This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (November 2024) |
Umê (Tibetan: དབུ་མེད་, Wylie: dbu-med, IPA: [ume]; variant spellings include ume, u-me) is a semi-formal script used to write the Tibetan alphabet used for both calligraphy and shorthand.[1] The name ume means "headless" and refers to its distinctive feature: the absence of the horizontal guide line ('head') across the top of the letters. Between syllables, the tseg mark (་) often appears as a vertical stroke, rather than the shorter 'dot'-like mark in some other scripts. There are two main kinds of umê writing:
- Drutsa (Tibetan: འབྲུ་ཚ་, Wylie: 'bru-tsa), used for writing documents.
- Bêtsug (Tibetan: དཔེ་ཚུགས་, Wylie: dpe-tshugs), used for writing scriptures.
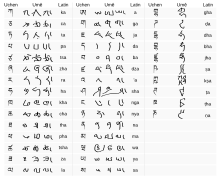
Other Tibetan scripts include the upright block form, uchen (Tibetan: དབུ་ཅན་, Wylie: dbu-can; IPA: [utɕɛ̃]) and the everyday, handwritten cursive, gyug yig (Tibetan: རྒྱུག་ཡིག་, Wylie: rgyug-yig). The name of the block form, uchen means "with a head", corresponding to the presence of the horizontal guide line.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Chen, Jinhua (2024-02-08). Esoteric Buddhism and Texts: Volume I, Manuscript Culture and Transborder Transmission. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-003-85355-8.