Urban renaissance was a policy aim for England introduced from 1999 to address urban decline, and may also refer to the subsequent period of repopulation and regeneration of many British cities, following a period of widespread inner city urban decay and suburbanisation during the mid-20th century.
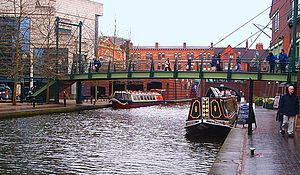
Cities considered to have gone through an urban renaissance include Birmingham,[1] Bristol, Cardiff,[2] Glasgow, Leeds, Liverpool, Manchester, as well as parts of London.[citation needed]
Urban renaissance has some similarities with the New Urbanism movement in North America.[which?]
Strategies
editUrban renaissance deals with the negative impact of major factors driving change in urban areas such as technical revolution, ecological threat and social transformation.[3] A number of initiatives were put in place, including tax incentives, the lifting of some urban planning restrictions, as well as state incentives encouraging business and residents back into city centre areas.[citation needed] Redundant land, such as 17th and 18th-century canals and docks, railway yards and derelict industrial sites have often been the focus of regeneration 'urban renewal companies' and regional development agencies.
Outcomes
editLarge developments such as the London Docklands project have helped to encourage people back into the city, assisted by gentrification.[citation needed] The most common re-development is mixed use, with flats, townhouse and offices, often with public art and high-quality streetscapes.[citation needed] Derelict but attractive historical buildings have been converted into residential or commercial premises with generous grants or tax relief.[citation needed]
Urban renaissance in the United States
editThis section may contain information not important or relevant to the article's subject. (May 2024) |
Many American cities have seen at least a modest bounce in interest in core cities and older neighborhoods in recent years with a special emphasis on condominium projects, often in formerly non-residential structures. In the United States, efforts to revitalise urban areas often involve ideas of downtown/city centre as an art and cultural hub or arts district, somewhat akin to Richard Florida's concept of making the urban core friendly to the Creative Class. City leaders may promote events such as First Friday art walks and the construction of convention centers and theatres in order to attract visitors who live in suburbs. The word 'renaissance' was used by some cities in the USA in a similar period. For example, the city of Rochester, New York introduced Rochester 2010 - The Renaissance Plan in April 1999.[4]
Criticism
editIn a 2008 report, Policy Exchange argued that regeneration policies in general were of little use, saying the inescapable issue was that northern English towns which had "enjoyed the conditions for creating wealth in the coal-powered 19th-century are often poorly positioned today" which meant they would necessarily have to accept lower wages to attract economic opportunities. The report recommended that residents move to London and south east England instead, and thus that the government should focus its home-building efforts there.[5] The report was criticised by a number of British politicians from all three major parties.[6]
See also
editNotes
edit- ^ The beginnings of an urban renaissance? Recent migration flows into and out of English cities, as revealed in a new study, just may be the glimmerings of a new pro-urban movem...
- ^ "The Regeneration Game". BBC News. 2003-11-05. Retrieved 2010-05-27.
- ^ Caves, R. W. (2004). Encyclopedia of the City. Routledge. p. 716. ISBN 978-0415862875.
- ^ ""The Renaissance Plan" History, Issues and Opportunities". City of Rochester Bureau of Planning and Zoning Planning Division. 11 July 2014. Retrieved 7 May 2024.
- ^ Leunig, Tim; Swaffield, James (2008-08-13). "Cities Unlimited: Making Urban Regeneration Work" (PDF). Policy Exchange. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 8, 2008. Retrieved 2008-08-13.
- ^ "Northern cities 'beyond revival'". BBC News. 2008-08-13. Retrieved 2008-08-13.