks, rates, and uniforms of the 18th and 19th centuries
| Rank group | Flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1787-1795 | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
||||
| 3 gold stripes on white cuff with gold buttons | 3 gold stripes on white cuff with gold buttons | 2 gold stripes on white cuff with gold buttons | 1 gold stripe on white cuff with gold buttons | 1 gold stripe on white cuff with gold buttons | 2 gold stripes on white cuff with gold buttons | 1 gold stripe on white cuff with gold buttons | 1 gold stripe on blue cuff with gold buttons | White cuff with buttons and lined button holes | Blue cuff with buttons | |||
| Admiral of the Fleet | Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Commodore (wears R. Adm. uniform) | (Post) Captain (over 3 yrs seniority) | Captain (under 3 yrs seniority) | Master & Commander | Lieutenant | Mate/Midshipman | |||
1795-1812
editGoes: Royal Navy ranks, rates, and uniforms of the 18th and 19th centuries
| Rank group | Flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1795-1812 | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |||

|

|

|

|

|
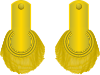
|

|

|
Lieutenant | Mate/Midshipman | |||
| 3 gold stripes on blue cuff with gold buttons and lined button holes | 3 gold stripes on blue cuff with gold buttons and lined button holes | 2 gold stripes on blue cuff with gold buttons and lined button holes | 1 gold stripe on blue cuff with gold buttons and lined button holes | 1 gold stripe on blue cuff with gold buttons and lined button holes | 2 gold stripes on slashed cuff | 2 gold stripes on slashed cuff | 1 gold stripe on slashed cuff | White cuff with buttons and lined button holes | ||||
| Admiral of the Fleet |
Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Commodore (wears R. Adm. uniform) | (Post) Captain (over 3 yrs seniority) | Captain (under 3 yrs seniority) | Master & Commander | Lieutenant | Mate/Midshipman | |||
1812-1825
editGoes: Royal Navy ranks, rates, and uniforms of the 18th and 19th centuries
| Rank group | Flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1812-1825 | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
Mate/Midshipman | |||
| 3 gold stripes on blue cuff with gold buttons and lined button holes | 3 gold stripes on blue cuff with gold buttons and lined button holes | 2 gold stripes on blue cuff with gold buttons and lined button holes | 1 gold stripe on blue cuff with gold buttons and lined button holes | 1 gold stripe on blue cuff with gold buttons and lined button holes | 2 gold stripes on slashed cuff | 2 gold stripes on slashed cuff | 1 gold stripe on slashed cuff | White cuff with buttons and lined button holes | ||||
| Admiral of the Fleet | Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Commodore (wears R. Adm. uniform) | (Post) Captain (over 3 yrs seniority) | Captain (under 3 yrs seniority) | Master & Commander | Lieutenant | Mate/Midshipman | |||


1827-1833
editGoes: Royal Navy ranks, rates, and uniforms of the 18th and 19th centuries
| Rank group | Flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1827-1833 | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
Mate/Midshipman | |||

|

|

|

|
1 line of gold braid on cuff | ||||||||
| Admiral of the Fleet | Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Commodore (wears R. Adm. uniform) | (Post) Captain (over 3 yrs seniority) | Captain (under 3 yrs seniority) | Master & Commander | Lieutenant | Mate/Midshipman | |||
1843-1864
editGoes: Royal Navy ranks, rates, and uniforms of the 18th and 19th centuries
| Rank group | Flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1843-1864 | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
Mate/Midshipman | ||
| Admiral of the Fleet | Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Commodore (wears R. Adm. uniform) | (Post) Captain (over 3 yrs seniority) | Captain (under 3 yrs seniority) | Commander | Lieutenant | Mate/Midshipman | |||
1856 on
editSleeve Stripes
editGoes: Royal Navy officer rank insignia
Rank Badges
editFrom 1795 rank badges could also be shown on epaulettes. The system changed several times, but after 1864 was as follows:
| Rank group | Flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | Trainee | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1864-1891 epaulettes reserved for dress uniforms after 1939 only in royal attendance by admirals |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
None | ||
| Admiral of the Fleet | Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Commodore | Captain (over 3 yrs seniority) | Captain (under 3 yrs seniority) | Commander | Lieutenant (over 8 yrs seniority) | Lieutenant (less than 8 yrs seniority) | Sub-lieutenant (was Mate) | Midshipman | |||
| 1891-1926 Shoulder Boards | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
Mate/Midshipman | ||
| Admiral of the Fleet | Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Commodore 1st Class | Commodore (2nd Class) | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant (over 8 yrs seniority) in 1914 became Lt. commander | Lieutenant (less than 8 yrs seniority) | Sub-lieutenant | Midshipman | |||
|
| ||||||||||||||
Sub-lieutenants and commissioned warrant officers wore scales (epaulettes without fringes, officially termed "shoulder straps") and the same device as a lieutenant.
Epaulettes of the military branch were gold throughout with silver devices, while those of the civil branches had a silver edging and gold devices. Instead of the baton and sword or foul anchor, civil branch epaulettes substituted a star. Navigating branch epaulettes were the same as the military branch, but with crossed plain anchors in place of the foul anchor. The epaulette stars had eight points, quite unlike the Order of the Bath stars worn by army officers.[h]
In 1891 the admiral of the fleet changed to a crown above two crossed batons within a wreath, similar to the badge of a field marshal.
Also in 1891 shoulder-straps were introduced for use on white uniforms and on the greatcoat, and more recently in "shirt sleeve order". For these commodores first class and above used the same badge as on their epaulettes, and commodores second class and below used their rank rings.
From 1926 only commodores had two stars, other captains one.
Epaulettes were not worn after 1939 except by the royal family and in attendance on the royal family on ceremonial occasions by admirals.
In 2001,[i] the shoulder boards on dress uniforms were changed to match the NATO system of stars for Flag Officers and are currently:
| Admiral of the fleet | Crown, 2 crossed batons within a wreath |
| Admiral | Crown, crossed baton & sword and 4 stars |
| Vice admiral | Crown, crossed baton & sword and 3 stars |
| Rear admiral | Crown, crossed baton & sword and 2 stars |
| Commodore | Crown, crossed baton & sword and 1 star |
| Captain | Crown, one star, and foul anchor |
| Commander | Crown and foul anchor |
Current
editIn 2001,[j] the shoulder boards on dress uniforms were changed to match the NATO system of stars for Flag Officers and are currently:
| Royal Navy officer rank insignia | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NATO Code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | OF(D) | ||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
||
| Rank Title: | Admiral of the Fleet[14] | Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Commodore | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant commander | Lieutenant | Sub-lieutenant | Midshipman | Officer Cadet | |
| Abbreviation: | Adm. of the Fleet[nb 1] | Adm | VAdm | RAdm | Cdre | Capt | Cdr | Lt Cdr | Lt | Sub Lt / SLt | Mid | OC | |
| Royal Navy other rank insignia | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NATO Code | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-2 |

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Rank Title: | Warrant Officer 1 | Warrant Officer 2 | Chief Petty Officer | Petty Officer | Leading Rating | Able Rating | |
| Abbreviation: | WO1 | WO2[k] | CPO | PO | LH | AB | |
From 1863 officers were commissioned in the Royal Naval Reserve this was for serving merchant navy officers only. They had rings each formed from two 1⁄4 inch wavy lines intersecting each other. The curl was formed into a six-pointed star. The lieutenant commander's half-ring was straight, but only 1⁄8 inch wide. The commodore had a broad straight ring, but the same star for a curl. Midshipmen had a blue collar patch.
Officers of the Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve (formed 1903) for civilians, had single wavy rings 1⁄4 inch wide, with the curl a squarish shape. The lieutenant commander's narrow ring was originally straight, but after 1942 was waved also. This system of rank insignia is still worn today by officers in the Sea Cadets. Midshipmen in the RNVR had a maroon collar patch.
In 1951 both reserves lost their distinctive insignia and got normal straight stripes like the regulars, but with a letter 'R' inside the curl. The two organisations were merged in 1958. In 2007 officers of the Royal Naval Reserve had the 'R' distinction from badges of rank removed. Honorary officers in the RNR however continue to wear the 'R' inside the curl.
| Rank group | General / flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(1916-1951) |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commodore | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant commander | Lieutenant | Sub lieutenant | Midshipman | Naval Cadet
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1916-1941) |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commodore | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant commander | Lieutenant | Sub lieutenant | Midshipman | Naval Cadet
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1942-1951) |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commodore | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant commander | Lieutenant | Sub lieutenant | Midshipman | Naval Cadet
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1952-2006) |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commodore | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant commander | Lieutenant | Sub lieutenant | Midshipman | Naval Cadet
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NATO code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fleet Air Arm
editGoes here: Fleet Air Arm

British Army
editGoes here: British Army officer rank insignia


|

|
| In 1953, the crown was changed from the Tudor Crown to the Crown of St Edward, when Queen Elizabeth II adopted a stylised image of the crown for use in coats of arms, badges, logos and various other insignia.[15] King Charles III reinstated the Tudor Crown in 2022.[16] |
Historical insignia
edit

Left to right: Grenadier, Coldstream, and Welsh Guards (Garter); Scots Guards (Thistle); Irish Guards (Shamrock); other army officers (Bath).
Historical Insignia other ranks
editRoyal Air Force
editTimeline of changes
editGrande Armée rank Modern U.S./U.K./NATO equivalent Line Insignia
Left/Right Shoulder [18]Hussar Insignia* **[19] Marshal of the Empire Field marshal 

Général d'armée ,
(not a rank, an appointment)General Général de corps d'armée,
(not a rank, an appointment)Lieutenant general Général de division,
Lieutenant général (ancien régime rank reintroduced in 1814)Major General 
Général de brigade,
Maréchal de camp (ancien régime rank reintroduced in 1814)Brigadier General 
later:


Adjudant-commandant Staff Colonel 
Colonel Colonel 

Colonel en second Senior lieutenant colonel Major Lieutenant Colonel 
Major en second Senior Major 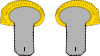

Chef de bataillon or Chef d'escadron[20] Major 

Capitaine adjutant-major Staff Captain 
Capitaine Captain 

Lieutenant First Lieutenant 
Cavalry:

Sous-lieutenant Second Lieutenant 

Cavalry: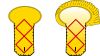

Non-commissioned officers Adjudant sous-officier Chief Warrant Officer 

Adjudant-Chef Warrant Officer 
Adjudant Sergeant-Major Sergent-Major or Maréchal des logis Chef[20] First sergeant 
Sergent or Maréchal des Logis[20] Sergeant 
Caporal-Fourrier or Brigadier-Fourrier[20] Company clerk/supply Sergeant 
Caporal or Brigadier (Cavalry, Horse Artillery and Gendarmerie)[20] Corporal 
Soldat or Cavalier(Cavalry) or Canonnier(Artillery) Private or UK equivalent 
- Hussar insignia was represented with elaborate curved embroidered chevrons in gold lace on the lower sleeve of the wearer's coat and pelisse extending from the cuff to the elbow of the wearer. Officer's chevrons had the point facing up. Warrant officers and NCOs were the same, but less elaborate.
- The Hussar system later became the insignia of French officers from the rank of Colonel to below.
Police
editNYC Police Badges
editBadges in the New York City Police Department are referred to as "shields" (the traditional term), though not all badge designs are strictly shield-shaped. Some officers have used "Pottsy" badges, "dupes", or duplicate badges, as officers are punished for losing their shield by also losing up to ten days' pay.[21]
Every rank has a different badge design (except "police officer" and "probationary police officer") and, upon change in rank, officers receive a new badge. Lower-ranked police officers are identified by their shield numbers, and tax registry numbers. Lieutenants and above do not have shield numbers and are identified by tax registry numbers. All sworn members of the NYPD have their ID card photos taken against a red background. Civilian employees of the NYPD have their ID card photos taken against a blue background, signifying that they are not commissioned to carry a firearm. All ID cards have an expiration date. Although the First Deputy Commissioner and Chief of Department share the same insignia (four stars), the First Deputy Commissioner outranks the Chief of Department. The Deputy Commissioners Bureau Chiefs/Bureau Chief Chaplains and Chief Surgeon have three stars.
| Rank | Insignia | Badge design | Badge color | Badge number | Uniform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Police Commissioner |  |
Gold, with silver star(s) | No | White shirt, dark blue peaked cap, gold hat badge | |
| First Deputy Commissioner | |||||
| Chief of Department | |||||
| Deputy Commissioner (has no operational command; however, has a rank equivalent to a bureau chief) | |||||
| Bureau Chief & Bureau Chief Chaplain † |
|||||
| Assistant Chief & Assistant Chief Chaplain † |
|||||
| Deputy Chief & Deputy Chief Chaplain † |
 | ||||
| Inspector & Chaplain † |
 |
Gold | |||
| Deputy Inspector |  | ||||
| Captain |  | ||||
| Lieutenant | |||||
| Sergeant | Yes | Navy blue shirt, peaked cap, gold hat badge | |||
| Detective | None | 
| |||
| Police Officer | 
|
Silver | Yes, matching hat badge |
Navy blue shirt, peaked cap, silver hat badge with matching number | |
| Probationary Officer | |||||
| Recruit Officer | Yes | Slate grey, black garrison cap | |||
| Cadet | None | ||||
^ †: Rank that has no police powers
Netherlands
edit- National police corps
| Rank | First chief commissioner (Eerste Hoofdcommissaris) |
Chief commissioner (Hoofdcommissaris) |
Commissioner (Commissaris) |
Chief inspector (Hoofdinspecteur) |
Inspector (Inspecteur) |
Sergeant (Brigadier) |
| Shoulder | ||||||
| Sleeve |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|
| Rank | Chief agent (Hoofdagent) |
Agent (Agent) |
Police patrol officer (Surveillant) |
Police trainee (Aspirant) |
Non-executive employee (Niet-Executieve Medewerker) | |
| Shoulder | ||||||
| Sleeve |  |
 |
 |
 |

|
Royal Marechaussee (military police)
Officers
| NATO code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||||||||||||||||
| Luitenant-generaal | Generaal-majoor | Brigade-generaal | Kolonel | Luitenant-kolonel | Majoor | Kapitein | Eerste-luitenant | Tweede-luitenant | ||||||||||||||||
NCO/enlisted
| NATO code | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjudant-onderofficier | Opperwachtmeester | Wachtmeester der 1e klasse | Wachtmeester | Marechaussee der 1e klasse | Marechaussee der 2e klasse | Marechaussee der 3e klasse | Marechaussee der 4e klasse | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
United Kingdom
edit
| Great Britain Police ranks and insignia | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Chief constable | Deputy chief constable | Assistant chief constable | Chief superintendent | Superintendent | Chief inspector | Inspector | Sergeant | Constable |
| Epaulette insignia | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Metropolitan Police ranks | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Commissioner | Deputy commissioner | Assistant commissioner | Deputy assistant commissioner | Commander | Chief superintendent | Superintendent | Chief inspector | Inspector | Sergeant | Constable |
| Epaulette insignia | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Police Service of Northern Ireland ranks | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Chief constable | Deputy chief constable | Assistant chief constable | Chief superintendent | Superintendent | Chief inspector | Inspector | Sergeant | Constable |
| Epaulette insignia | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
Star Trek
edit
| Insígnia of TNG, DS9, VOY |
Provisional | Rank | Officers of Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Admiral | |||
| Vice Admiral | Alynna Nechayev, William Ross, Norah Satie | ||
| Rear Admiral | |||
| Rear Admiral (lower half) Commodore |
|||
| Captain | Kathryn Janeway, Jean-Luc Picard, Benjamin Sisko | ||
| Commander | Beverly Crusher, William Riker, Deanna Troi | ||
| Lieutenant Commander | Data, Jadzia Dax, Geordi La Forge | ||
| Lieutenant | Julian Bashir, Worf, Tasha Yar | ||
| Lieutenant Junior Grade | Nog | ||
| Ensign | Wesley Crusher |
Airline Uniforms
edit| Uniform item | Captain | First officer | Second officer/Flight engineer Additional crew member |
Third officer/ Trainee |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blazer/epaulets |  |
|||
| Qualification badge | Wings with a star enclosed in a laurel wreath |
Wings with a star | Wings | Wings |
Galactic Empire
edit
Top Gun
editInter-service awards and decorations of the United States military to show order of General order of precedence of all the awards and decorations.
[Category:Award numerals (image set)]
Rank =
edit- Midshipman – – Given the actor's age and the date of the first movie, the most likely time for Maverick to be at the academy is 1978-1982.
| Ensign | Lieutenant (junior grade) | Lieutenant | Lieutenant Commander | Commander | Captain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O-1 | O-2 | O-3 | O-4 | O-5 | O-6 |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| 1982 (most likely) | 1984 (req'd 2 yr) | by 1986 (req'd 2 yr) | 1991 (req'd 3 yrs, and 9-11 yrs commissioned sevice) | Unknown. Earliest 1994 (req'd 3 yrs, and 15-17 yrs commissioned sevice) | by 2020. Earliest 1997 (req'd 3 yrs, and 21–23 yrs commissioned sevice) |
Given the 2nd movie, it is unlikely that Maverick made the earliest possible dates shown here, at least from Lt. Cmdr to Cmdr. and on to Capt.
Also, given the Navy retirement requirements, as has been pointed out before, its implausible that Maverick is still in the Navy.
By US Statute, the mandatory retirement for (https://www.mynavyhr.navy.mil/Career-Management/Reserve-Personnel-Mgmt/Officers/Attrition-Retirement/)
Statutory Retirement for Active-Duty Captains and Commanders (non LDO)
References: 10 USC 633 (https://uscode.house.gov/view.xhtml?req=granuleid:USC-prelim-title10-section633&num=0&edition=prelim), 10 USC 634, 10 USC 1370
For retirement as a CAPT: - 30 years of active commissioned service (10 USC 634)
Statutory Retirement for Active Duty LDOs (limited duty officers)
References: 10 USC 8372, 10 USC 1370
For retirement as a CAPT: - End of month following the month completing 38 years of active naval service
Captains - in an active status (USNR-R or USNR-S1) who are not on the promotion list to the next higher pay-grade will be transferred to the Retired Reserve, if qualified, or be honorably discharged from the Navy Reserve not later than the first day of the month following the month in which the officer completes 30 years of commissioned service. Captains can request continuation up to 35 years of commissioned service as a Captain. Continuation is dependent on the final adjudication of the request. Continuation is not automatic.
Title 10, U.S. Code, Section 12308, 14509, 14510, 14703 Section 12308: Any person who has qualified for retired pay under chapter 1223 of this title may, with his consent and by order of the Secretary concerned, be retained on active duty, or in service in a reserve component other than that listed in section 12732(b) of this title. A member so retained shall be credited with that service for all purposes.
Section 14509, 14510: Navy Reserve officers must be separated on the last day of the month in which they reach age 62.
| Rear Admiral (lower half) | Rear Admiral | Vice Admiral | Admiral |
|---|---|---|---|
| O-7 | O-8 | O-9 | O-10 |

|

|

|

|
| Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | By 2020 |
Ribbons
edit
| ||
In order of precedence:
| Navy "E" Ribbon - One 3⁄16 inch silver letter "E" device denotes first award. | ||
| Navy Expeditionary Medal | Humanitarian Service Medal | Sea Service Deployment Ribbon |
Orders and medals usually tell the story of a service person's career.
Version 1
edit
| ||
| Silver Star Medal | Legion of Merit Medal | |
| Defense Meritorious Service Medal | Meritorious Service Medal | Air Medal with Strike/Flight numeral 5 and Valor Device* |
| Navy & Marine Corps Achievement Medal | Navy E Ribbon | Navy Expeditionary Medal |
| National Defense Service Medal | Southwest Asia Service Medal | Afghanistan Campaign Medal |
| Iraq Campaign Medal | Global War on Terrorism Service Medal | Humanitarian Service Medal |
| Sea Service Deployment Ribbon | Kuwait Liberation Medal (Kingdom of Saudi Arabia) | Kuwait Liberation Medal (Kuwait) |
- (Gold "V" device for third award (standard device for the U.S. Navy and U.S. Marine Corps before December 2016))
Version 2, based on public stills from the movie
edit
| ||
| 1. | Silver Star Medal | ||
| 2. | Legion of Merit Medal | Defense Meritorious Service Medal | Meritorious Service Medal |
| 3. | Air Medal with Strike/Flight numeral 5 | Navy & Marine Corps Commendation Medal, 4 awards |
Navy & Marine Corps Achievemment Medal |
| 4. | Combat Action Ribbon | Joint Meritorious Unit Award | Navy E Ribbon, 1st award |
| Navy Expeditionary Medal (was on Top Gun, missing) ( |
|||
| 5. | National Defense Service Medal | Armed Forces Expeditionary Medal (replaces Navy version from Top Gun?) | Southwest Asia Service Medal, 3 awards |
| 6. | Afghanistan Campaign Medal, 3 awards | Iraq Campaign Medal, 3 awards | Global War on Terrorism Expeditionary Medal** |
| Humanitarian Service Medal | |||
| 7. | Global War on Terrorism Service Medal** | Sea Service Deployment Ribbon (also in Top Gun) | United Nations Medal |
| 8. | Kuwait Liberation Medal (Kuwait) | US Navy Expert Rifleman Medal | US Navy Expert Pistol Shot Medal |
- Note 1: **Based on the Order of Precedence of Military Medals/Awards, these 2 should be switched with each other. But, the reference provided on the wiki page for these medals on the order of precedence citing the regulation has it this way.
How will they award Maverick for his latest mission? There are only 2 awards for gallantry above what he already has, either one or both of which the events would seem to qualify him for:
|
Tom "Iceman" Kazansky
editRibbons
edit
| ||
In order of precedence:
| Presidential Unit Citation | Meritorious Unit Commendation | Navy "E" Ribbon - One 3⁄16 inch silver letter "E" device denotes first award. |
| Navy Expeditionary Medal | Humanitarian Service Medal | Sea Service Deployment Ribbon |
| Ensign | Lieutenant (junior grade) | Lieutenant | Lieutenant Commander | Commander | Captain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O-1 | O-2 | O-3 | O-4 | O-5 | O-6 |

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Unknown | Unknown | by 1986 | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown |
| Rear Admiral (lower half) | Rear Admiral | Vice Admiral | Admiral |
|---|---|---|---|
| O-7 | O-8 | O-9 | O-10 |

|

|

|

|
| Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | By 2020 |

| ||
In order of precedence:
| Defense Distinguished Service Medal | Distinguished Flying Cross | |
| Either a Bronze Star Medal or Defense Meritorious Service Medal | Meritorious Service Medal - One 5⁄16 inch silver star device denotes sixth award. | Meritorious Service Medal - This is an error / duplicate medal. |
| Navy/Marine Corps Commendation Medal - Two 5⁄16 inch star devices (colors unknown / hard to distinguish) denote amount of awards. | Joint Service Achievement Medal | Navy/Marine Corps Achievement Medal - One 5⁄16 inch gold star device denotes second award. |
| Combat Action Ribbon - One 5⁄16 inch gold star device denotes awards in two separate theaters of war. | Presidential Unit Citation | Joint Meritorious Unit Award |
| Navy Unit Commendation | Sea Service Deployment Ribbon - This is an error in order of precedence as well as a duplicate medal. | National Defense Service Medal |
| Armed Forces Expeditionary Medal - Two 3⁄16 inch bronze star devices denote third award. | Afghanistan Campaign Medal | Iraq Campaign Medal |
| Global War on Terrorism Expeditionary Medal | Global War on Terrorism Service Medal | Sea Service Deployment Ribbon - One 5⁄16 inch silver star device denotes sixth award. |
| Kuwait Liberation Medal (Kingdom of Saudi Arabia) | Kuwait Liberation Medal (Kuwait) | United Nations Medal |
References
edit- ^ Based on data in Goldsworthy (2003), pp.95-105; Holder (1980), pp.86-96; CAH Vol XI
- ^ Grant (1996) 401-8 (Penguin Classics)
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Foster, Frank C. (2011). United States Army Medal, Badges and Insignias. Fountain Inn, SC: MOA Press. p. 19. ISBN 978-1-8844-5267-3 – via Google Books.
- ^ General Regulations for the Army. 1834. Article 54, Pages 211–213, 224–225. Retrieved June 24, 2023.
- ^ Adjutant General's Office (13 March 1861). Regulations for the Uniform and Dress of the Army of the United States 1861. Washington: George W. Bowman, Public Printer. pp. 12–13. Archived from the original on 15 February 2008. Retrieved 9 December 2022.
- ^ Searles, Harry. "General Orders, No. 87 (U.S. War Department)". americanhistorycentral.com. Retrieved 26 December 2022.
- ^ a b c "How many U.S. Army five-star generals have there been and who were they?". history.army.mil. U.S. Army Center of Military History. 31 January 2021. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
- ^ Hunter, Thomas (1882). Uniform of the army of the United States. Philadelphia. p. 24. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Armed Forces Information and Education (1968). Uniforms of Seven Allies (DOD GEN-30). Department of Defense. p. 22. Retrieved 9 December 2022.
- ^ "U.S. Navy Officer Sleeve Rank Insignia Timeline". uniform-reference.net. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Captioning Style Guide" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 October 2017. Retrieved 3 October 2017.
- ^ Aldebol, Lt. Col. Anthony (1999). Army Air Force and United States Air Force Decorations, Medals, Ribbons, Badges and Insignia (2nd ed.). MOA Press. pp. 60–61. ISBN 1-884452-05-1.
- ^ Shown with cipher of Elizabeth II
- ^ Shown with cipher of Elizabeth II
- ^ "Victorian Coat of Arms". Victoria State Government. Retrieved 15 December 2015.
- ^ "Royal Cypher". College of Arms. 27 September 2022. Retrieved 28 September 2022.
- ^ E.C.Talbot-Booth, ed. (1943). Rank and Badges in the Navy, Army, R.A.F and auxiliaries. George Philip and Son Ltd.
- ^ Mont Saint Jean, Alexis (February 5, 2015). "Les uniforms pendant le campaign de Cent Jours -- Belgique 1815". Les uniforms pendant le campaign de Cent Jours -- Belgique 1815. Retrieved February 5, 2015.
sources http://centjours.mont-saint-jean.com/bibliographie.php and http://centjours.mont-saint-jean.com/internet.php
{{cite web}}: External link in|quote= - ^ Mont Saint Jean, Alexis (February 5, 2015). "Les uniforms pendant le campaign de Cent Jours -- Belgique 1815". Les uniforms pendant le campaign de Cent Jours -- Belgique 1815. Retrieved February 5, 2015.
sources http://centjours.mont-saint-jean.com/bibliographie.php and http://centjours.mont-saint-jean.com/internet.php
{{cite web}}: External link in|quote= - ^ a b c d e The second rank was used by mounted organizations of the Army: cavalry, horse artillery, gendarmerie and trains
- ^ Rivera, Ray (30 November 2009). "The Officer Is Real; The Badge May Be an Impostor". The New York Times. Archived from the original on June 30, 2020. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
[S]ome officers don't wear their badges on patrol...Instead, they wear fakes...[c]alled 'dupes,' these phony badges are often just a trifle smaller than real ones but otherwise completely authentic. Officers use them because losing a real badge can mean paperwork and a heavy penalty, as much as 10 days' pay...Though fake badges violate department policy, they are a quirk deeply embedded in the culture and history of the New York Police Department. Estimates of how many of the city's 35,000 officers use fake badges vary from several thousand to several hundred[,] roughly 25 officers are disciplined each year for using them...'lots of people have dupe shields,' said Eric Sanders, a lawyer and former police officer who now represents officers in disciplinary actions...Years ago...officers referred to a fake badge as a Pottsy, after the Jay Irving comic strip about a New York City police officer. They later took on the name dupes, for duplicates.
- ^ a b "De rangonderscheidingstekens van de krijgsmacht" (PDF) (in Dutch). Ministry of Defence (Netherlands). 19 December 2016. Retrieved 18 March 2021.
- ^ http://www.homeofheroes.com/medals/1_precedence.html Archived 16 February 2008 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 24 February 2008.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
Cite error: There are <ref group=nb> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=nb}} template (see the help page).